Introduction
This article provides an in-depth exploration of electric transformers.
Key topics covered include:
- Principle of Electric Transformers
- Types of Electric Transformers
- Applications and Benefits of Electric Transformers
- And Much More...
Chapter 1: Understanding the Principle of Electric Transformers
This section explores electric transformers in detail, covering their construction, operational principles, and functionality.
Understanding Electric Transformers
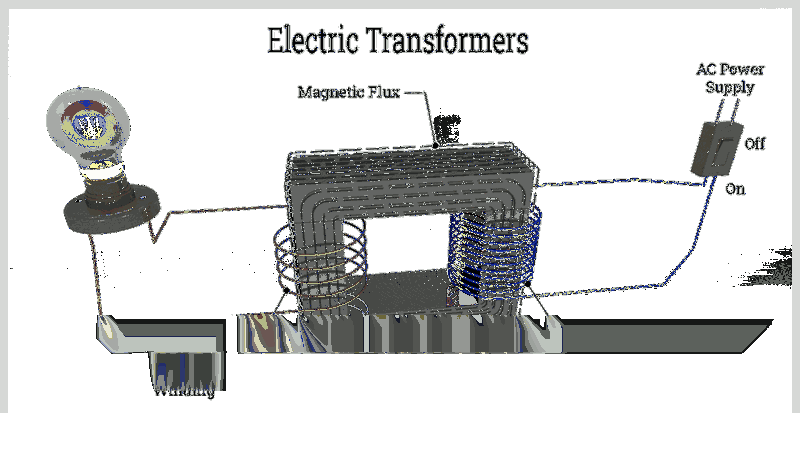
Electric transformers are stationary devices that transfer electrical power between circuits while maintaining frequency. Designed to modify voltage levels, they can increase or decrease voltage, inversely affecting current flow. Their operation relies on electromagnetic induction and mutual induction principles.
Operational Mechanism of Electric Transformers
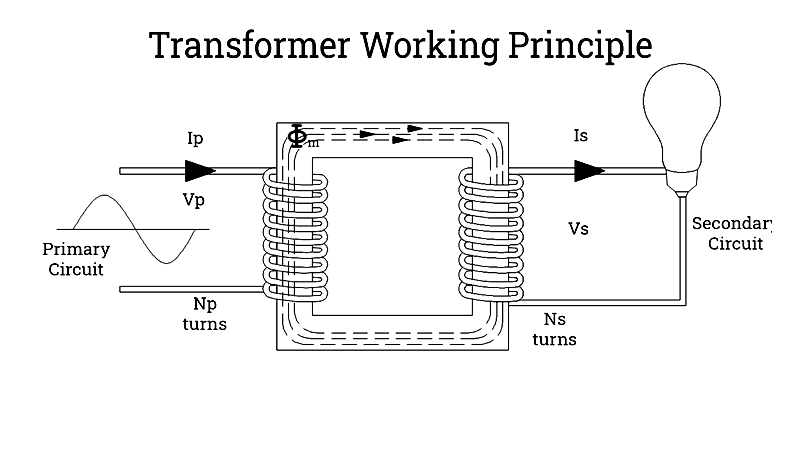
Electric transformers operate based on Faraday's laws of electromagnetic induction. The fundamental principle states that electricity generates magnetic fields, and magnetism can induce electricity.
Magnetism plays a crucial role in electrical systems. Transformers utilize magnetic properties to adjust voltage levels, either increasing or decreasing them. By altering the magnetic field strength within the transformer, changes in electrical force and power occur. When conductive materials like copper are involved, electron movement enables electrical transmission.
Transformers modify voltage through coil configurations around their core. As alternating current passes through, the magnetic field varies. The core's output wire winding experiences induced current from this changing field.
For long-distance electricity transmission, high voltages are necessary for efficiency. At destinations, voltage is reduced to protect equipment and minimize hazards. Substations gradually lower high voltages to manageable levels. Local transformers further reduce voltage for household devices like appliances and electronics. Industrial settings often require higher voltages, achieved through transformers.
Voltage reduction requires more primary winding turns than secondary, while voltage increase needs fewer primary turns. Equal turns on both windings would maintain existing voltage without modification.
All transformers experience energy loss, primarily as heat. Managing this heat is challenging due to their static nature. Excessive heat can damage wiring insulation. Cooling methods include air circulation and oil immersion. Transformer windings connect through a magnetic core, typically made of iron or ferrite with laminated copper or enamel coatings.
Components of Electric Transformers
Electric transformers consist of several essential components for optimal performance.
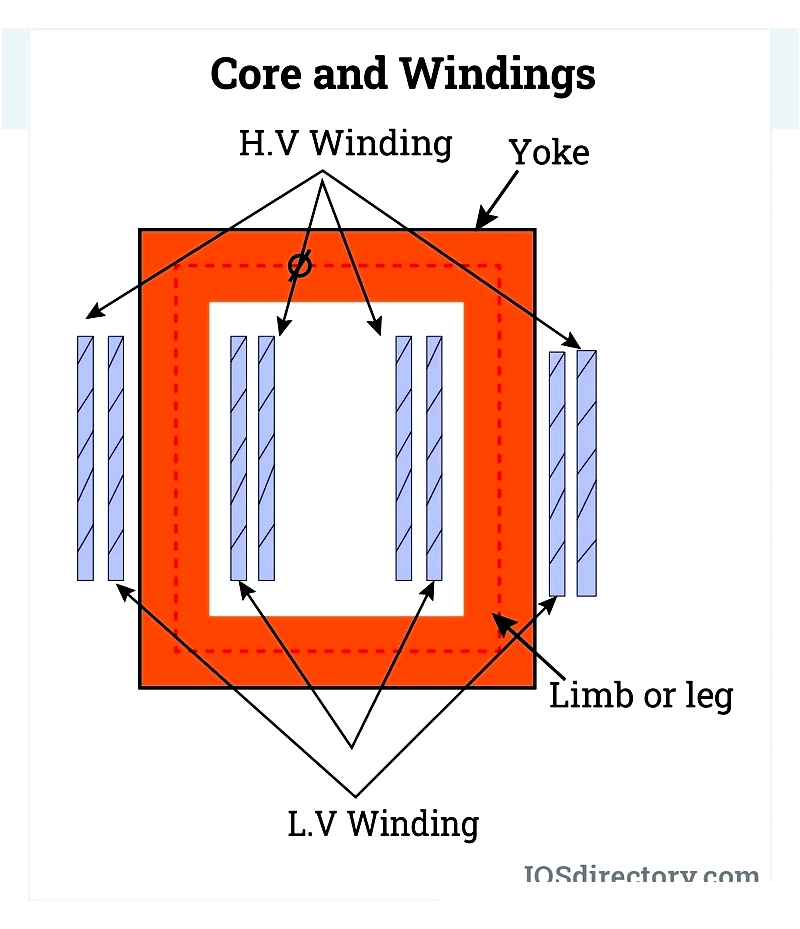
Transformer Core
The core supports primary and secondary windings while providing a low-reluctance path for electromagnetic flux. Constructed from thin, high-grade silicon steel sheets with insulating separators, it minimizes hysteresis and eddy currents. The steel contains under 0.1% carbon with added silicon to further reduce eddy currents. Three-phase transformers have core limbs for each phase's windings, connected by magnetic yokes. Core types include core-type and shell-type designs.
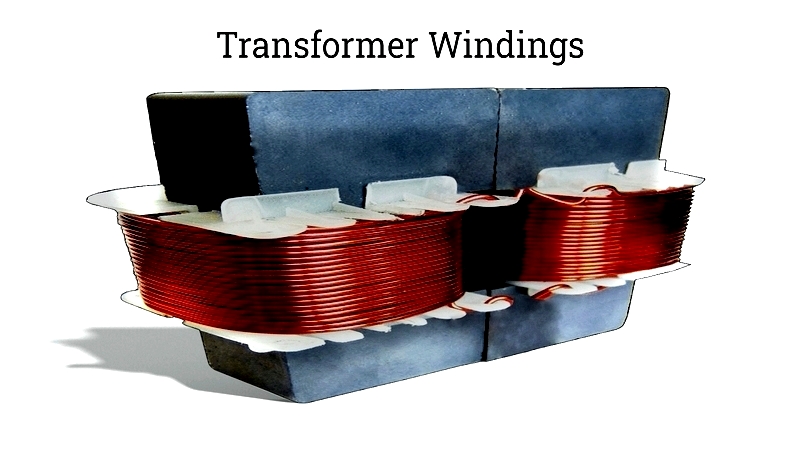
Transformer Winding
Each phase features primary and secondary windings made of insulated copper or aluminum conductors. Winding configuration depends on current rating, short circuit strength, temperature rise, impedance, and voltage surges.
High voltage (HV) and low voltage (LV) windings differ in conductor thickness and placement relative to the core.

Shell-type transformers may position HV windings between LV coils in segments. Core-type transformers offer four winding classifications based on current capacity and turn count.
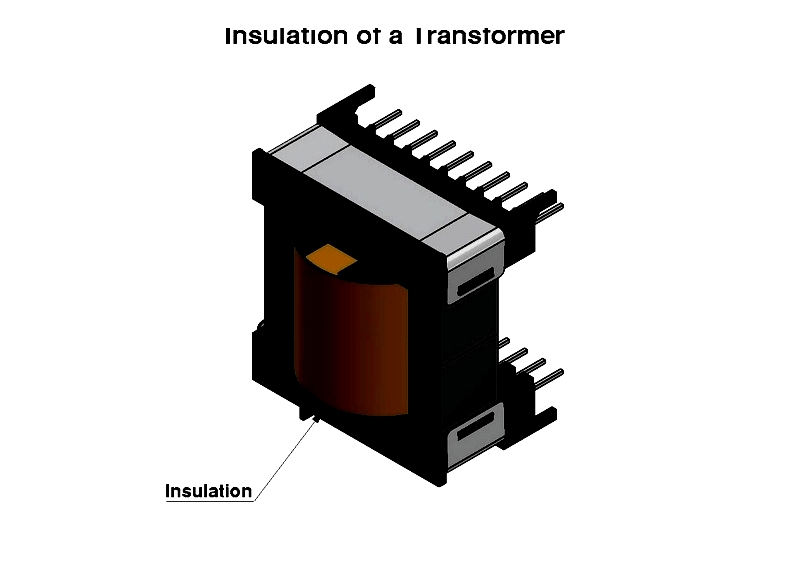
Transformer Insulation
Proper insulation is critical for transformer safety and performance. Materials must exhibit high dielectric strength, temperature resistance, and mechanical durability. Common insulators include cotton, synthetic fibers, and paper, applied between windings, core, and active components.
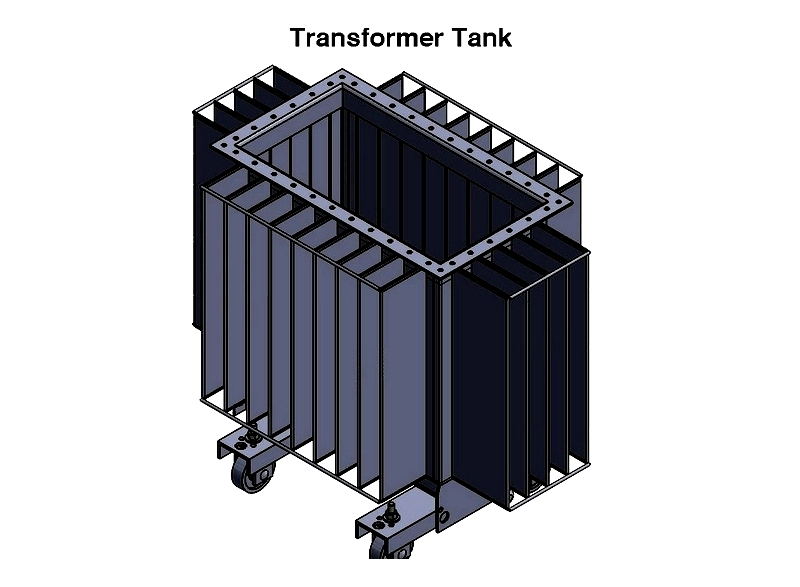
Transformer Tank
The tank protects core and windings from environmental factors while containing oil and supporting accessories. Typically steel, aluminum may be used for weight reduction despite higher cost.
Transformer Oil
Oil enhances insulation, aids cooling, and helps identify faults in oil-immersed transformers.
Connections and Bushings
Internal terminals connect cables through insulating bushings at winding ends. Common bushing materials include epoxy resins and porcelain.
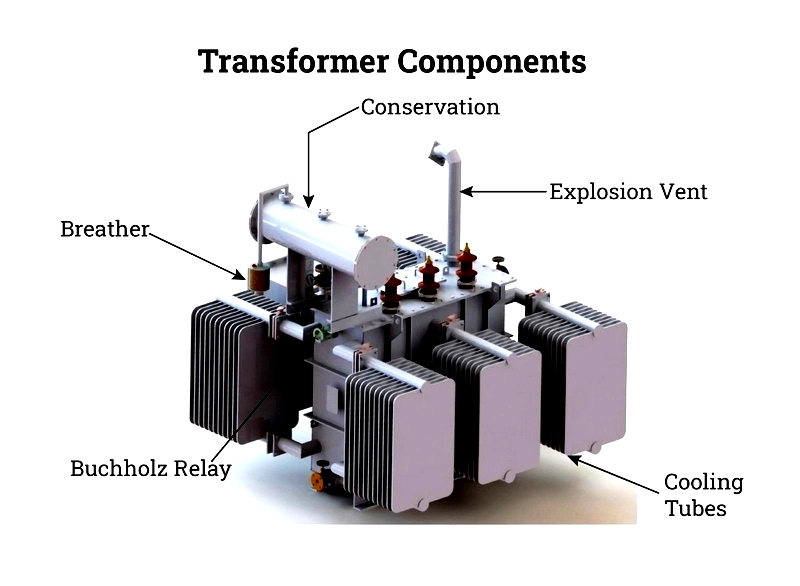
Oil Conservators
Positioned above the tank, conservators accommodate oil expansion/contraction with rubber bladders. A level indicator and connecting pipe complete the system.
Electric Transformer Breather
Breathers maintain oil dryness using silica gel to remove moisture from incoming air during temperature changes.
Cooling Systems: Radiators and Fans
Heat management varies by transformer type. Oil-immersed transformers use radiators and fans based on power rating and cooling needs. Large transformers employ forced cooling with integrated radiators.
Emergency Release: Explosion Vent
This safety feature releases excess pressure through a diaphragm-equipped pipe when internal oil pressure becomes dangerous.
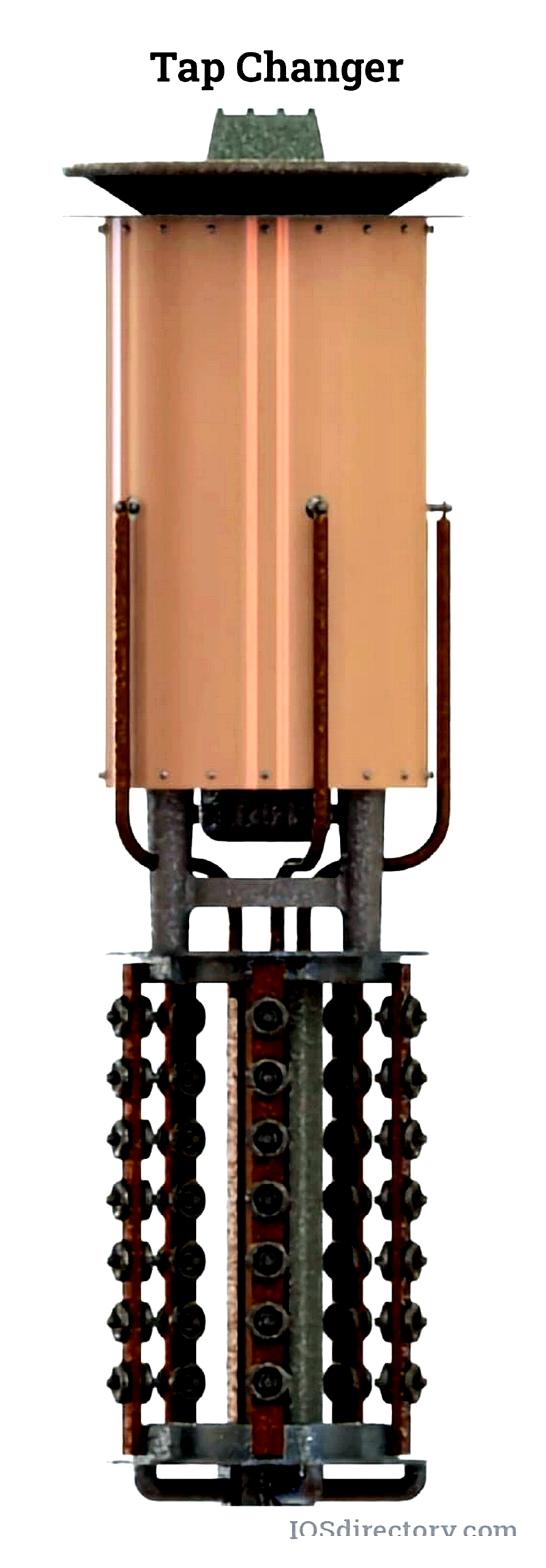
Voltage Regulation with Tap Changers
Tap changers adjust secondary voltage by modifying turns ratio. On-load changers operate during current flow; off-load types require deactivation.
Protective Measures: Buchholz Relay
This device detects fault gases in oil-immersed transformers over 500 kVA, triggering alarms and circuit breakers when necessary.
Additional components may include sensors, heat exchangers, and protection relays in larger transformers.
Chapter 2: Types of Electric Transformers
While all transformers operate on electromagnetic induction principles, they vary in design for specific applications. Understanding these types is essential for electrical system professionals involved in power distribution, transmission, or electronics manufacturing. Each type optimizes voltage regulation, efficiency, and safety for diverse commercial, industrial, and residential needs.
Iron Core Transformers
These highly efficient transformers feature laminated silicon steel cores that minimize eddy currents and hysteresis. Widely used in power plants and industrial systems, they excel in energy transfer applications requiring maximum efficiency.

Insulated silicon steel cores support high-frequency operation and extended service life, making them ideal for grid power systems.
Isolation Transformers
These specialized units provide galvanic isolation between power sources and devices, protecting sensitive equipment while reducing electrical noise. Applications include medical devices, audio equipment, and industrial control systems.
Ferrite Core Transformers
Designed for high-frequency applications like SMPS, these transformers feature ceramic cores with high magnetic permeability. Their low core losses make them suitable for power electronics and telecommunications equipment.
Step Up Transformers
Essential for power transmission, these units




