Introduction
This article provides an in-depth exploration of heat treating.
It covers detailed information on various topics including:
- The Function of Heat Treating
- Different Types of Heat Treatment Processes
- Applications and Advantages of Heat Treating
- And More...
Chapter 1: Understanding the Role of Heat Treating
This section explores the heat treatment process and its importance.
Defining Heat Treating
Heat treatment involves heating and cooling cycles to enhance a material's properties, strength, and performance.

Applying heat treatment to metals can improve malleability for easier shaping or increase hardness for greater strength. This process includes various techniques to modify a material's physical properties by heating or cooling metals to achieve desired characteristics.
The Mechanics Behind Heat Treating
This section explains the fundamentals and objectives of heat treatment.
Principles of Heat Treatment
Heat treatment processes involve heating and cooling metals, differing primarily in three aspects: heating temperatures, cooling rates, and quenching methods used to achieve specific properties.

Using appropriate equipment is essential for effective metal heat treatment. This ensures precise control over heating, cooling, and quenching conditions. The heating chamber must be properly equipped with the correct size, type, and gas mixture to accurately regulate temperature. Additionally, selecting a suitable quenching medium ensures proper metal cooling.
Steps in Heat Treating metals
The heat treatment process typically consists of three main steps:
- Gradually heating the metal to maintain uniform temperature distribution.
- Soaking or holding the metal at a target temperature for a set duration.
- Cooling the metal to room temperature.
The Heating Phase
The primary goal during heating is to achieve even temperature distribution across the metal. Gradual heating prevents uneven expansion that could cause distortion or cracking. The optimal heating rate depends on several factors:
- The metal's thermal conductivity. metals with higher conductivity heat faster.
- The metal's condition. Hardened or stressed objects require slower heating.
- The size and cross-section of the metal. Larger or uneven items need slower heating to minimize warping or cracking risks.
The Soaking Phase
During this stage, the metal is held at a specific temperature until the desired internal structure forms. The "soak time" depends on the metal's chemical composition and mass. For uneven cross-sections, the soak time typically corresponds to the largest section.

metals should not be heated directly from room temperature to the soaking temperature. Gradual heating to just below structural transformation points ensures uniform temperature distribution.
After preheating, the metal is quickly heated to the final temperature. Complex items may require multiple preheating stages to minimize warping.
The Cooling Phase
This phase involves cooling the metal to room temperature, tailored to the metal type and potentially using liquids, gases, or combinations. The cooling rate significantly impacts the metal's final properties.
Quenching, a rapid cooling process, uses air, water, oil, brine, or other substances. While often associated with hardening, quenching doesn't always result in hardening. For example, water quenching is part of copper annealing, while some metals require slow cooling to harden.

Quenching isn't suitable for all metals due to potential cracking or warping. Generally, water or brine cools metals rapidly, while oil mixtures provide slower cooling. Carbon steels typically use water for hardening; alloy steels use oil, and nonferrous metals use water.
The Goals of Heat Treating
Heat treatment achieves several key objectives:
- Enhancing mechanical properties like hardness, tensile strength, shock resistance, ductility, and corrosion resistance.
- Improving machinability and reducing brittleness.
- Relieving internal stresses from heated or cold working.
- Modifying or refining grain size.
- Enhancing magnetic and electrical properties.
- Increasing resistance to corrosion and wear.
- Hardening material surfaces.
- Improving fatigue limits in medium to small parts like gears and shafts.
- Creating clean, aesthetically pleasing surfaces.
- Producing tough cores through case hardening.
- Enhancing steel's ability to cut other metals.
- Ensuring structural consistency.

Chapter 2: Types of Heat Treatment Processes
The various heat treatment processes include:
Carburizing Treatment Process
The carburizing heat treatment process introduces carbon atoms into steel's surface layers to increase surface hardness. This case-hardening method produces a harder, more wear-resistant surface, particularly valuable for high-friction components.
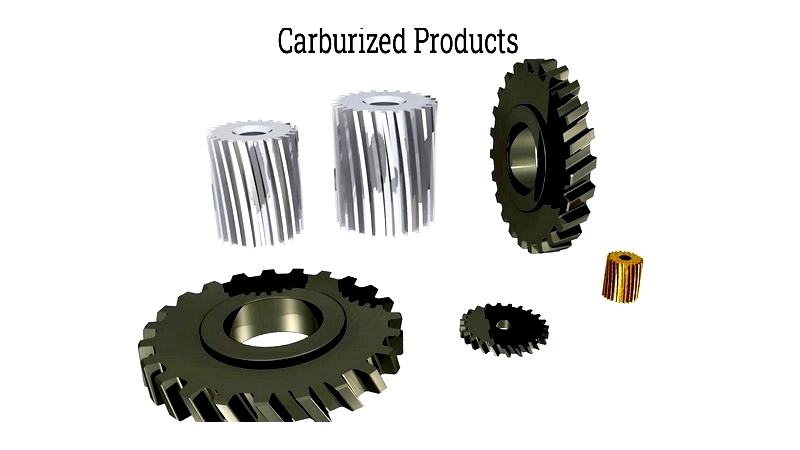

The depth of carbon diffusion depends on factors like furnace atmosphere, material type, temperature, and exposure duration. Hardening occurs after rapid quenching to lock carbon atoms in place. Carburizing significantly improves fatigue strength, impact resistance, and durability.
This process suits low carbon steels (0.05% to 0.3% carbon content) and can be applied to various parts like gears and shafts. Carburizing occurs at 1562°F to 1832°F (850°C to 1000°C). Common methods include gas, pack, and vacuum carburizing.
Nitriding Treatment Process
Nitriding diffuses nitrogen into ferrous alloys' outer layers to enhance surface hardness, fatigue strength, and wear resistance. This process is valuable in aerospace, automotive, and power generation industries.
Nitriding occurs at 752°F to 1094°F (400°C to 590°C) in a nitrogen-rich atmosphere. It works best on alloy steels containing chromium, molybdenum, or aluminum.
Nitrided components gain anti-galling, anti-seizing, and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for bearings, dies, and gears. The nitride layer maintains hardness at elevated temperatures.
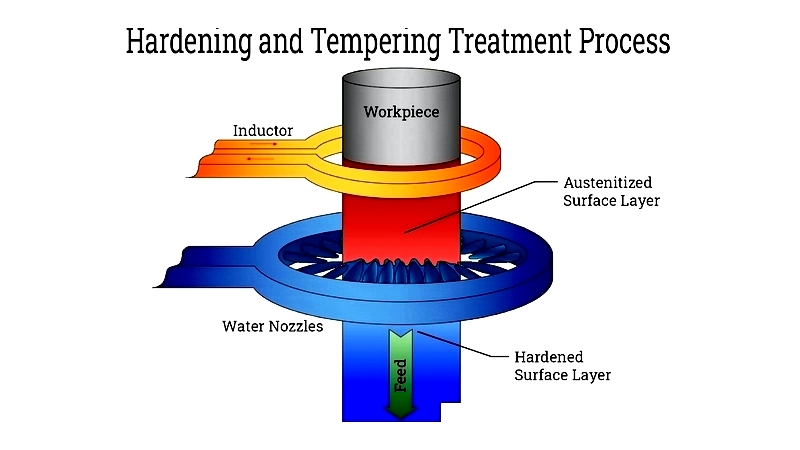
Hardening and Tempering Treatment Process
Hardening increases metal strength throughout without altering surface carbon levels. This through-hardening method is essential for tools and machine parts requiring maximum strength.