Introduction
Discover comprehensive lists of high pressure die casting manufacturers and detailed process information.
You will learn about:
- The fundamentals of High Pressure Die Casting
- Differences between Hot and Cold High Pressure Die Casting
- Common metals used in High Pressure Die Casting
- Typical applications of High Pressure Die Casting
- And much more...
Chapter 1: Understanding High Pressure Die Casting
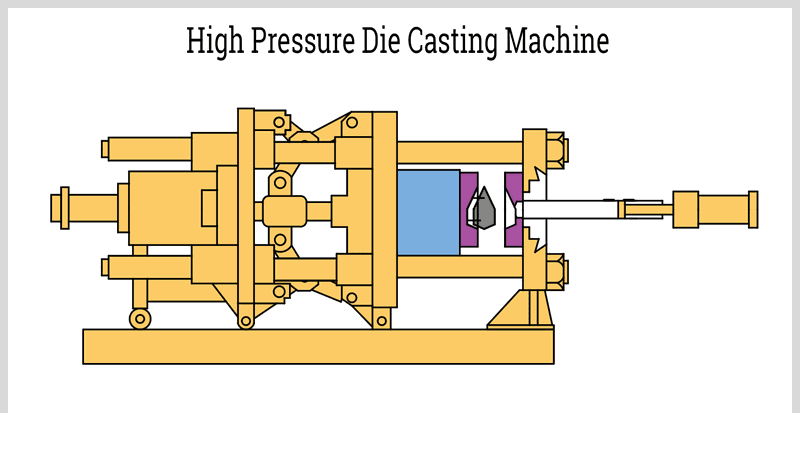
High pressure die casting (HPDC) is a manufacturing process where molten metal is injected into a mold under high pressure to produce complex components. This method delivers exceptional dimensional accuracy, tight tolerances, and smooth surface finishes, often eliminating the need for additional machining. Manufacturers prefer HPDC for its rapid production cycles, high-volume capabilities, and cost efficiency.
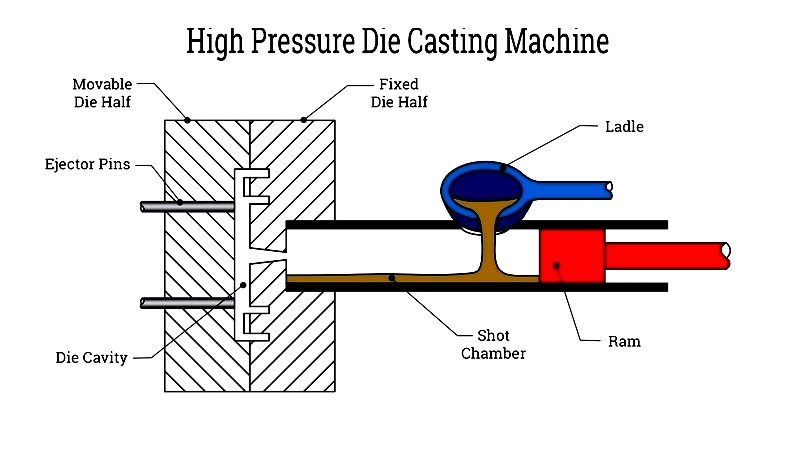
The process utilizes hydraulic systems and pressurized gas to force molten metal into the mold cavity. A robust clamping mechanism maintains mold integrity during solidification, transforming liquid metal into near-net-shape parts within seconds.
HPDC excels at producing lightweight, large alloy components in bulk quantities. The resulting parts feature excellent surface finishes, uniformity, and mechanical properties. While some flash removal may be necessary, most components require minimal post-processing. The process can create intricate geometries as single pieces.
Chapter 2: The High Pressure Die Casting Process
Die casting has been fundamental to precision metalworking for over 200 years, enabling efficient production of complex metal parts. Modern HPDC processes utilize various non-ferrous metals like aluminum, zinc, and magnesium to create durable, lightweight components for automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods industries.
The HPDC process begins with collaboration between manufacturers and clients to define project requirements. Customers typically provide 3D models or technical drawings that engineers evaluate for manufacturability and feasibility.
Mold Design
Custom projects require specially designed molds created using CAD software. Engineers optimize mold designs with proper draft angles, uniform wall thickness, and strategic gate placement to minimize defects and maximize efficiency.
Mold systems consist of cavities, cores, inserts, and ejection mechanisms. These modular systems allow for quick tooling changes and high-volume production.
Proper mold preparation includes applying specialized lubricants that facilitate part ejection and maintain surface quality. This step is crucial for producing precision components with tight tolerances.
High Pressure Die Casting metals
Material selection depends on component requirements and cost considerations. Common HPDC metals include:
- Aluminum - Lightweight with excellent corrosion resistance, ideal for automotive and aerospace applications
- Zinc - Offers superior fluidity for intricate designs and thin walls
- Magnesium - The lightest structural metal, perfect for weight-sensitive applications
- Copper Alloys - Provide excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance
- Lead and Tin - Used for specialized applications requiring corrosion resistance
Cold chamber casting suits high-melting-point metals, while hot chamber casting works best with low-melting-point alloys.

High Pressure Die Casting Injection Methods
Two primary injection methods exist: hot chamber and cold chamber processes.
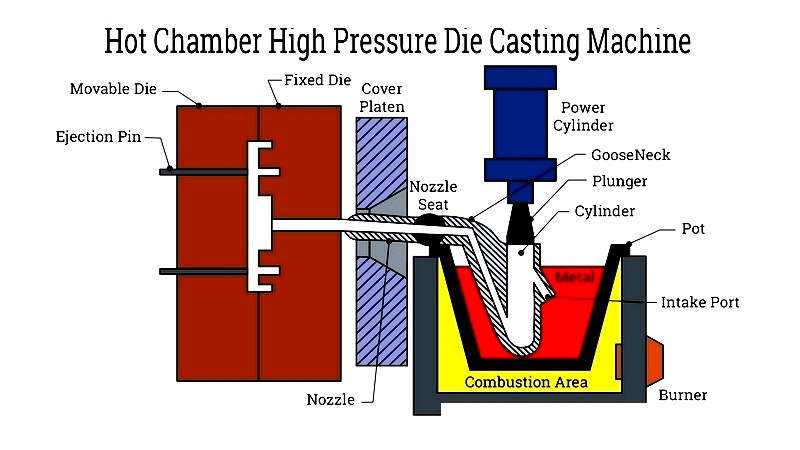
Hot Chamber High Pressure Die Casting
Ideal for low-melting-point alloys, this method features integrated melting and injection systems for efficient, high-volume production.
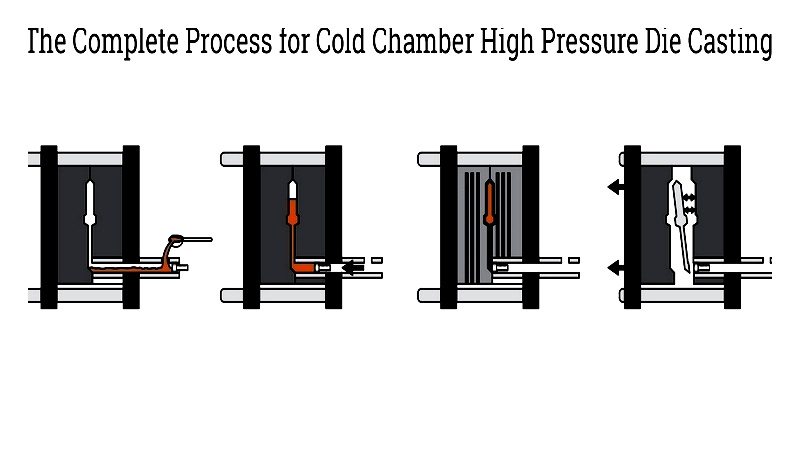
Cold Chamber High Pressure Die Casting
Used for high-melting-point metals, this process involves external melting and high-pressure injection for strong, precise components.
Trimming
This secondary operation removes excess material to achieve final part geometry and improve surface quality. Automated trimming systems enhance production efficiency for high-volume orders.
Chapter 3: High Pressure Die Casting vs Low Pressure Die Casting
Manufacturers choose between HPDC and LPDC based on production requirements, material properties, and cost considerations. Each method offers distinct advantages for different applications.
Cost Factors Related to High Pressure Die Casting
Key cost considerations include tooling expenses, production volumes, cycle times, and energy consumption.
Tooling Costs
HPDC requires durable tooling to withstand high pressures, making it suitable for large production runs. LPDC tooling costs are lower, benefiting smaller production quantities.
Volume
HPDC excels in high-volume production, while LPDC is better suited for limited runs or specialty components.
Cycle Times
HPDC offers faster cycle times, increasing output and reducing labor costs. LPDC features slower cycles but produces parts with superior metallurgical quality.
Energy Consumption
HPDC systems consume more energy due to high-pressure requirements. LPDC is generally more energy efficient per cycle.
Complexity of Geometries
Both methods can produce complex parts, but HPDC delivers superior speed and precision for high-volume production.




