Introduction
This article provides an in-depth exploration of fractional horsepower motors.
You'll discover key topics including:
- What Fractional Horsepower Motors Are
- Different Types of Fractional Horsepower Motors
- Design Principles of Fractional Horsepower Motors
- Applications of Fractional Horsepower Motors
- And much more...

Chapter One – What is a Fractional Horsepower Motor?
A fractional horsepower motor is an electric motor that operates on either alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC), delivering less than one horsepower (746 watts). These motors are particularly suited for compact electronic devices and simple consumer products due to their modest power output. They can even serve as backup power sources in larger systems like vehicles when primary power fails.
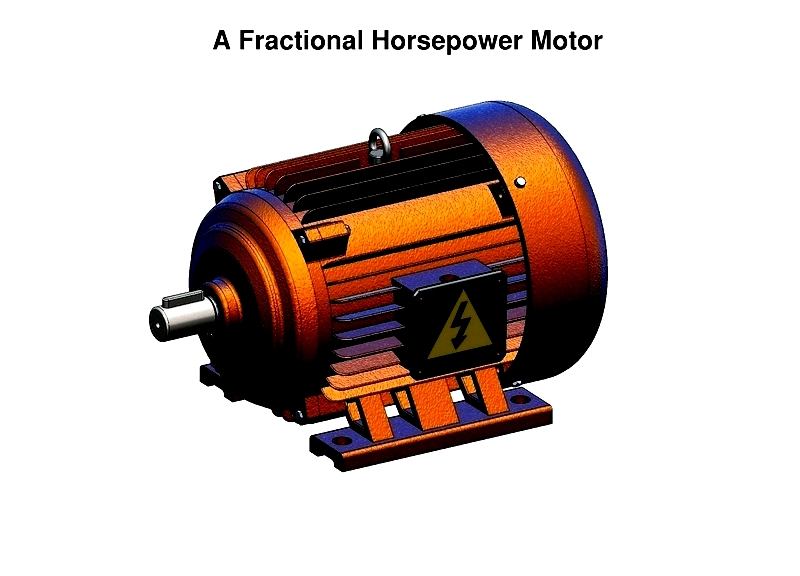
With numerous applications, fractional horsepower motors are valued for their minimal vibration, making them ideal for precision equipment. Common types include stepper and servo motors, both offering exceptional input accuracy. Their precision and controllability make them particularly useful in robotics applications.
Chapter Two – Types of Fractional Horsepower Motors
Despite their compact size, fractional horsepower motors share fundamental design principles and performance characteristics with larger electric motors. These versatile electrical machines find widespread use across industries due to their ability to integrate into space-constrained devices with specific torque or speed requirements. Like their larger counterparts, they convert electrical energy into mechanical energy through electromagnetic fields, delivering reliable rotation and motion control for diverse applications.
Fractional horsepower motors are classified by current type (AC or DC), current application method, mechanical construction, and intended use. Available in various frame sizes, power ratings, voltages, and configurations (from open to fully enclosed), their adaptability makes them essential components in household appliances, HVAC systems, medical devices, pumps, fans, robotics, office equipment, and other compact machinery requiring efficient, low-power motion.
Selecting the right fractional horsepower motor requires consideration of application-specific factors like efficiency needs, starting/running torque, duty cycle, mounting options, speed control, and noise levels. Proper evaluation ensures optimal performance and longevity by matching motor characteristics to operational requirements.
Types of Fractional Horsepower Motors
Brush Series Motors
Brushed series motors, dating back to the Industrial Revolution, remain relevant in applications valuing simple speed control and cost-effectiveness. Modern versions feature key components including an axle, rotor, commutator, stator, permanent magnets, and carbon brushes.
In these motors, permanent magnets form the stationary stator while the rotating armature serves as the rotor. When energized, the armature's electromagnet interacts with the stator's field, causing 180° rotation. Brushes maintain rotation by adjusting polarity via the commutator. Common applications include power tools, appliances, and automotive systems needing variable speed and moderate torque.

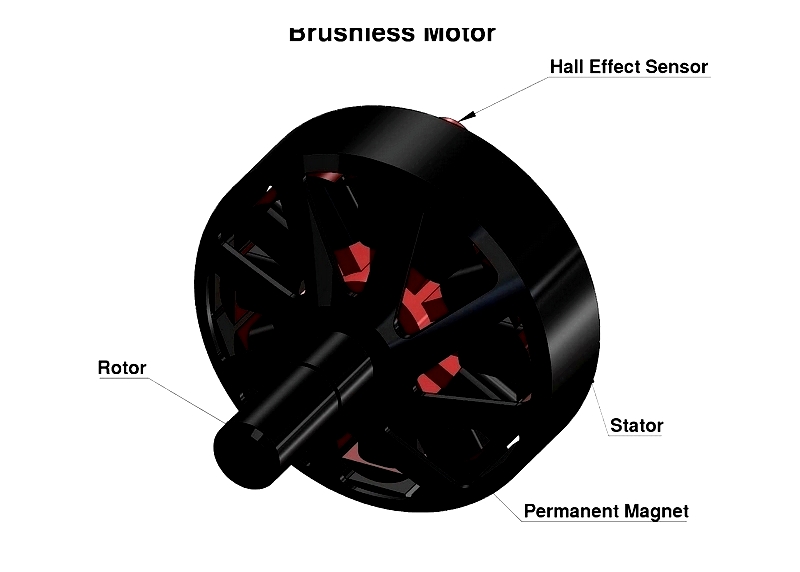
Brushless Motor
Brushless motors are synchronous electric motors that use controllers instead of commutators for rotation. Their windings reside on the stator, eliminating brushes and reducing electrical noise. This design decreases friction, heat generation, and maintenance while improving efficiency.
Compared to brushed motors, brushless DC (BLDC) motors offer superior speed ranges, power density, speed control, and lifespan. These advantages make them ideal for industrial automation, consumer electronics, computer cooling, and medical equipment.
Permanent Split Capacitor
PSC motors feature a cage rotor with main and auxiliary windings, plus a permanently connected capacitor enabling self-starting. This configuration creates smooth torque and quiet operation, making them popular for HVAC fans, blowers, and pumps.

Reluctance Motor
Operating similarly to single-phase induction motors, reluctance motors align rotor speed with the stator's rotating field for synchronous operation. Their high power density and cost-effectiveness suit timing devices, instrumentation, and low-voltage control systems requiring precision.

Series Motor
Series motors excel in high-starting-torque applications due to their series-connected windings. Large conductors handle substantial current, creating powerful magnetic fields. Ideal for vacuum cleaners, small tools, and portable appliances needing initial power bursts.

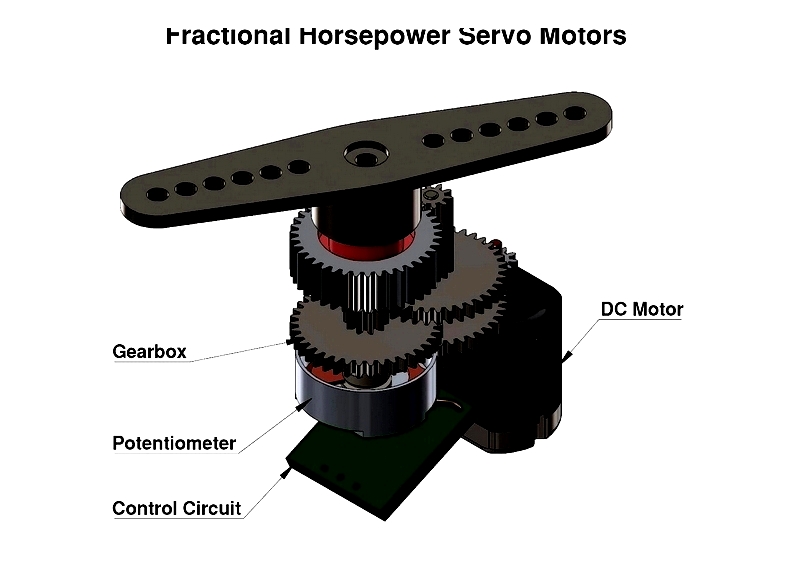
Servo Motor
Servo motors provide precise angular position, acceleration, and velocity control in closed-loop systems. Their feedback mechanisms enable exceptional accuracy in robotics, automation, and CNC applications. Compact and lightweight, they're widely used in industrial devices, medical equipment, cameras, and aerospace systems.
Shaded-Pole Motor
As the simplest AC motors, shaded-pole types feature copper-ring-shaded windings that create starting torque. Their unidirectional operation suits washing machines, small fans, exhaust systems, and desk appliances where low cost and simplicity are priorities.

Split Phase
Split phase motors use two 90°-spaced windings with different resistance characteristics to create starting torque 1.5-2 times running torque. The starting winding disengages at synchronous speed. Economical for light-duty applications like small pumps, blowers, and washers.

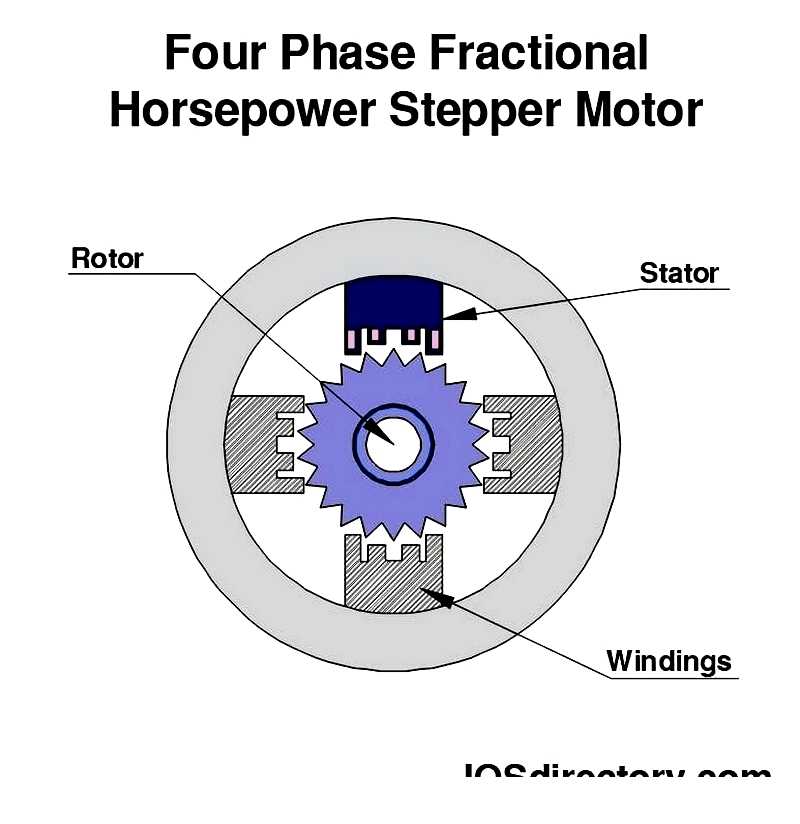
Stepper Motor
Stepper motors move in precise angular increments when their phased coils are energized sequentially. This digital control makes them ideal for 3D printers, robotics, CNC machines, and medical devices requiring repeatable, high-resolution motion.
Synchronous Fractional Horsepower Motor
Synchronous motors maintain shaft rotation perfectly synchronized with current frequency. Their stator's rotating field synchronizes with the rotor's permanent magnet or winding. This precise speed regulation benefits timing devices, clocks, recorders, and process controls requiring constant speed regardless of load.





