Introduction
This article provides an in-depth exploration of high voltage power supplies.
Key topics covered include:
- Working Principles of High Voltage Power Supplies
- Different Types of High Voltage Power Supplies
- Applications and Advantages of High Voltage Power Supplies
- Additional Relevant Information
Chapter 1: Fundamental Principles of High-Voltage Power Supplies
This section examines the core concepts of high voltage power supplies, including their design, construction, and operational principles.
Understanding High Voltage Power Supplies
A high voltage power supply converts low voltage input into significantly higher output voltage, typically ranging from 1kV to 360kV, with some advanced systems reaching 500kV. These devices can process both AC and DC inputs, with DC inputs like 12Vdc or 24Vdc often being more cost-effective.
High voltage outputs serve diverse applications in scientific research, industrial processes, medical equipment, and telecommunications. Designed to deliver electrical energy to various loads, these power supplies are utilized in lighting systems for homes and factories, as well as in electrical components such as power transformers, high voltage capacitors, and specialized units like Cockcroft-Walton and Van de Graaff generators.

Many high voltage power supplies feature adjustable outputs controlled through computer interfaces or onboard controls. They are employed across multiple industries, including healthcare, telecommunications, and energy analysis. These units typically offer high output voltage stability (within ±1%), efficiency exceeding 70%, and safety protections against overcurrent and short circuits, with minimal leakage current when powered off.
When using high voltage power supplies, specialized output connectors are essential to prevent insulation failure, arcing, and accidental contact. For operations above 20kV, proper connectors ensure both safety and reliability.
Voltage Classification Systems
Voltage is categorized into high, medium, and low ranges, with specific thresholds varying by region. In the United States, organizations like the National Electrical Code (NEC) and National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) establish guidelines for these classifications. Industries working with electrical currents adhere to these standardized specifications.
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) also regulates these standards. According to ANSI standard C84.1-1989, voltages are divided into five categories:
- High (HV) - 115,000 to 230,000 VAC
- Extra-High (EHV) - 345,000 to 765,000 VAC
- Ultra-High (UHV) - 765,000 to 1,100,000 VAC
- Medium (MV) - 2,400 to 69,000 VAC
- Low (LV) - 240 to 600 VAC
The NEC voltage standards classify voltages as:
- High Distribution - 1000 to 4160 volts
- Medium Distribution - 50 to 1000 volts
- Low Distribution - 0 to 49 volts
High, Extra-High, and Ultra-High Voltage Applications
High and extra-high voltages are generated at power plants to enhance long-distance electricity transmission efficiency.
Medium Voltage Characteristics
Medium voltage ranges from 1kV to 69kV, though global standards may vary. This voltage level is distributed from substations to various end-users, including industrial, commercial, and residential consumers. The higher voltage enables efficient electricity transmission over extended distances.
Low Voltage Applications
Low voltage spans 0 to 1000 volts in AC systems and up to 1500 volts in DC systems. This range powers numerous applications, from computers and home lighting to industrial machinery, providing a safe and reliable electricity source.
High Voltage Power Supply Operation
The primary function of a high voltage power supply involves converting low-frequency input voltage into higher output voltage using SMPS (Switched-Mode Power Supply) technology. An SMPS employs a switching regulator for efficient power conversion.
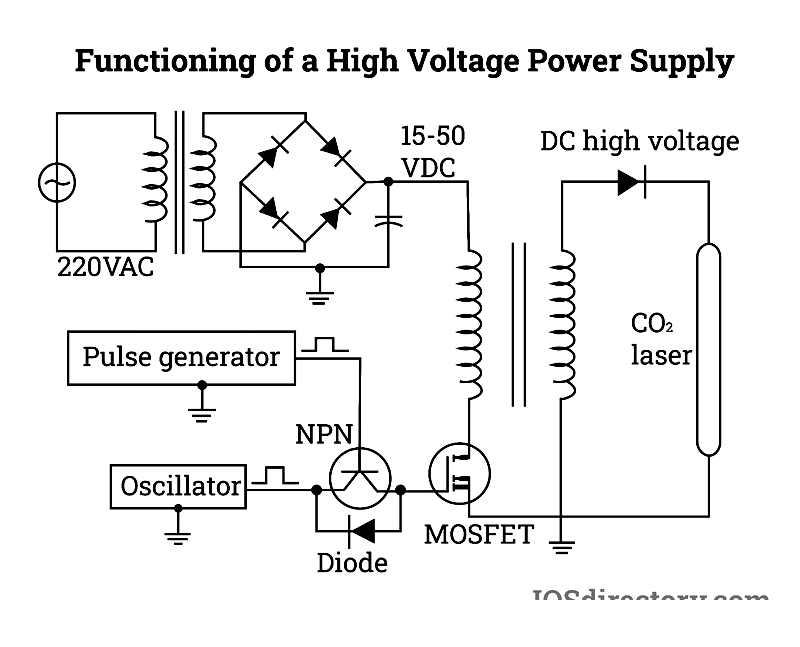
Power transfer from an AC or DC source to a DC load utilizes high-frequency switches like MOSFETs and high-frequency transformers. These components enable the conversion of low input voltage to higher output voltage. The switches rapidly alternate between on and off states, with energy storage components like capacitors or inductors bridging power gaps during off periods. This switching mechanism minimizes energy waste.
Fundamentally, a high voltage power supply is an advanced conversion circuit that transforms filtered DC bus voltages from rectified mains input into high-frequency AC. High-frequency switches adjust duty cycles to control power transfer effectively.
The resulting high-frequency AC is boosted using a high-frequency transformer. After voltage increase, the signal undergoes rectification, multiplication, and filtration in the transformer's secondary stage to achieve the desired output voltage.
Additionally, high voltage power supplies incorporate circuitry for output voltage adjustment and include fail-safe protection systems to ensure safe operation.
Key Components of High Voltage Power Supplies
High voltage power supplies consist of several specialized components:
Transformer – This essential component transfers electrical energy between circuits while maintaining frequency. It can increase (step-up) or decrease (step-down) AC voltage levels and isolates electronic components from the AC power source. The primary winding connects to the AC source, generating AC current, while the secondary winding connects to loads. These windings are electrically isolated, with voltage induced in the secondary winding through electromagnetic induction. High-frequency transformers are predominantly used in high voltage power supplies.
Rectifier – This component converts alternating current (AC) into pulsating direct current (DC). A basic example is a rectifying diode that functions when forward-biased.
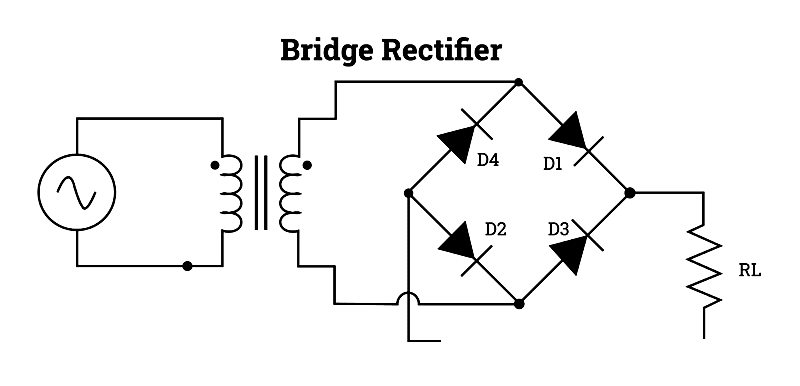
Rectifier circuits are primarily classified as half-wave, full-wave center-tapped, and full-wave bridge rectifiers.
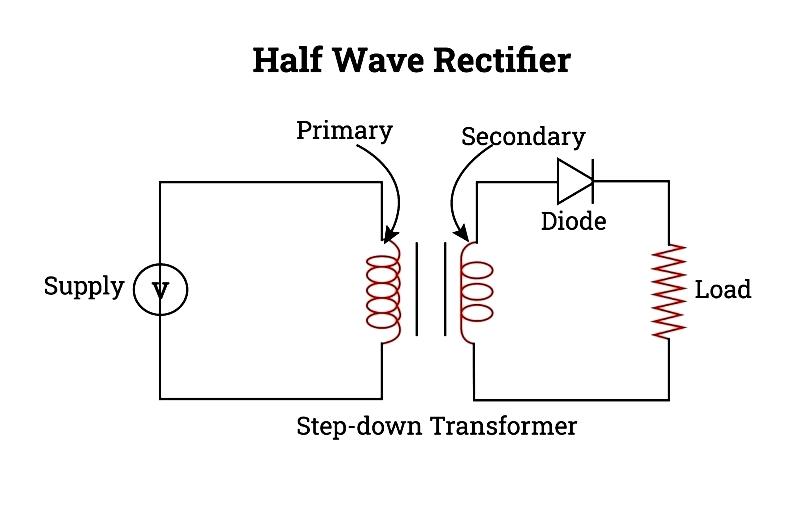
Filter – Filters remove ripple content from DC outputs, converting pulsating DC into smoother signals. Common filter types include capacitance filters and resistor-capacitor (RC) filters. Capacitance filters are simple and economical, while RC filters allow selective frequency passage, including high-pass and low-pass configurations.
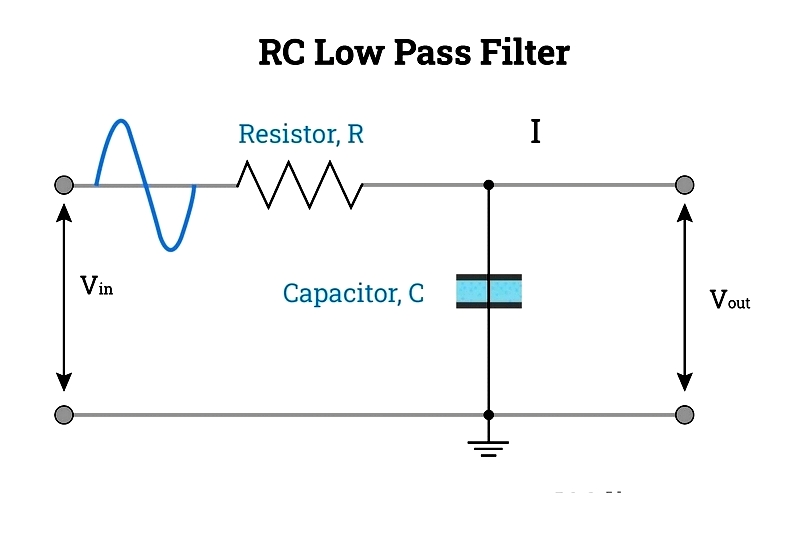
Ripple refers to unwanted AC content remaining after rectification, which can damage loads. Filters smooth signals and reduce AC content.
Regulator Circuits – These circuits maintain stable DC output voltage, crucial for consistent load operation despite input fluctuations.
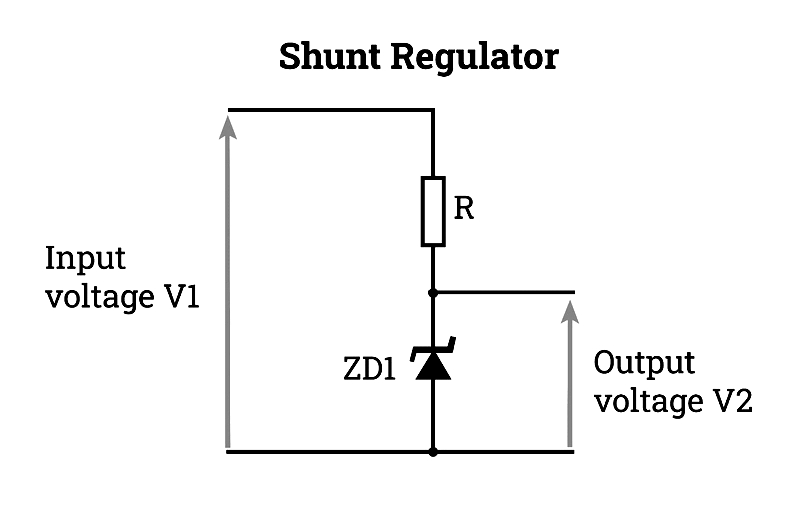
Common voltage regulator types include shunt and series configurations.





