Introduction
This article provides a comprehensive overview of plastic rod manufacturing.
Key topics covered include:
- Definition of Plastic Rods
- Plastic Rod Varieties
- Applications and Advantages of Plastic Rods
- Additional Relevant Information
Chapter 1: Understanding Plastic Rods and Their Principles
This section examines the nature of plastic rods, their applications, and the materials used in their production.
Defining Plastic Rods
Plastic rods are solid plastic forms primarily manufactured through extrusion or co-extrusion processes. Unlike hollow plastic profiles, these rods maintain complete solidity throughout. They serve diverse applications across industries including aerospace, electronics, petrochemicals, marine, and transportation.
In these sectors, plastic rods often function as raw materials for machining into various components such as seals, gaskets, corrosion-resistant parts, bearings, and insulation elements.
Additionally, plastic rods find extensive use in construction and commercial applications, providing essential structural support for industrial machinery and retail displays.
Manufacturing Process of Plastic Rods
Plastic rod production primarily involves extrusion or co-extrusion techniques, which we will examine in detail.
The Plastic Extrusion Process
Extrusion stands as the predominant method for plastic rod fabrication. This process begins with raw plastic materials, typically small resin beads called nurdles, being fed into an extruder's barrel through a top-mounted hopper. Additives such as colorants and UV inhibitors are blended with the resin before entering the hopper.
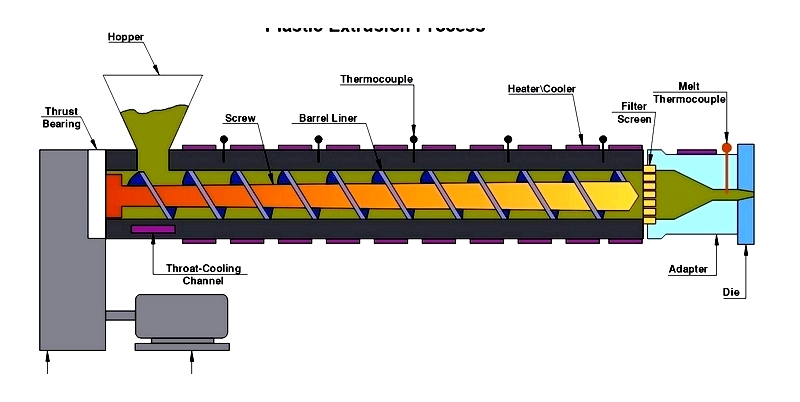
While sharing similarities with injection molding, extrusion operates continuously. The process involves a rotating screw that propels plastic material through heated barrel zones, gradually melting the plastic through controlled temperature increases.
The molten plastic then passes through a screen pack and breaker plate to remove impurities before entering a die that shapes the final product. Cooling occurs through water baths or air cooling methods, depending on the product specifications.
Plastic Co-Extrusion Technique
Co-extrusion combines multiple materials into a single product by merging different polymer streams before they enter the die. This method allows for enhanced material properties and cost-effective production.
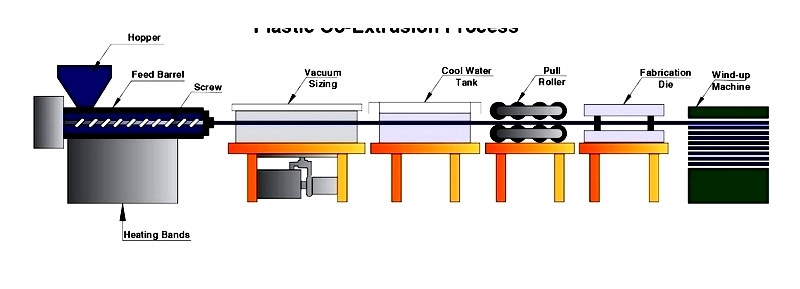
This process proves particularly valuable when creating rods requiring structural reinforcement or specific performance characteristics unattainable with single materials.
Extruder Varieties
The market offers various extruder types, categorized primarily by their operation mechanism: continuous (rotating elements) and discontinuous (reciprocating parts).
Single Screw Extruders
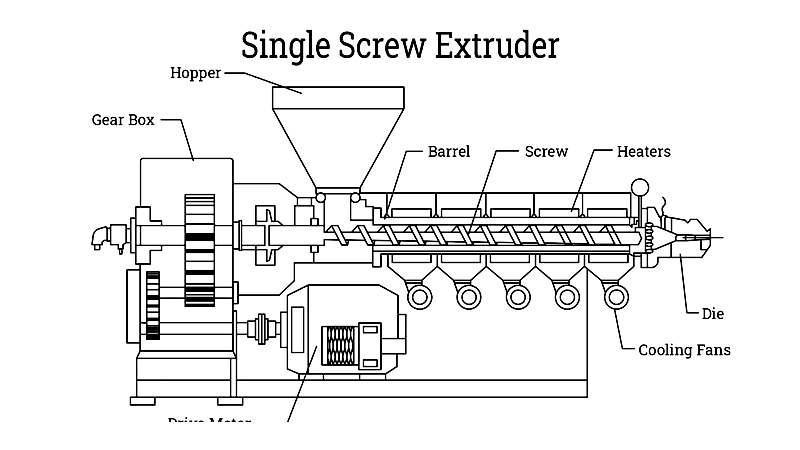
These extruders feature three distinct zones (feed, compression, and metering) determined by a screw with varying channel depths. Their simplicity, durability, and cost-effectiveness make them popular choices.
Thermoplastics vs. Thermosets
Plastic extrusion primarily utilizes thermoplastics, which soften when heated and harden upon cooling, allowing for repeated processing. Common thermoplastics include PVC, ABS, and polypropylene.
In contrast, thermosets undergo irreversible curing during processing, making them unsuitable for remelting. Examples include epoxies and polyimides, valued for their heat resistance and structural stability.
Chapter 2: Leading Machines for Plastic Rod Production
The North American market offers advanced plastic rod manufacturing equipment to meet modern industrial demands. These machines enable efficient, precise production of plastic rods for various sectors including construction, aerospace, and automotive industries.
Davis-Standard DS-RE
Manufacturer: Davis-Standard, LLC
This versatile extruder offers precise control over production parameters, ensuring consistent rod quality and dimensional accuracy. Its user-friendly interface accommodates operators of all experience levels.
KraussMaffei Berstorff ZE BluePower Series
Manufacturer: KraussMaffei Group GmbH
These energy-efficient extruders deliver high output with excellent melt homogeneity, featuring advanced screw technology and optimized temperature control systems.
Chapter 3: Plastic Rod Varieties
Plastic rods, available in various materials, offer unique properties including lightweight construction, electrical insulation, and corrosion resistance. Material selection depends on application requirements such as load capacity, temperature tolerance, and chemical exposure.
Acetal Plastic Rods
These high-strength, low-friction rods excel in precision machining applications, offering excellent wear resistance and dimensional stability.

Acrylic Plastic Rods
Known for glass-like clarity and impact resistance, acrylic rods serve well in signage, displays, and protective applications.

Polyimide Plastic Rods
These high-temperature resistant rods perform exceptionally in demanding environments, making them ideal for aerospace and electronics applications.





