Introduction
This article provides comprehensive information about aluminum casting.
You'll explore key topics including:
- What aluminum casting is
- Different aluminum casting processes
- Aluminum alloys used in casting
- Benefits of aluminum casting
- And more...
Chapter One – What is Aluminum Casting?
Aluminum casting involves pouring molten aluminum into specially designed dies, molds, or forms to create high-precision, quality parts. This effective method produces intricate, complex components that precisely match design specifications.

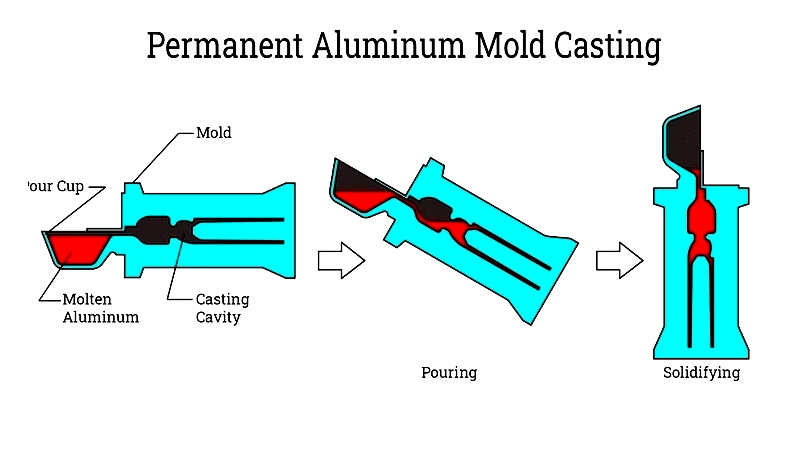
Chapter Two – Advantages of Reusable Aluminum Mold Casting
This efficient casting method uses steel or iron molds engineered for dimensional accuracy and smooth finishes. These durable molds, made from high-melting-point metals like tool steel, withstand molten aluminum temperatures, making them ideal for casting applications.
Permanent molds suit high-volume production, as they endure thousands of casting cycles. This process creates complex geometries and thin-wall parts with minimal labor costs and high repeatability. It generates little waste, maximizing material use and reducing costs. Mold recycling also supports sustainable manufacturing.
However, initial mold creation requires significant upfront investment in CNC machining and tooling. While setup costs are higher than sand casting, long-term benefits like lower per-unit costs, consistent quality, and shorter lead times often justify the investment for medium to large projects.
Permanent Mold Casting
Major costs involve precision machining and thermal treatment of gray iron or steel molds. These molds, often split into halves, are clamped tightly during casting to prevent defects. Preheating the mold reduces thermal shock and improves surface finish.
After pouring, the aluminum cools rapidly in the mold, minimizing grain defects. The casting is then ejected for trimming or deburring. This technically advanced method is favored in automotive, aerospace, and industrial sectors for producing strong, reliable components.
Die Casting
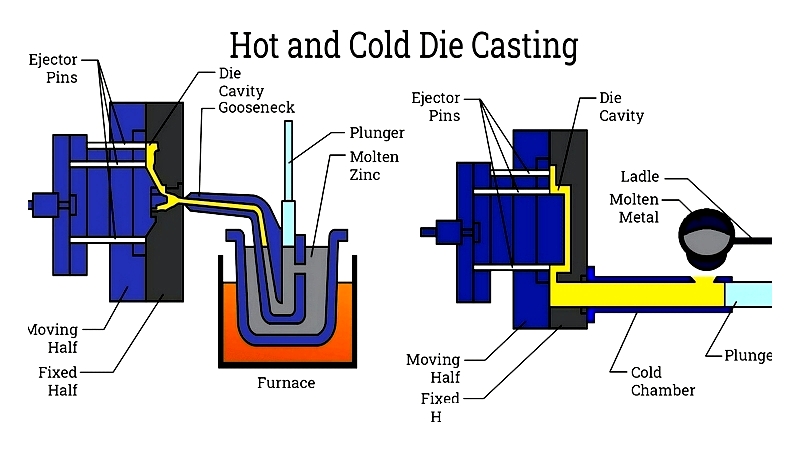
This high-precision process forces molten aluminum under pressure into steel dies. It produces parts with tight tolerances and smooth surfaces, often eliminating secondary machining. Its speed and automation make it cost-effective for mass-producing components like automotive housings and electronics frames.
Two main types exist: hot chamber and cold chamber die casting. Hot chamber casting, for lower-melting-point metals, connects directly to the melting pot. Cold chamber casting, better for aluminum, ladles metal into a cooled chamber before injection. This protects machinery and maintains metal integrity.
Understanding these differences helps select the optimal casting method based on cost, speed, precision, and material needs.
Vacuum Die Casting
This advanced method uses a vacuum to draw molten aluminum into the die cavity. The pressure difference ensures complete filling with minimal porosity. After solidification, the mold opens for quick part ejection, supporting high-volume production.
Precise vacuum control improves fill rates and part quality, producing dense castings with few defects. It's ideal for pressure-resistant parts like hydraulic components and aerospace castings. Submerging the sprue reduces oxidation, yielding cleaner castings.
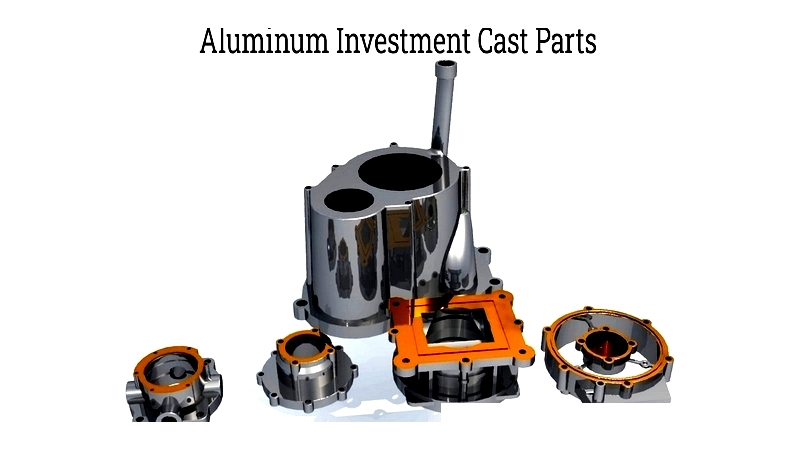
Investment Casting
Also called lost wax casting, this process begins with wax patterns mounted on a sprue system. A ceramic shell forms around the assembly, then the wax is melted out. Molten aluminum fills the preheated shell, capturing fine details. After cooling, the shell is broken away to reveal precision castings.
This method excels at producing complex, thin-walled components for aerospace and medical applications when production volume doesn't justify permanent molds but quality is paramount.


Lost Foam Casting
This process uses polystyrene foam patterns instead of wax. The foam vaporizes when molten aluminum is poured, leaving a precise casting. It's popular for automotive engine blocks and intake manifolds, enabling complex shapes with minimal finishing.
Choosing the Right Aluminum Casting Method
Consider part complexity, volume, material needs, costs, and performance requirements. Permanent mold and die casting suit mass production, while investment and lost foam casting work for complex, lower-volume parts. Consulting a foundry helps determine the best process for your application.
Chapter Three – Expendable Aluminum Mold Casting
This method uses non-permanent molds destroyed to remove castings. It includes lost wax, sand, and lost foam casting. While less precise than permanent molds, it's cost-effective for prototypes and custom parts in automotive and aerospace industries.
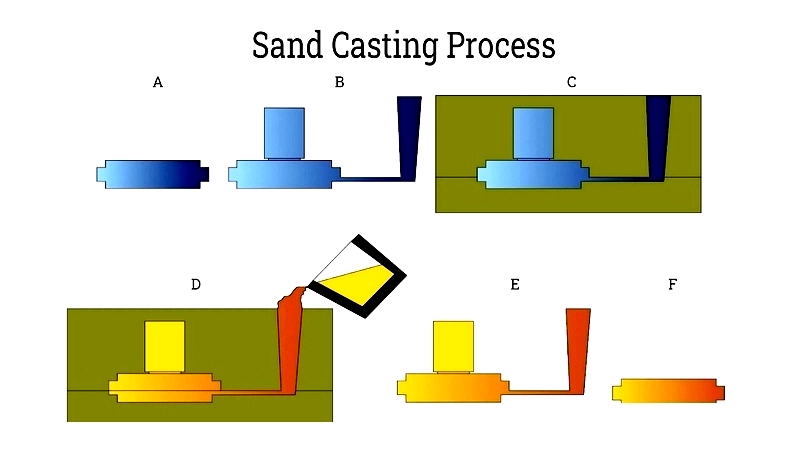
Sand Casting
One of the oldest methods, it compacts foundry sand around patterns. The sprue channels molten aluminum into the cavity. Modern applications range from engine blocks to architectural hardware.
Investment Casting
This precision method creates wax patterns coated in ceramic. After wax removal, molten aluminum fills the shell, producing detailed parts for aerospace and medical uses.
Lost Foam Casting
Using polystyrene patterns, this method vaporizes foam when aluminum is poured. It's economical for complex shapes with minimal machining.
Selecting an Expendable Casting Process
Consider complexity, tolerances, volume, and material needs. Sand casting works for large, simple parts; investment casting for precision; lost foam for complex shapes. Consult foundries to choose the best method.
Chapter Four – Leading Aluminum Casting Machine Manufacturers
Specialized equipment performs aluminum casting. Here are five brands available in North America:
Bühler – Carat:
Modular die casting machine with advanced controls for precise aluminum casting.
Toshiba Machine – DC-J Series:
Robust die casting machines with real-time monitoring for consistent quality.
Italpresse Gauss – Italpresse AL:
High-productivity machines featuring energy-saving technologies.
LK Machinery – Evolution Series:
Reliable machines with remote diagnostics capabilities.
Frech – DAK Series:
Customizable machines with integrated process visualization.
For current models and features, consult manufacturers directly.




