Introduction
This article provides an in-depth examination of AC power cords.
It covers detailed information on various aspects including:
- Working Principles of AC Power Cords
- Different Varieties of AC Power Cords
- Practical Uses and Advantages of AC Power Cords
- Additional relevant information...

Chapter 1: Understanding the Fundamentals of AC Power Cords
This section explains the core principles of AC power cords, describing their design and operational mechanisms.
What is an AC Power Cord?
An AC power cord is a detachable cable that transmits alternating current (AC) from a power source to electrical devices. Widely used in retail, industrial, electronics, entertainment, and residential settings, these cords power equipment ranging from lighting and power tools to home appliances and musical instruments.
How AC Power Cords Are Constructed
AC power cords carry alternating current where electrons periodically reverse direction, transferring energy from the source to devices. They consist of conductive wires, typically copper, insulated and protected by an outer rubber or polymer jacket. Construction varies based on application requirements.
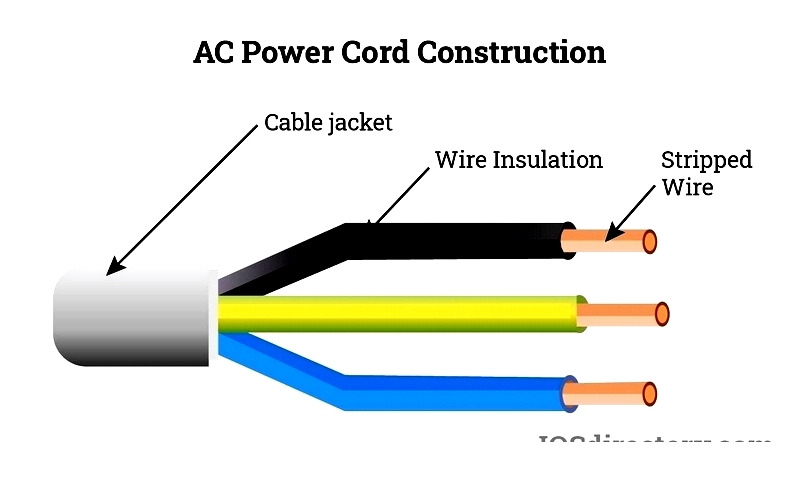
Key factors in cord construction include:
- Operating voltage, which determines insulation thickness
- Current capacity, affecting conductor size
- Environmental conditions like impact, moisture, chemicals, and sunlight that influence jacket material selection
Copper Wire Conductors
Copper serves as an excellent conductor for wiring applications, essential for power generation, electronics, telecommunications, and manufacturing. Nearly half of mined copper becomes wire and cable conductors, with construction wiring being the primary market.
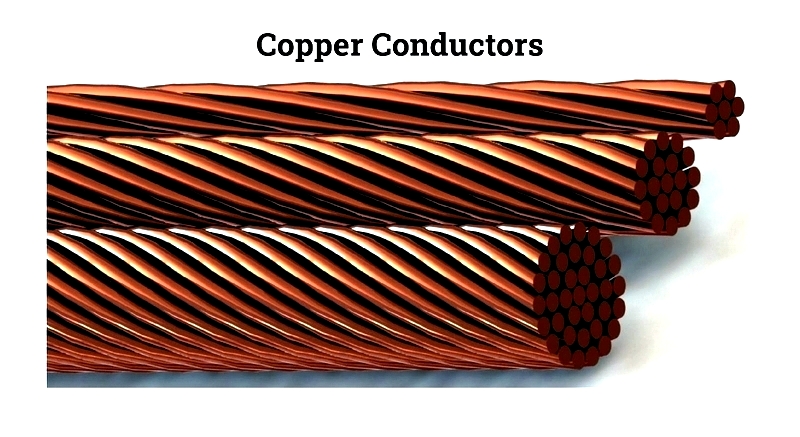
Copper wires are often stranded for flexibility and may be bare or plated with tin, silver, or gold to reduce oxidation and improve longevity. Coaxial and twisted pair designs minimize electromagnetic interference while maintaining signal quality.
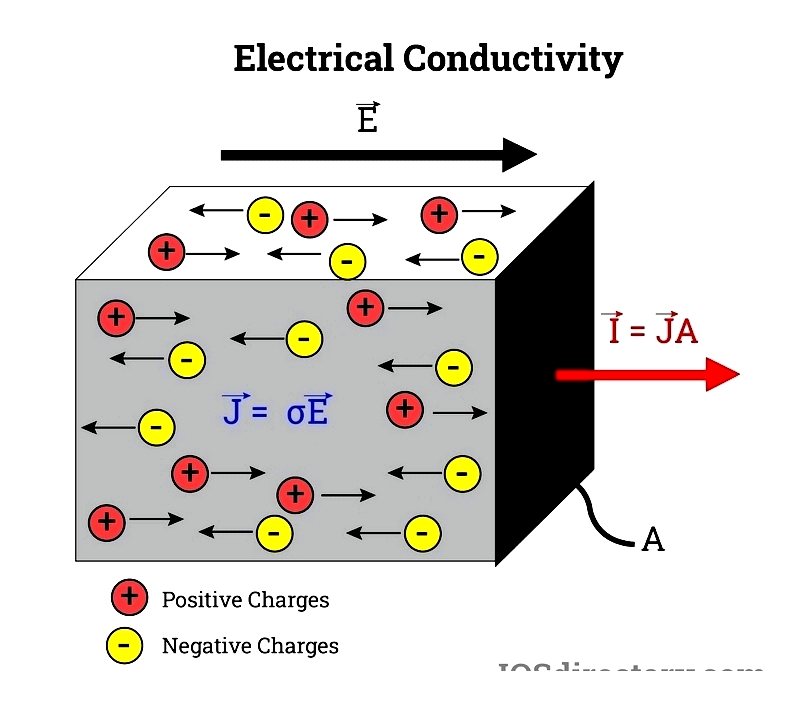
Electrical Conductivity Properties
Copper's exceptional conductivity stems from its partially filled conduction band, allowing efficient electron flow. With a resistivity of 16.78 nΩm at 20°C, it outperforms aluminum (requiring 1.56x larger cross-section) and is only slightly surpassed by silver (15.9 nΩm).
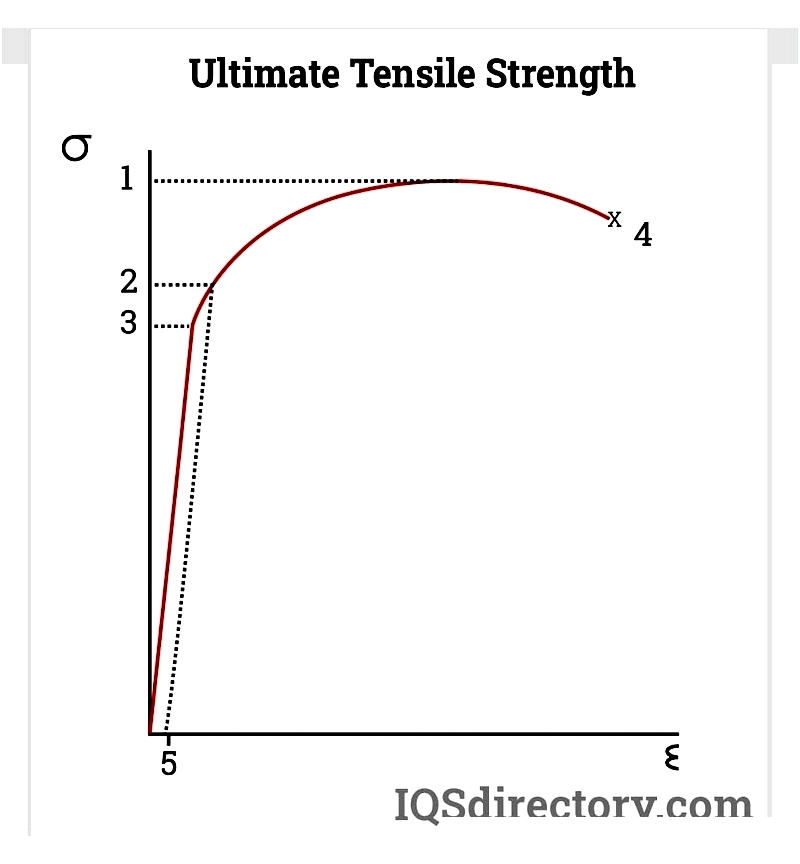
Strength and Flexibility
Copper's high tensile strength resists stretching and deformation while maintaining excellent ductility for fine wiring applications. Its balance of hardness and flexibility simplifies installation without special tools.
Aluminum Wire Conductors
Aluminum wiring offers a lightweight, cost-effective alternative for power grids and transmission lines, though with 60% of copper's conductivity. Its lower density makes it prone to eddy currents and magnetic field effects.
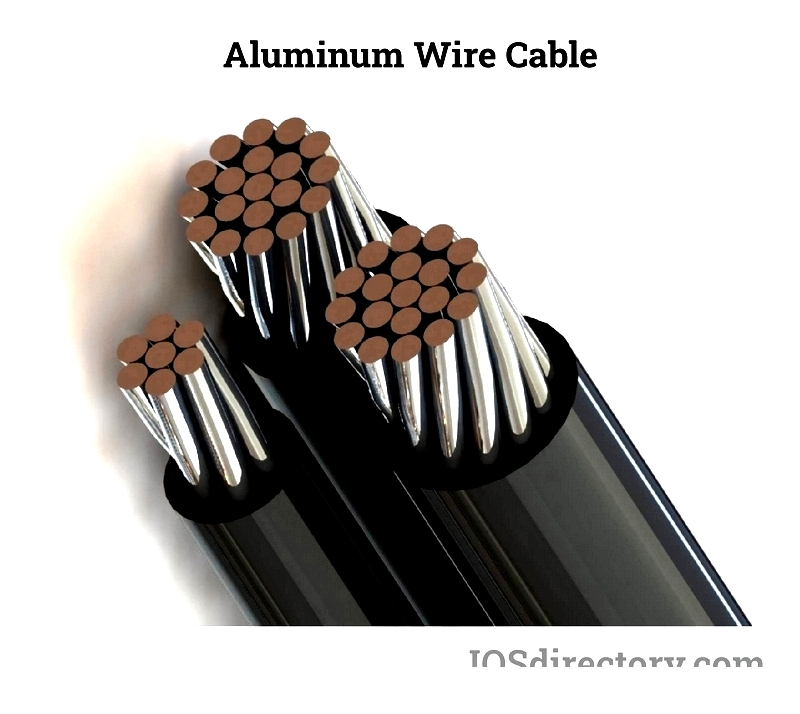

Challenges include higher resistance requiring thicker wires, faster fatigue, galvanic corrosion risks, oxidation issues, and thermal expansion concerns that can degrade connections over time.
Wire Insulation Materials
Insulation protects against current leakage and environmental damage. Common types include:
Plastic Insulation Options
- PVC: Economical, flame-resistant, but limited flexibility
- PE: Low capacitance for high-speed transmission
- PUR: Flexible and chemical-resistant
Rubber Insulation Varieties
- Neoprene: Excellent cut-through and oil resistance
- Silicone: High-temperature tolerance
- EPR: Suitable for high-voltage applications

Power Cord Connectors
- NEMA standards define voltage and pin configurations
- Hard-wired cords feature permanent connections
- International standards like IEC 60320 ensure compatibility
Selection Criteria
Key considerations include:
- Current rating for safe operation
- Voltage requirements affecting insulation design
- Environmental conditions
Chapter 2: AC Power Cord Varieties
AC power cords safely deliver electricity from outlets to devices through standardized connectors. Understanding these types ensures proper power transmission and safety compliance.
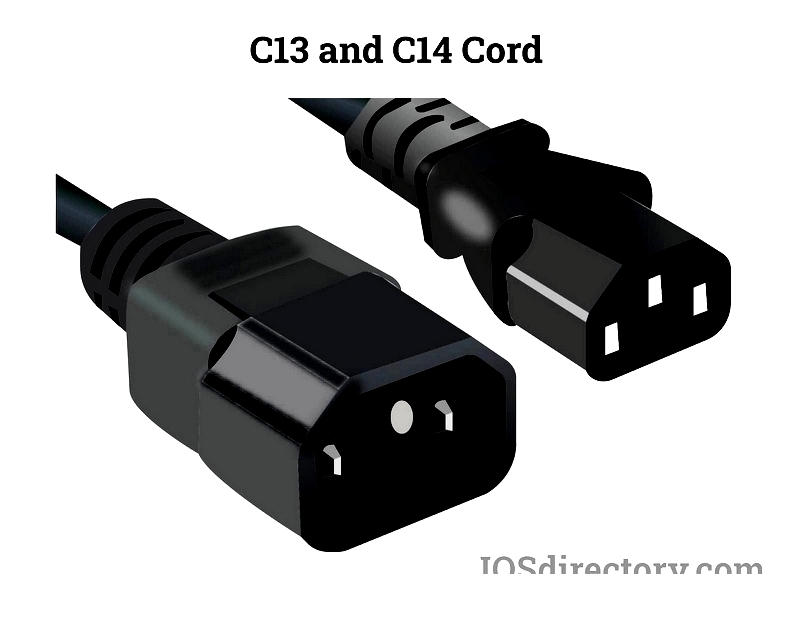
C13/C14 Power Cords
Common in IT equipment, these IEC 60320 connectors handle up to 10-15A at 250V for computers, PDUs, and networking gear.

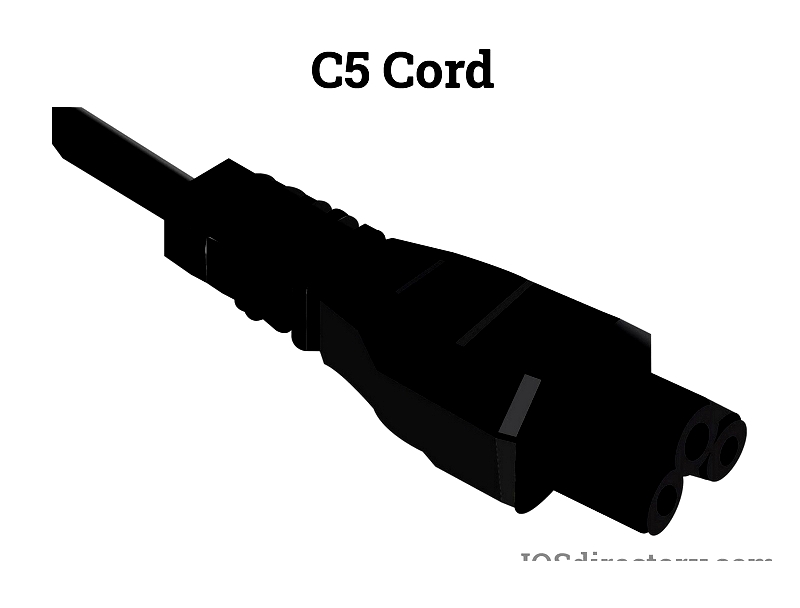
C5 "Cloverleaf" Cords
Used for laptops and projectors, this polarized connector features three circular prongs in a triangular pattern.
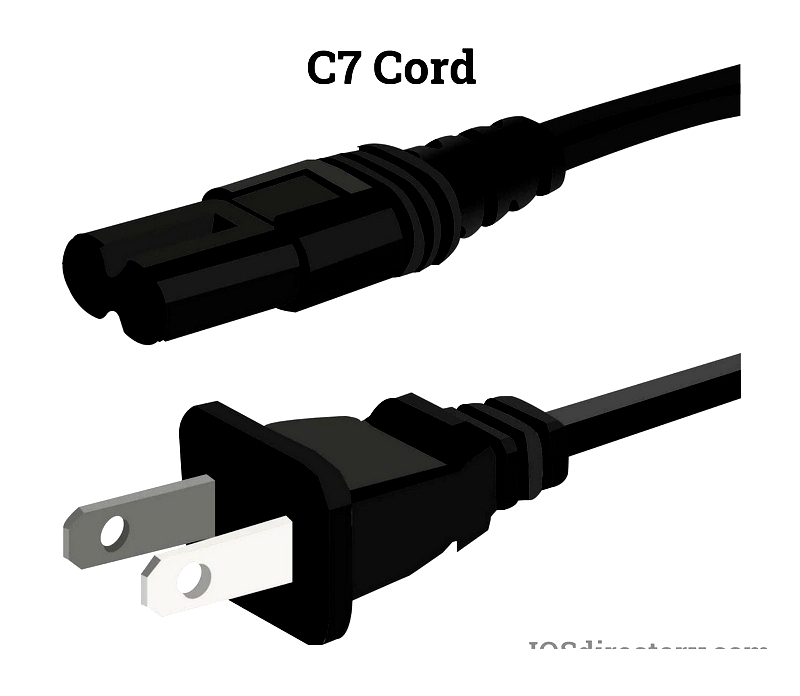
C7 "Figure-8" Cords
This non-polarized 2-prong design powers small electronics like audio equipment and game consoles.

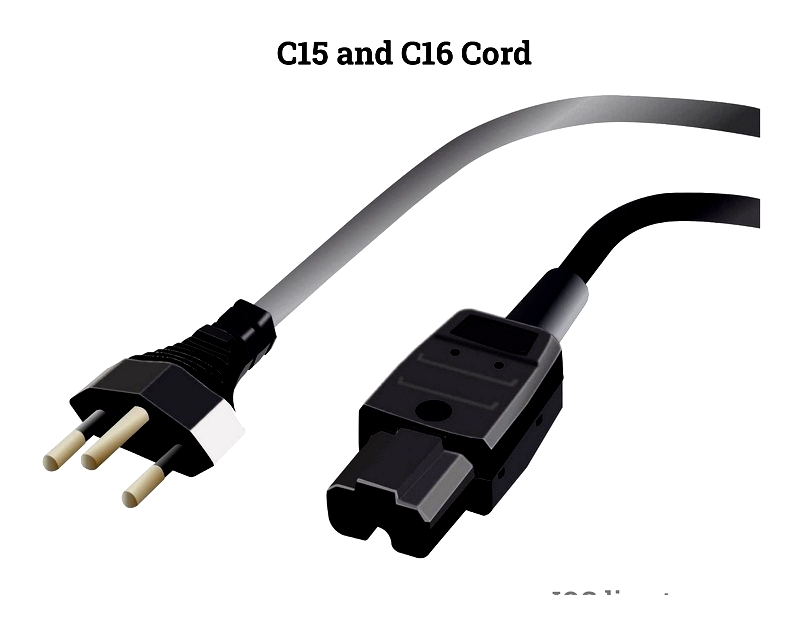
High-Temperature C15/C16 Cords
Designed for hot environments like server rooms, these handle up to 120°C (155°C for C15A/C16A variants).

Heavy-Duty C19/C20 Cords
Supporting up to 20A, these power servers and industrial equipment with secure, high-current connections.