Introduction
This article covers everything you need to know about drum mixers.
You will learn about:
- What a Drum Mixer is
- How Drum Mixers Work
- Types of Drum Mixers
- Components of a Drum Mixer
- Uses for Drum Mixers
- And much more...

Chapter 1: What is a Drum Mixer?
Drum mixers are specialized machines designed to mix free-flowing materials through rotational motion in both directions. They use welded chutes or flights to create fluidized mixtures, making them ideal for materials with varying consistencies, from granular substances to powders with different densities and particle sizes. A common example is the concrete mixer, also known as a tilting mixer, used for single-batch concrete mixing.
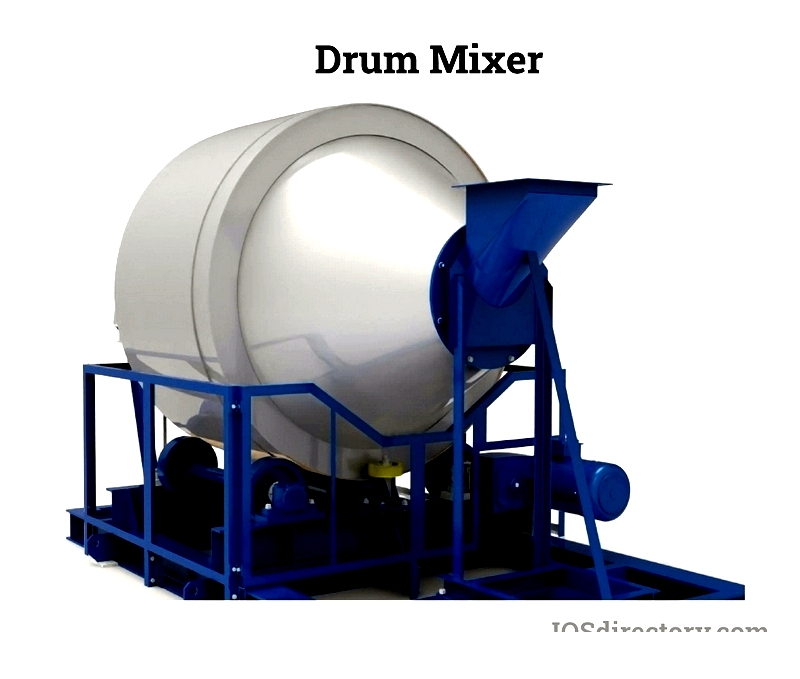

In a drum mixer, the mixing process begins by loading ingredients into the barrel. As the barrel rotates around its central axis, materials move up and down as well as forward and backward. Also called dimensional mixers, rotating horizontal mixers, rotary drum blenders, or rotary drum mixers, these devices are known for their compact size and small footprint. They operate quietly and safely, making them easy to use, and are particularly common in the food and pharmaceutical industries for gently combining powders and granules.
Chapter 2: How Drum Mixers Work
Understanding drum mixer operation is essential for selecting the right industrial mixing solution. Various drum mixer types are available to meet different processing needs in industries like chemical manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, food processing, and construction. Common variations include 55-gallon drum mixers, direct drive mixers, cement mixers, and rotary drum mixers. Each type offers unique performance benefits, with 55-gallon drum mixers and direct drive mixers being popular due to their simple design, minimal components, and easy integration into production lines. When choosing a drum mixer, consider material viscosity, mixing objectives (blending, dissolving, or dispersing), batch size, and required mixing speed.
How 55-Gallon Drum Tumblers Work
A 55-gallon drum tumbler is a specialized mixer for efficiently blending sealed drum contents. These mixers are commonly used to homogenize powders, granules, liquids, and semi-solids in industries where product consistency is critical. Operating like rolling a drum across the floor, they ensure even component distribution without internal agitators. There are two main types:
- End-to-end Tumblers: These lift and rotate the drum end over end, mimicking bottle shaking. This motion is ideal for powder blending, pigment dispersion, or mixing volatile materials as it minimizes leakage risk.
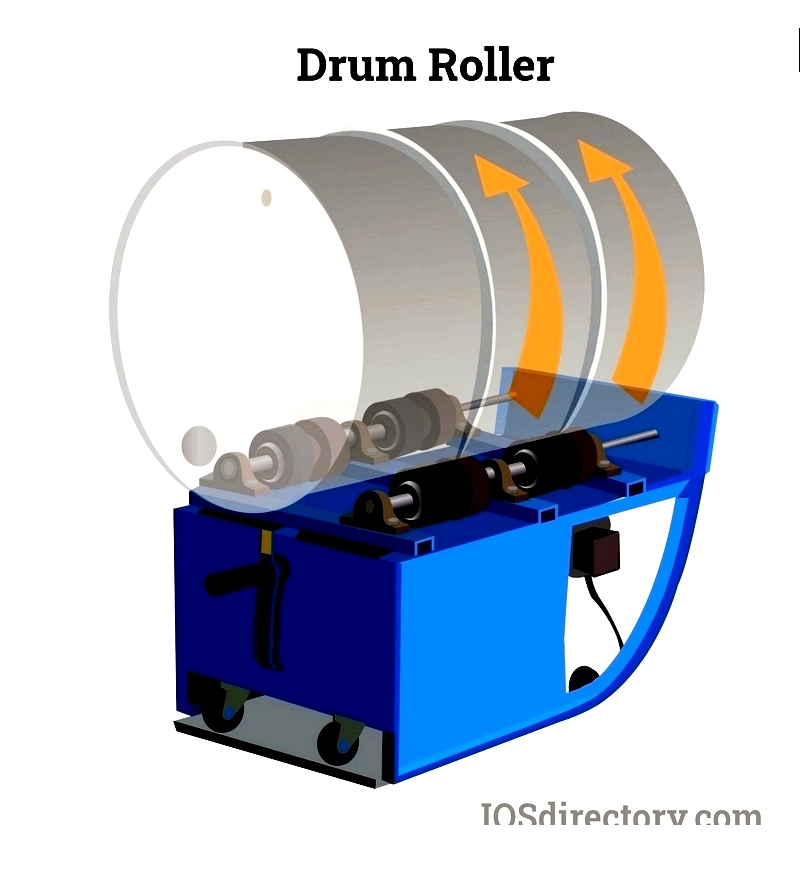
- Drum Rollers: These support drums horizontally and rotate them using rollers. The smooth rolling motion gently agitates mixtures, re-suspends settled solids, or combines liquids and solids in closed containers, making it suitable for hazardous or sensitive compounds.

How a Direct Drive Mixer Works
Direct drive mixers provide robust, high-speed mixing for large drums in process industries. These industrial-grade drum top mixers are larger versions of standard hand mixers, typically mounted on 55-gallon drums or bulk containers. Their powerful electric or pneumatic motors handle low to medium viscosity fluids, slurries, chemicals, and polymer solutions. Installation options include placement in the drum's bunghole or clamping onto the drum lid.
Direct drive drum mixers feature a 36-inch mixing shaft connected to a high-performance motor coupler. Various impeller designs, secured with set screws, allow customization for emulsifying, dispersing, or dissolving tasks. Mounting options—plate, cup, clamp, or angle brackets—cater to different drum configurations and material characteristics, enhancing safety and flexibility.
Unlike gear drive mixers, direct drive units operate at fixed high speeds (around 2000 rpm), making them ideal for applications requiring intense shearing, such as additive dispersion or paint blending. Specialized impellers create high-velocity turbulence, breaking down agglomerates for thorough homogenization in small batches. For frequent batch changes or mobile mixing, direct drive drum mixers offer unmatched portability.

How a Cement Mixer Works
Cement mixers, or concrete drum mixers, efficiently blend cement, aggregates, sand, and water. Designed for heavy-duty mixing, they feature angled fins or blades inside the rotating drum to lift, tumble, and fold ingredients, ensuring uniform consistency and preventing clumping.
A large opening at the top allows easy loading. once activated, the drum rotates continuously at a controlled speed, thoroughly integrating all components for optimal hydration and structural integrity in the final concrete. Industrial cement mixers are essential for large-scale ready-mix concrete production, while portable models suit smaller projects and testing labs.

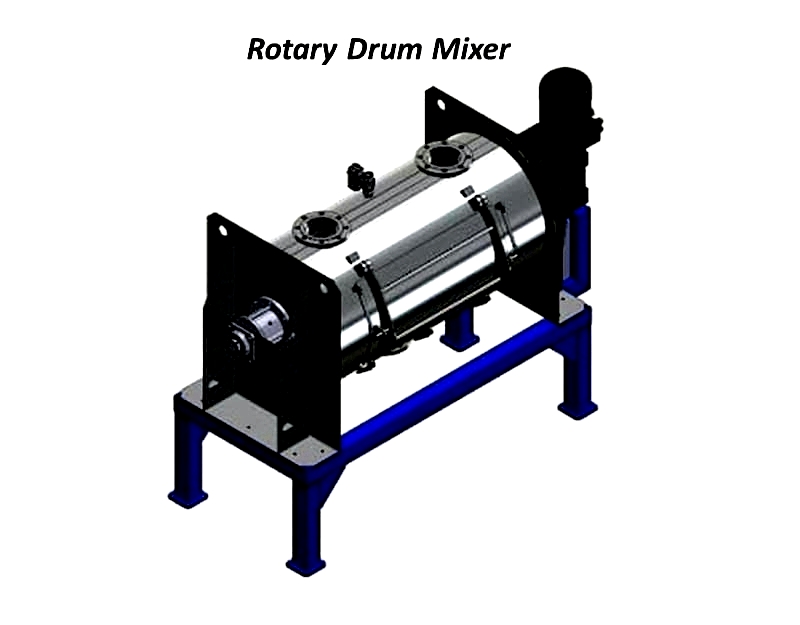
How a Rotary Drum Mixer Works
Rotary drum mixers represent advanced industrial mixing technology for gentle, thorough blending of granular and powdered materials. Raw materials are gravity-fed through a top inlet. As the drum rotates slowly, internal flights or chutes continuously fold and turn the contents, promoting optimal mixing while minimizing material degradation and dust.
Valued in bulk material handling, pharmaceuticals, and fertilizer blending, these mixers operate energy-efficiently. After mixing, the homogeneous mixture discharges via a gravity gate or screw auger for packaging or further processing. Automated feeding and customizable parameters enhance efficiency and product quality.
Choosing the Right Drum Mixer: Consider material compatibility, drum size, agitation level, energy efficiency, cleaning ease, and safety standards. Manufacturers offer features like explosion-proof motors, variable speed controls, and washdown-capable designs. Select a mixer that meets your process requirements and budget for optimal performance and long-term value.
Chapter 3: Different Types of Drum Mixers
Drum mixers, or barrel mixers, come in various types to meet diverse industrial mixing needs. Their versatility, ease of use, rugged construction, and consistent efficiency make them essential in industries like construction, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and food processing. This guide explores main types, from compact portable mixers to large-scale horizontal rotary models, each engineered for specific applications and materials.
Drum mixers are classified by container type (typically 55-gallon drums) and blending method. They ensure thorough mixing, homogenizing, and suspension of powders, liquids, slurries, and granules. Key categories include concrete mixers, 55-gallon drum mixers, direct drive mixers, and rotary drum mixers. Horizontal rotary models are vital for continuous, large-scale industrial processing.
Barrel Drum Mixers
Barrel drum mixers blend loose and granular materials like powders and dry chemicals in rotating barrels. A rigid hoop secures the barrel during smooth rotation, ensuring thorough mixing without friction or material degradation. This frictionless action prevents heat-related issues, making them ideal for sensitive applications in food, pharmaceuticals, and pigments.
Available with pneumatic or electric drives, these mixers offer precision control and adaptability for low-volume batch mixing, dyeing, and specialty formulations. Their roll-on/roll-off design supports quick batch changes, perfect for labs and small-scale production.




