Introduction
This article summarizes and discusses spring hinges, focusing on their uses and construction.
You will learn about topics including:
- What is a Spring Hinge?
- Types of Spring Hinges
- Uses for Spring Hinges
- Materials Used to Make Spring Hinges
- Adjustment and Lubrication of Spring Hinges
- And Much More...
Chapter One – What is a Spring Hinge?
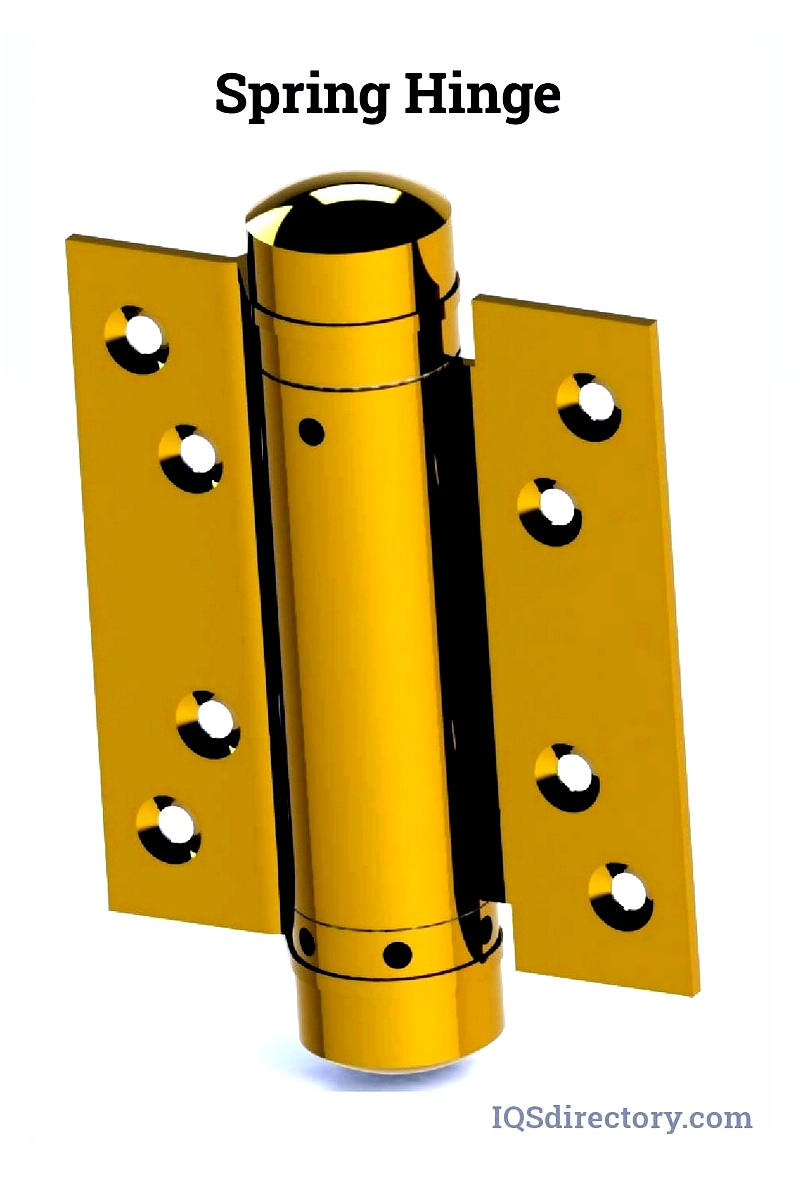
A spring hinge is an automatic closing device that connects two parts using an internal spring within the hinge's barrel. These hinges are widely used in applications like eyeglasses, cabinet doors, box lids, and handheld tools. Known for their strength and reliability, they are a top choice for hardware requiring self-closing functionality.

Spring hinges are commonly used on commercial-grade wood or metal doors. The spring in the hinge's barrel applies pressure to the wings, either pulling them together or pushing them apart. This allows tension adjustment, ensuring doors or lids operate with the desired resistance or ease.
Chapter Two – What are the different types of spring hinges?
Automatic door closure is essential in modern architecture for convenience, energy efficiency, and security. A popular method uses piston-operated door closers mounted at the top of the door. These hydraulic or pneumatic closers rely on an air cylinder for reliable self-closing. For heavy-duty applications, an additional closer may be installed at the bottom for smoother operation. However, traditional closers can be bulky, especially for large or fire-rated doors.
Spring hinges offer a compact alternative, automatically returning doors to their closed position without cumbersome hardware. Also called self-closing hinges, they replace standard butt hinges in residential and commercial settings. Available in various materials, finishes, and sizes, they suit light, medium, and heavy-duty applications. Their adjustable closing force and discreet design make them ideal for doors requiring consistent closure, access control, or ADA compliance.
Spring Hinge Types
Standard Spring Hinge
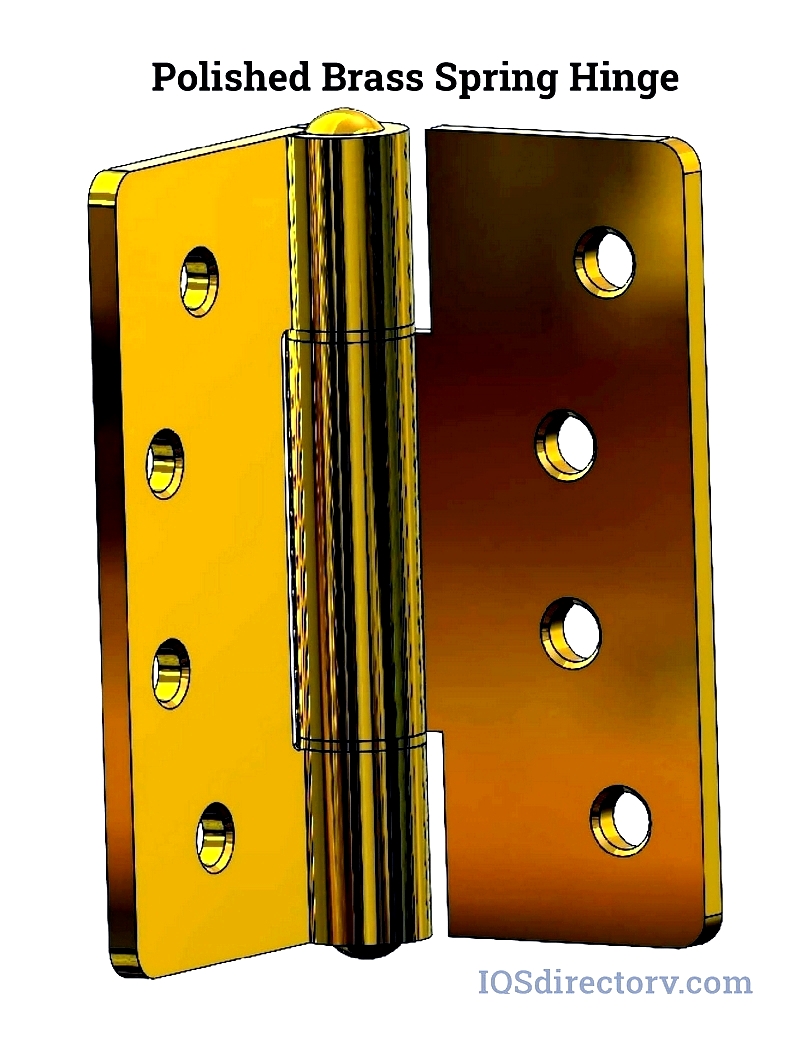
The standard spring hinge resembles a traditional butt hinge, mounted on the door jamb and door. A spring within the knuckles allows tension adjustment with an Allen wrench. This transforms the hinge into a self-closing mechanism, ideal for wood and metal doors in residential and light-commercial settings.
When opened, the internal spring compresses; upon release, the tension closes the door automatically. This simple mechanism is affordable and easy to install, making it preferable where adjustable closing speed isn't needed.
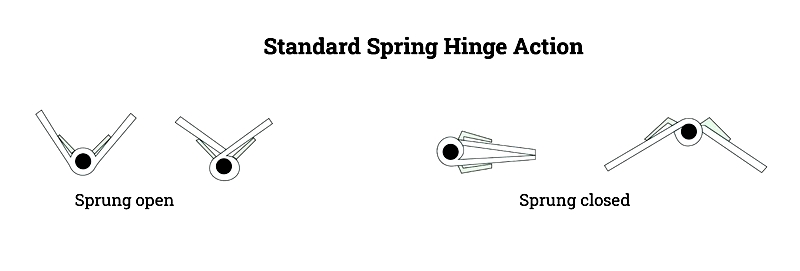
Double Action Spring Hinge
Double action spring hinges, or saloon hinges, allow doors to swing in both directions. With two spring-loaded pivots, they enable a 180-degree rotation (90 degrees each way). These hinges are ideal for restaurant kitchens, bistros, and partition doors with bi-directional traffic. They are often mortised for a flush appearance.
Closing speed is adjusted by spring tension: higher tension creates a swift return, while lower tension ensures a gentle closure. Made from durable materials like brass or stainless steel, they withstand frequent use in commercial settings.

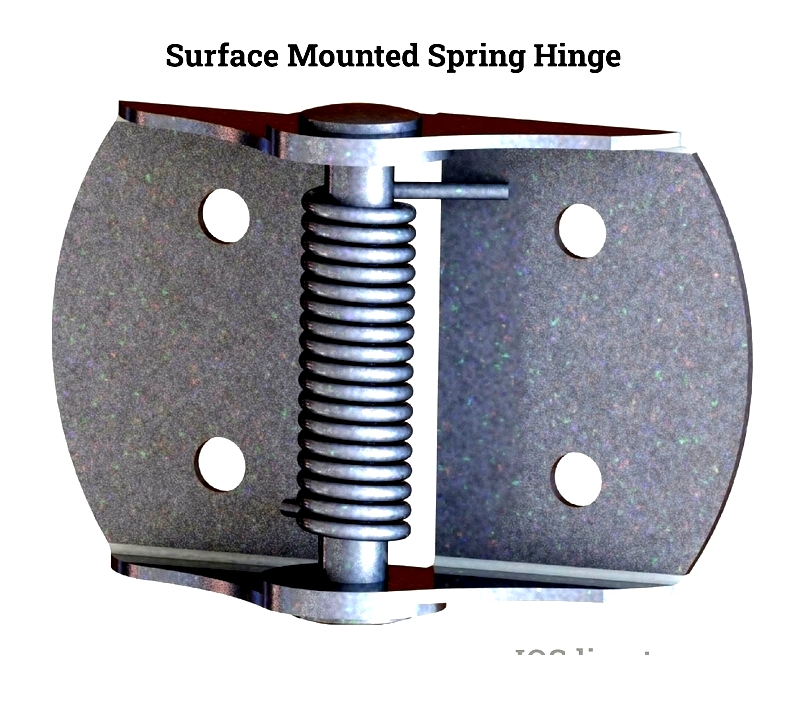
Surface Mounted Spring Hinge
Surface mounted spring hinges attach directly to the door frame, simplifying installation where recessing isn't possible. They are practical for gates, screen doors, and industrial settings. Available in finishes like zinc-plated or powder-coated steel, they often feature non-removable pins for security.
Horizontal Spring Pivot Hinges
Horizontal spring pivot hinges provide automatic closure for heavy or oversized doors. Installed in pairs (top and bottom), they integrate a tension spring for stable support. Unlike bulky door closers, they maintain a streamlined aesthetic while ensuring secure closure.

Spring Loaded Piano Hinges
Piano hinges run the full length of a door or panel. Spring-loaded versions feature centrally placed springs for self-closing action, ideal for lightweight doors, cabinets, and bathroom stalls.

Spring Strap Hinge
Strap hinges are robust, designed for gates and barn doors. Spring versions offer self-closing action with extended wings for strength. Non-removable pins enhance tamper resistance.

Square Corner Spring Hinge
Square corner spring hinges have rectangular wings for a clean look. With four screw holes per wing, they provide stable attachment for heavy or fire-rated doors.

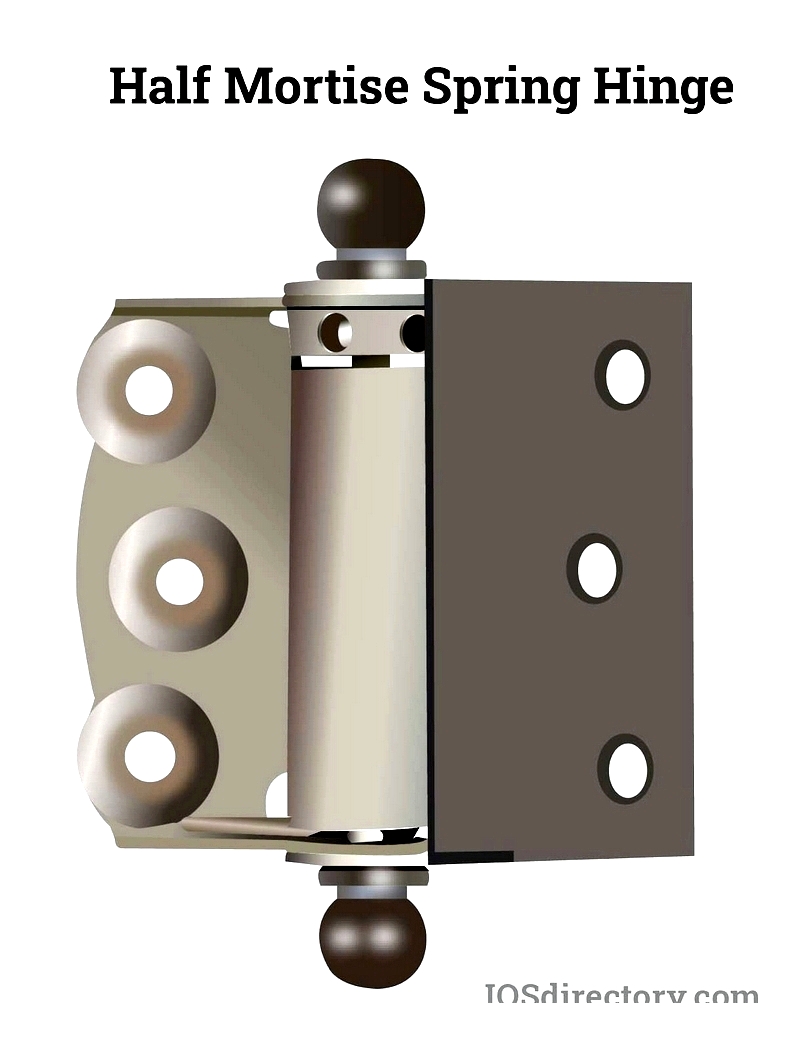
Half Mortise Spring Hinge
Half mortise spring hinges combine recessed and surface-mounted wings. They balance aesthetics with self-closing functionality, ideal for retrofits.
Non-Mortise Spring Hinge
Non-mortise spring hinges require no cutting, making them perfect for rentals or historical renovations. Their thin design minimizes gaps and suits interior or lightweight doors.

Wrap Around Spring Hinge
Wrap-around spring hinges provide multi-point attachment for stability. The visible barrel allows easy tension adjustment, making them suitable for custom cabinetry.

Swing Clear Spring Hinge
Swing clear hinges move the door edge fully clear of the doorway, ideal for ADA compliance. They are used in hospitals, schools, and public buildings for unobstructed access.

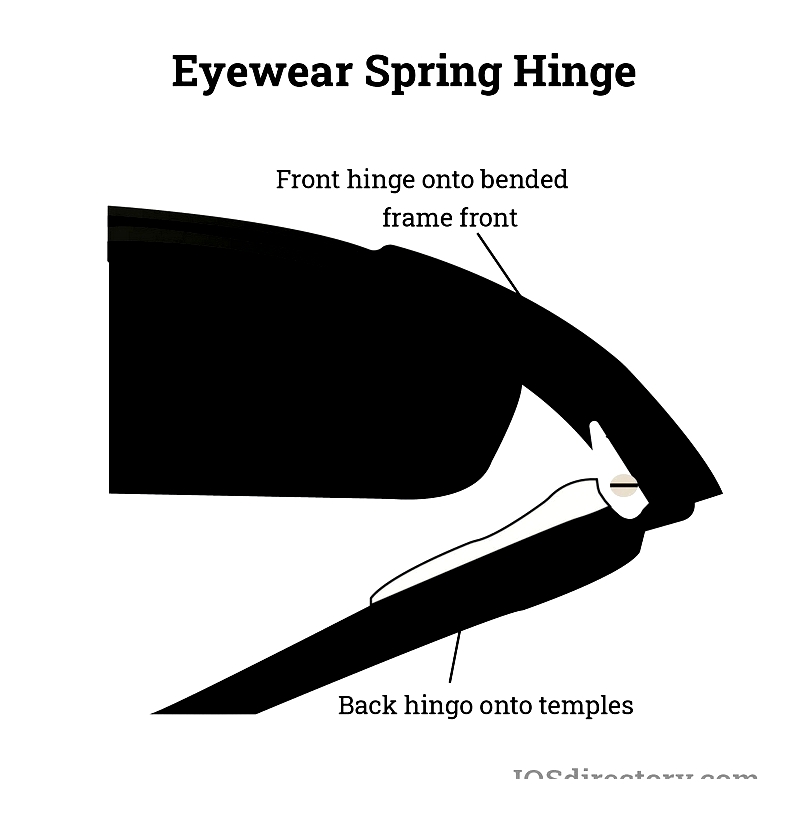
Eyewear Spring Hinges
Eyewear spring hinges, or flex hinges, ensure a snug fit for glasses. They allow frame arms to flex beyond 90 degrees, preventing slippage and extending frame life.