Introduction
This comprehensive guide covers everything about portable offices, including their manufacturing and applications.
You'll discover:
- What defines a Portable Office
- Construction of Portable Office Walls
- Essential Components of Portable Offices
- Varieties of Portable Offices
- Advantages of Portable Offices
- And additional valuable information
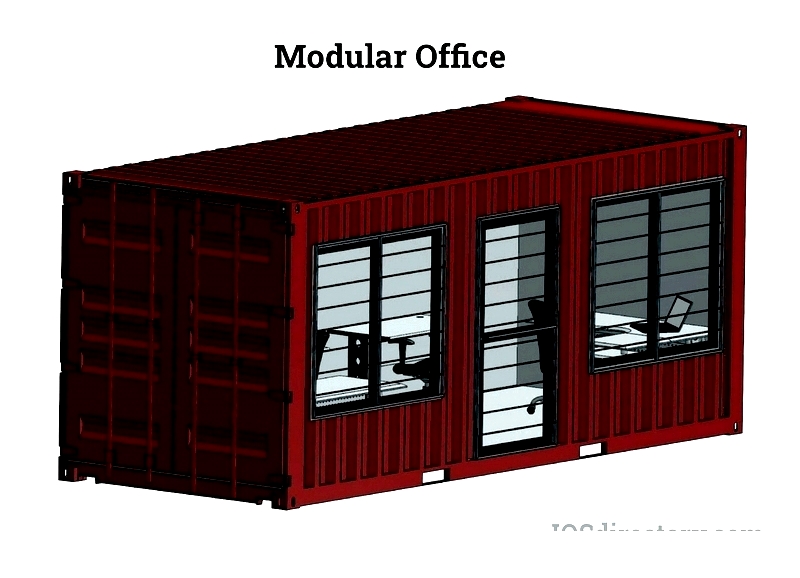

Chapter 1: Understanding Portable Offices
A portable office provides a versatile, movable workspace that can be easily transported, offering private and functional areas for meetings, document handling, or plan reviews. Built with premium materials and permanent office construction principles, these units ensure durability and practicality.
Available in multiple sizes, layouts, and materials to suit various needs and locations, portable offices are ready for immediate use. They can be assembled from prefabricated modules on-site or delivered as complete, functional units. Their sturdy design withstands frequent relocation without compromising structural integrity.
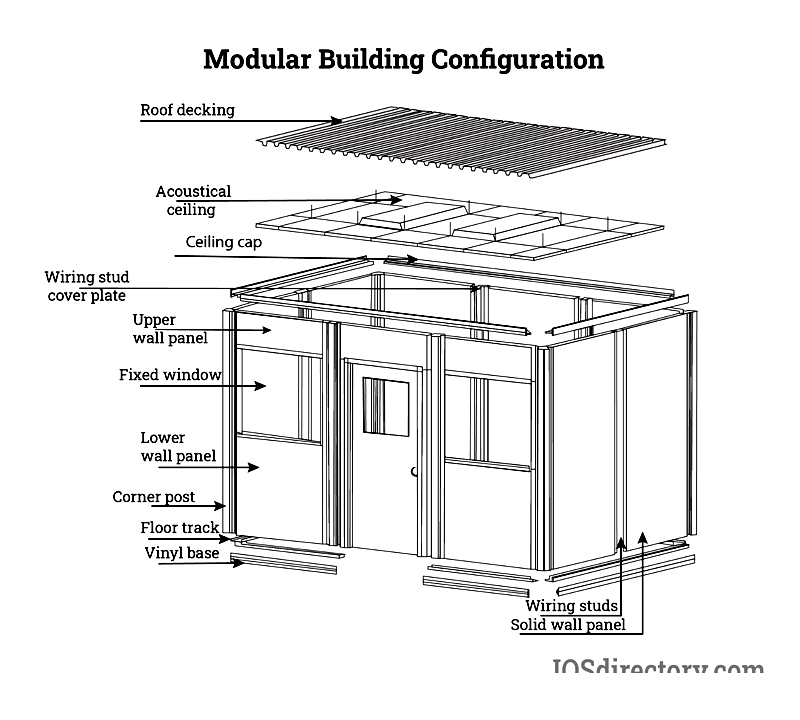
Chapter 2: Portable Office Wall Construction
Despite varying designs and sizes, portable offices must meet the same regulations as permanent structures. Compliance with building codes, safety standards, and local zoning laws is mandatory for all modular construction projects. Location determines applicable codes and inspection requirements, ensuring safe and compliant temporary workspaces.
Wall Systems
Portable office walls provide structural integrity and protection against weather, noise, and temperature fluctuations. Material choices include vinyl-covered panels with polystyrene cores, or panels with gypsum, steel, wood, or aluminum cores. Selecting appropriate wall systems is crucial for durable prefabricated offices in demanding conditions.
Modular panels typically use galvanized steel or aluminum stud frameworks for structural support. This modular steel framing offers excellent load-bearing capacity and easy installation. Panels are customized for specific needs, considering factors like soundproofing, fire resistance, or energy efficiency.
Available panel types include fire-rated and ballistic-rated options for hazardous environments, plus soundproofing and thermal insulation panels. Advanced options allow customization to meet operational needs, regulations, and budgets.
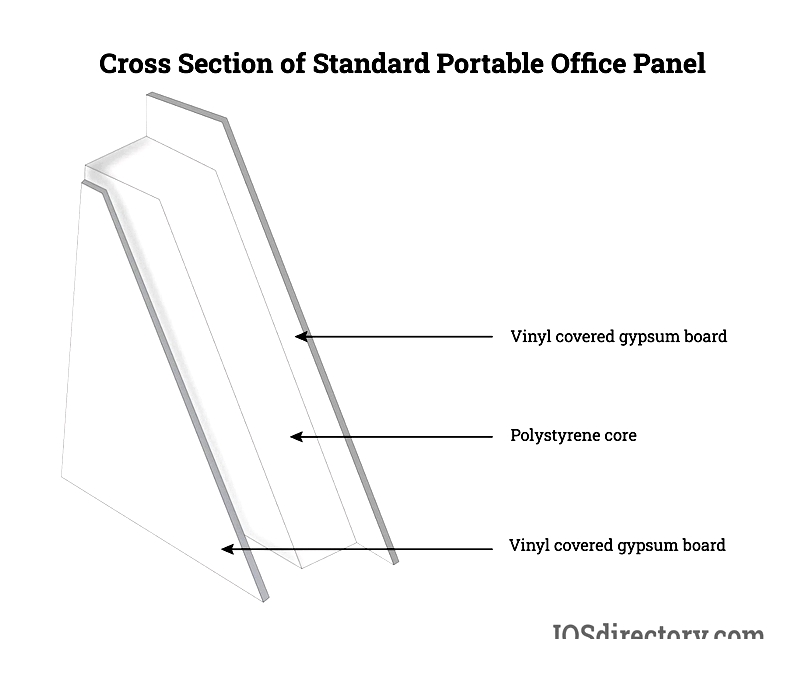
Wall panels typically feature a sandwich construction with three layers. Exterior surfaces use materials like gypsum, steel, wood, fiberglass, or vinyl-covered hardboard, often with durable vinyl coatings for easy maintenance.
The core insulation resembles residential insulation, using materials like mineral wool, polystyrene (EPS or XPS), polyisocyanurate, or advanced composites. Sealed cores prevent air/water penetration, with materials selected based on required strength, durability, and energy efficiency for each application.
Panels are rated by Sound Transmission Class (STC) (20-65) and R-value (thermal resistance). Fire ratings range from A (best) to D/E. These specifications guide selection for commercial/industrial use where safety compliance is critical.
Choosing panels involves balancing insulation, fire safety, acoustics, durability, and cost. Manufacturers offer custom solutions for educational, industrial, or workspace needs, with professional installation ensuring regulatory compliance.
Standard Panels
Traditional 3-4 inch thick panels feature EPS cores with 1/8-inch hardboard or 1/2-inch gypsum faces, vinyl-clad in various colors. With STC 22, R13, and Class C fire ratings, these panels are now less common for code-sensitive applications.
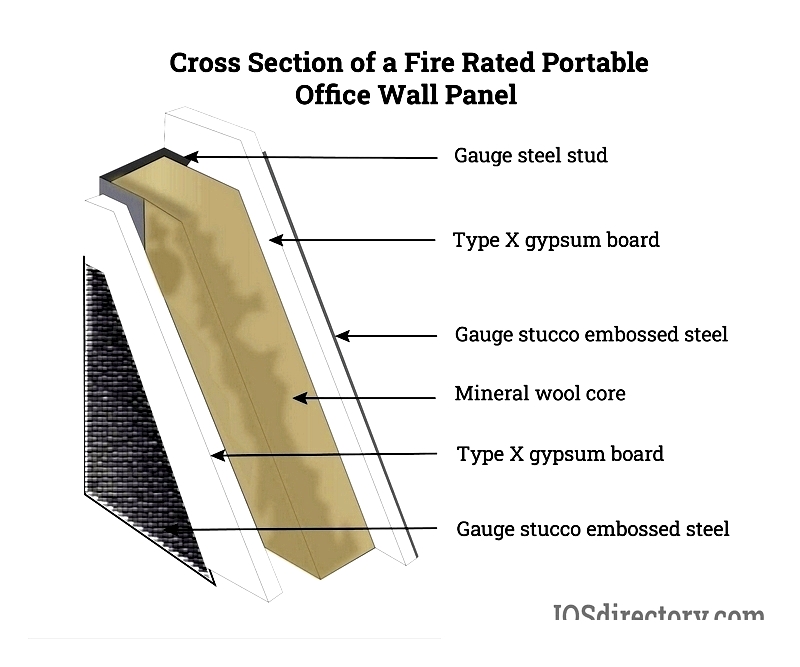
Fire-Rated Panels
Featuring 26-gauge stucco with 5/8-inch Type X gypsum and 2-inch mineral wool cores, these Class A rated panels (STC 28, R11) meet ASTM E119-00a standards after withstanding one-hour flame tests. Ideal for labs, plants, and utility rooms requiring maximum protection.
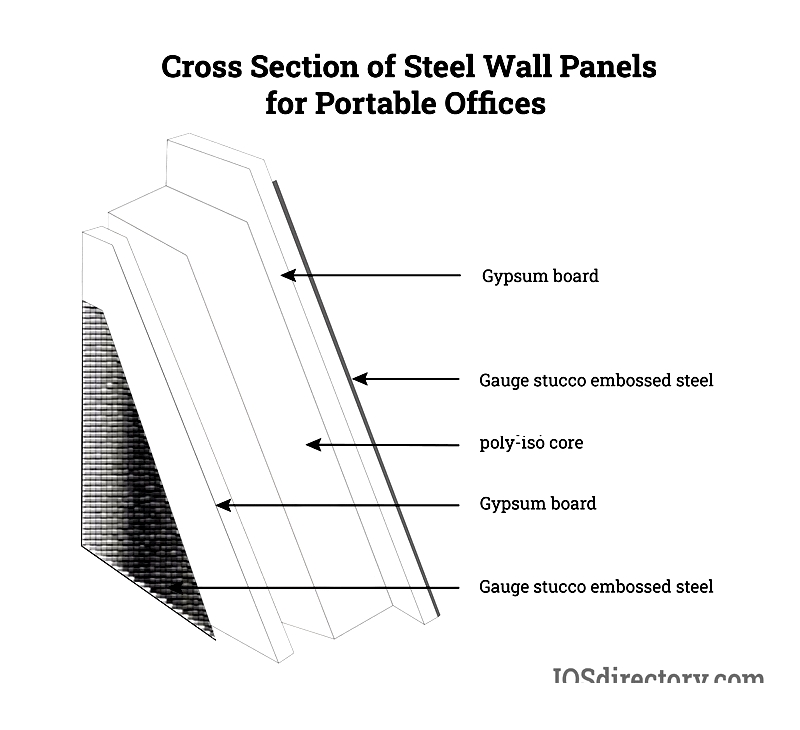
Steel Panels
Constructed with 26-gauge steel, 1/2-inch gypsum, and polyisocyanurate cores, these impact-resistant panels suit warehouse offices and workshops. Powder-coated finishes provide corrosion resistance and color retention.
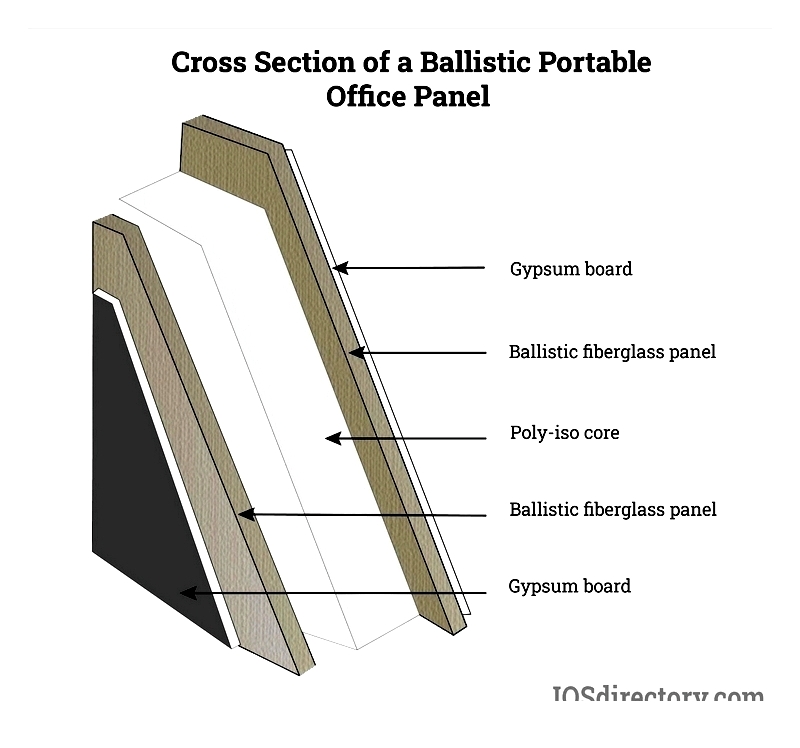
Ballistic Panels
UL-rated fiberglass ballistic panels (0.25-1.5 inch thick) meet NIJ standards for threat levels 1-4. Used in banks, military, and law enforcement facilities, these panels combine gypsum exteriors with ballistic fiberglass and polyisocyanurate cores.
Aluminum Honeycomb Panels
Lightweight 3-4 inch panels (STC 28, R1) with aluminum honeycomb cores suit temporary offices needing quick setup. Ideal for trade shows or classrooms, these moisture-resistant panels offer easy transport and reconfiguration.

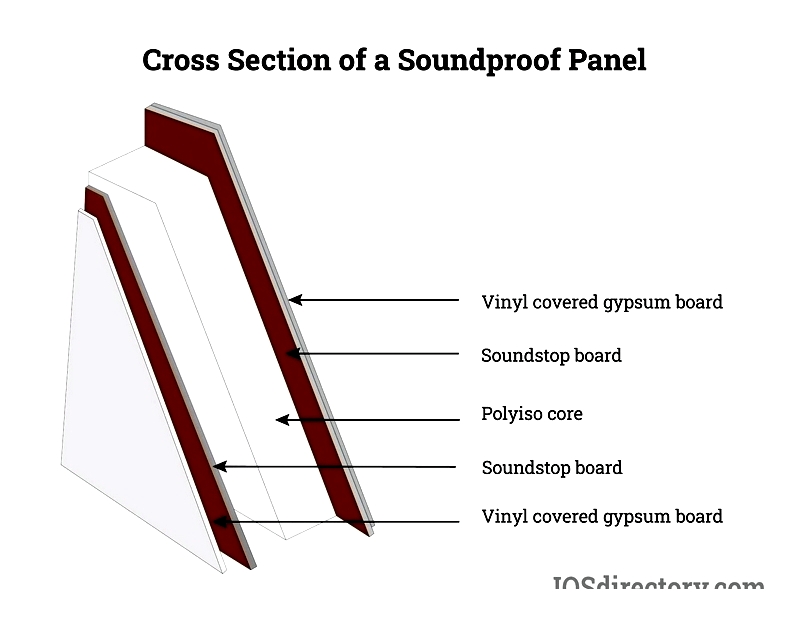
Soundproof Panels
Featuring vinyl-covered gypsum over sound-dampening layers with polyisocyanurate cores, these Class A panels (STC 23-35, R11) reduce noise in conference rooms and executive offices. Effective in 70-100 dB environments.
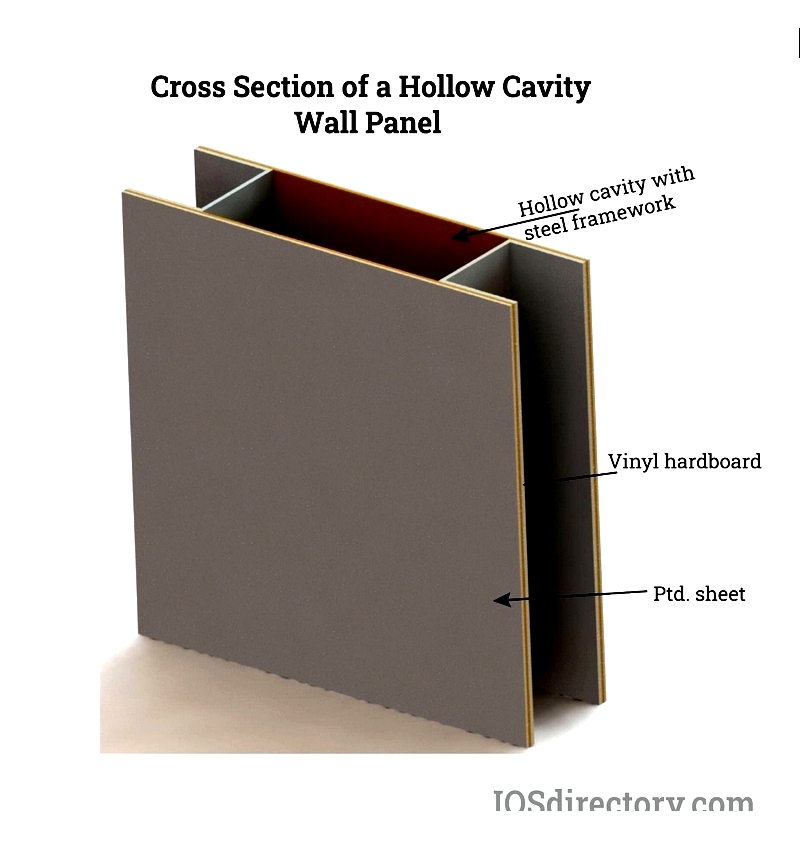
Hollow Cavity Panels
Steel-framed panels with empty cores accommodate utilities in cleanrooms and labs. With R1 and STC 20 ratings, these 3-4 inch panels support frequent modifications in technical environments.
Panel Finishes
Beyond standard vinyl laminate or painted steel, specialty options include:
- Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP)
- Textured FRP
- High Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
- Painted Aluminum/Steel
Custom panel solutions address specific needs for




