Introduction
This article provides an in-depth examination of metal washers and their applications.
You will explore various topics including:
- What metal Washers Are
- metal Washer Manufacturing Processes
- Applications of metal Washers
- Materials Used in metal Washer Production
- Different Varieties of metal Washers
- And more...
Chapter One – What is a metal Washer?
A metal washer is a thin, circular metal component with a central hole, primarily serving as a spacer, vibration dampener, or load distributor for fasteners. The central opening allows bolts or screws to pass through. Manufacturers use various techniques to produce metal washers, ensuring they meet strength requirements and withstand mechanical stress.
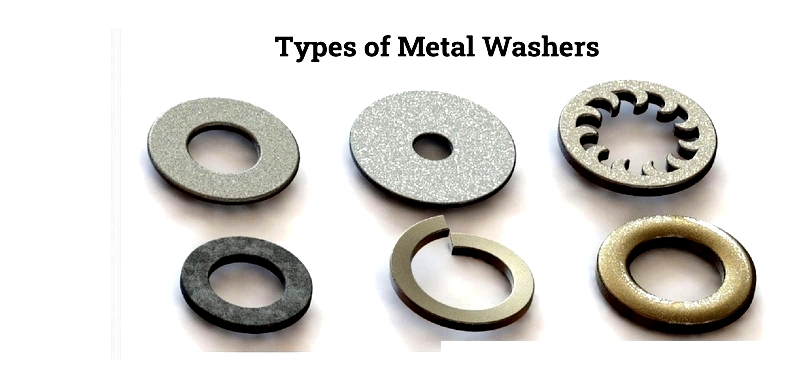
metal washers are typically made from materials like galvanized carbon steel and stainless steel. The combination of different metals and designs creates numerous washer types, including basic versions such as flat, spring, and locking washers. Additionally, specialized washers exist to meet specific application requirements.
Chapter Two – Applications of metal Washers
metal washers have countless applications across mechanical, architectural, and industrial fields, with custom washers designed for specialized uses. metal washers are fundamental hardware elements that distribute fastener loads—including screws, bolts, nuts, and other connectors—across wider surfaces to enhance security and durability. These components are vital in construction, automotive manufacturing, HVAC systems, electronics, and other industries requiring dependable fastening, load distribution, and wear protection.
Washers also simplify maintenance and assembly by making it easier to tighten, loosen, or remove nuts from bolts. Available in materials like steel, stainless steel, brass, copper, and zinc, they suit both household projects and industrial applications. From preventing pipe leaks to reinforcing joints under stress, metal washers enhance connection reliability and prolong component life.
metal Washer Applications
Load Distribution
Washers primarily distribute fastener loads evenly across connected materials. Without washers, high torque can cause surface damage, particularly in softer materials like wood or plastic. Flat washers and square washers prevent such damage by spreading mechanical forces, reducing the risk of warping or deformation. Effective load distribution is critical in structural engineering, electronics, and automotive manufacturing, where safety and component integrity are essential.

Spacing Function
metal washers often serve as spacers when fasteners exceed hole depths or when components need separation. For instance, if a four-inch bolt is used with three-inch material, washers can fill the gap to ensure a secure fit. Spacer washers are crucial for aligning parts, compensating for manufacturing variations, and maintaining precise clearances in machinery and robotics.

Sealing Applications
Sealing washers combine metal with resilient materials like rubber or silicone to create leak-proof seals in plumbing and HVAC systems. These washers protect surfaces from damage while preventing leaks. Proper installation is vital—over-tightening can compromise the seal. Besides leak prevention, sealing washers act as vibration dampeners in engines and industrial equipment.

Repair Uses
Fender washers repair connections with enlarged or corroded holes. Their large outer diameter covers damaged areas while accommodating standard fasteners. Commonly used in automotive and appliance repair, these washers restore structural integrity without full component replacement.

Other Types and Uses
Additional metal washer varieties include:
- Spring washers (split or wave) maintain tension and absorb vibration in dynamic assemblies.
- Lock washers prevent fastener loosening in automotive and aerospace applications.
- Shoulder washers insulate electronic components from short circuits.
- Belleville washers maintain pressure in valve and flange systems.
Selecting the right washer involves considering environment, load capacity, material compatibility, and corrosion resistance. High-quality washers improve performance, reduce maintenance, and lower operational costs.
For supplier information, product details, or bulk order quotes, consult our manufacturer directory or visit the metal washers supplier section.




