Introduction
This article provides an in-depth exploration of nylon tubing.
It covers various aspects including:
- Fundamentals of Nylon Tubing
- Varieties of Nylon Tubing
- Applications and Advantages of Nylon Tubing
- And More...
Chapter 1: What are the fundamentals of nylon tubing?
This section explores nylon tubing, examining its production methods and operational principles.
Overview of Nylon Tubing
Also called polyamide tubing, nylon tubing is made from polyamide resin and offers excellent abrasion resistance. Designed for high-pressure and high-temperature applications, certain nylon types effectively resist chemical degradation.
UV-stabilized nylon tubing performs well in sunny environments. Its flexibility allows for complex configurations, and its elastic memory enables repeated bending without damage.
Even in freezing temperatures, nylon tubing maintains impact resistance and absorbs minimal moisture, preserving its shape. It also resists solvents, alkalis, petroleum products, greases, oils, and various molds and fungi.
Nylon tubing is widely used in industries such as robotics, hydraulic systems, brake and air lines, fuel and vacuum lines, oil and chemical processing, and tool lubrication. It's also essential in food processing and pneumatic systems.
Compared to other resins, nylon tubing has a smaller bend radius and lighter weight. Its unique properties stem from its molecular structure, distinguishing it from plastics like polycarbonate. With a melting point around 374°F (190°C), it outperforms many other resins in thermal resilience.
Nylon's crystalline structure enhances its durability against wear and chemicals. The tubing consists of hollow channels made from solid nylon, which is also used in textiles and plastic products.
Nylon Tubing Production Process
Nylon tubing is created through plastic extrusion or co-extrusion, as detailed below.
Plastic Extrusion Method
The process begins with raw materials, typically small beads, fed into an extruder's barrel. Additives like colorants and UV stabilizers are mixed in during this stage.
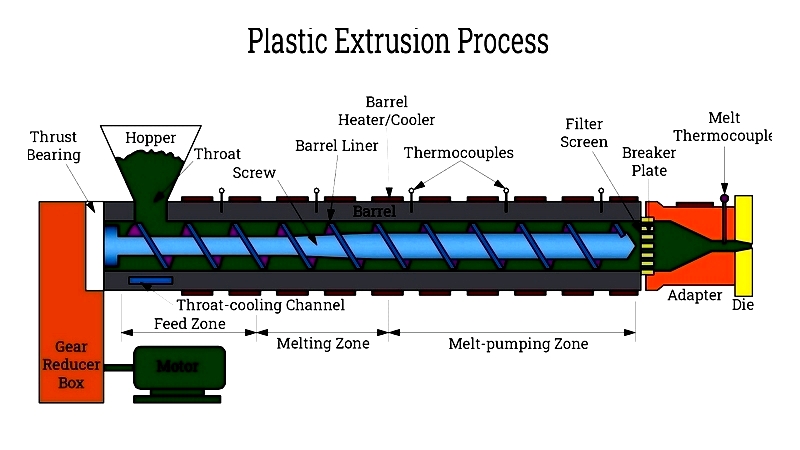
Extrusion is a continuous process similar to injection molding. The material enters the barrel, where a rotating screw propels it through heated zones. The temperature profile prevents overheating while ensuring proper melting.
Additional heat comes from internal pressure and friction. Some systems use cooling fans to manage excess heat. The molten plastic then passes through a screen to remove contaminants before reaching the die, which shapes the final product.
After extrusion, the product cools in a water bath or through other methods, depending on its form. The process can also incorporate recycled materials.
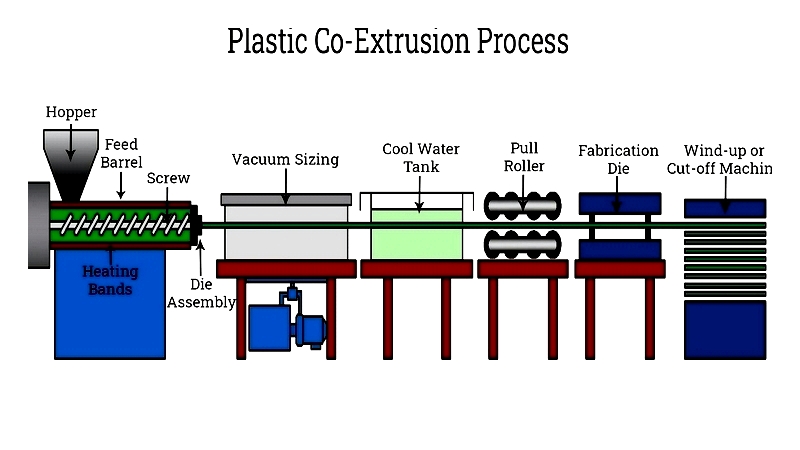
Plastic Co-Extrusion Techniques
Co-extrusion combines multiple materials in a single product. Separate extruders melt different polymers, which are then layered in the die to create enhanced properties.
This method can reduce costs or strengthen the core by using different materials. metal cores may be added for structural support, and co-extrusion can improve wear resistance and reduce oxygen permeation.
Plastic Pultrusion Method
Pultrusion involves drawing fiber-reinforced thermoplastic resin through a die, where polymerization occurs. This produces corrosion-resistant, low-thermal-conductivity tubing.
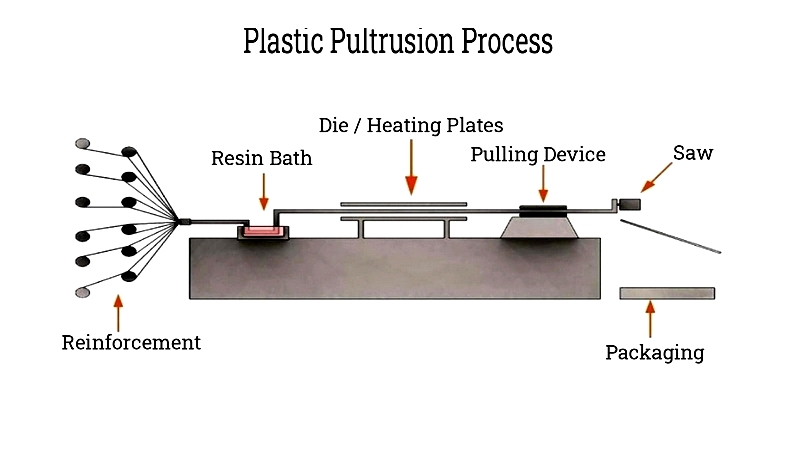
Radius pultrusion creates curved profiles with minimal distortion, useful for specialized applications.
Additional Nylon Tubing Processes
Secondary processes like drilling, painting, and powder coating may be applied. Nylon tubing comes in various colors and finishes.

Extruded nylon tubing is versatile, cost-effective, and durable, making it a preferred choice for manufacturers.
Nylon vs. Polyurethane Tubing
Nylon excels in high-pressure, high-temperature, and chemical-resistant applications, while polyurethane offers greater flexibility for tight bends. Both provide good abrasion resistance.
Chapter 2: What are the top machines for producing nylon tubing?
Advanced extrusion machines in the U.S. and Canada manufacture high-quality nylon tubing for industries like automotive, aerospace, medical, and food processing. Below are some leading models:
Davis-Standard DSREV Extruder
Manufacturer: Davis-Standard, LLC
Key Features: This reliable extruder uses PLC controls for precise temperature and pressure management, ensuring consistent tube dimensions. It's energy-efficient and compatible with various materials, including PA6 and PA12.
Conair MedLine® Co-Extruders
Manufacturer: Conair Group
Key Features: These co-extruders produce multi-layer tubing for medical and food-grade applications. They feature touchscreen controls and integrate with quality monitoring systems.
Allied Supreme Corp. Nylon Tube Extrusion Line
Manufacturer: Allied Supreme Corp.
Key Features: Custom-engineered for nylon tubing, this line offers tight tolerances and high output. It works with various nylon resins for flexible pneumatic and hydraulic lines.
Advanced Extruder Technologies Nylon Tubing Extruder
Manufacturer: Advanced Extruder Technologies (AET)
Key Features: This extruder's precision screw design ensures efficient melting and mixing. It's ideal for tight-tolerance industrial tubing and allows quick size changes.
American Kuhne Nylon Tubing Extrusion Lines
Manufacturer: American Kuhne, Inc.
Key Features: These lines provide precise dimensional control for medical and industrial tubing. They can be customized for specific applications and integrate with cooling and inspection systems.
When selecting equipment, consider tubing specifications, material needs, production volume, and compliance standards. Consult manufacturers for the latest technology and support.
Chapter 3: What are the different types of nylon tubing?
Nylon tubing comes in various forms for different industrial needs, including high-pressure, flexible, coiled, and DOT-approved types.
Standard Nylon Tubing
Made from nylon 6 resin, this tubing offers chemical resistance and rigidity, ideal for pneumatics and water treatment.
DOT Nylon Tubing
Engineered for brake systems, this tubing meets DOT specifications with enhanced flexibility and durability.
High Pressure Nylon Tubing
Designed for aggressive environments, this tubing withstands high pressures and temperatures up to 200°F (93°C).





