Introduction
This article provides comprehensive information about automated guided vehicles (AGVs).
Continue reading to learn about:
- What Automated Guided Vehicles are
- Types and applications of AGVs
- An overview of AGV navigation systems
- How AGV locomotion functions
- And much more...
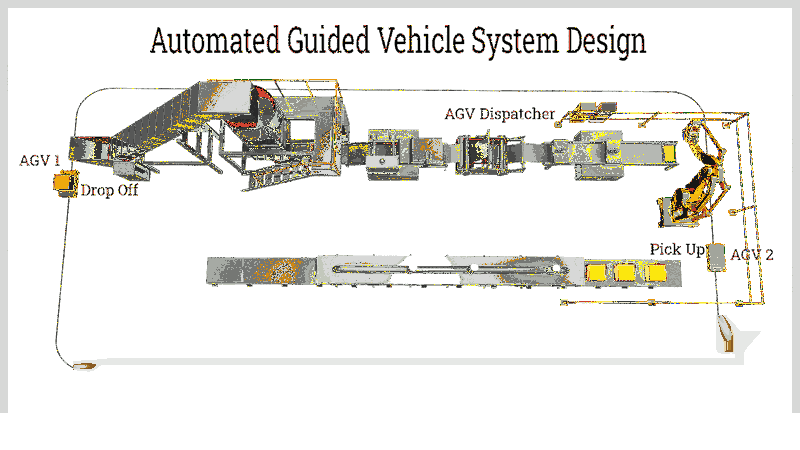
Chapter 1: Exploring Automated Guided Vehicles
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), often called mobile robots, are flexible robotic systems that navigate along predefined paths or within specific areas. Unlike stationary robotic arms fixed to base structures, AGVs operate autonomously with extensive mobility. When combined with robotic arms, their capabilities expand significantly.
AGVs paired with robotic arms create mobile workstations capable of performing various tasks like remote manipulation, scanning, and probing. These systems serve multiple industries including manufacturing, logistics, inspection, exploration, transport, and defense.

AGV technology involves sophisticated automation with advanced control mechanisms and guidance systems that enable long-distance travel and multifunctionality. These systems incorporate navigation techniques like perception, localization, path planning, and motion control, managed through onboard computers or centralized systems.
AGV routes are carefully designed to avoid obstacles and ensure smooth operation. They require flat, even surfaces as they cannot navigate uneven terrain with holes or bumps.
The 2020 pandemic accelerated AGV adoption due to social distancing needs and e-commerce growth. Factories implemented AGVs to maintain operations while moving products and resources safely.
As AGV technology advances, wireless connectivity has improved to ensure reliable, efficient operation.
Chapter 2: AGV Types and Industrial Applications
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are crucial in modern industrial automation, particularly in logistics and manufacturing. While primarily used in warehouse automation and distribution centers, AGVs also serve exploration, inspection, and specialized robotics. They are categorized by load capacity, navigation systems, and transport modes to optimize workflows and reduce labor costs.
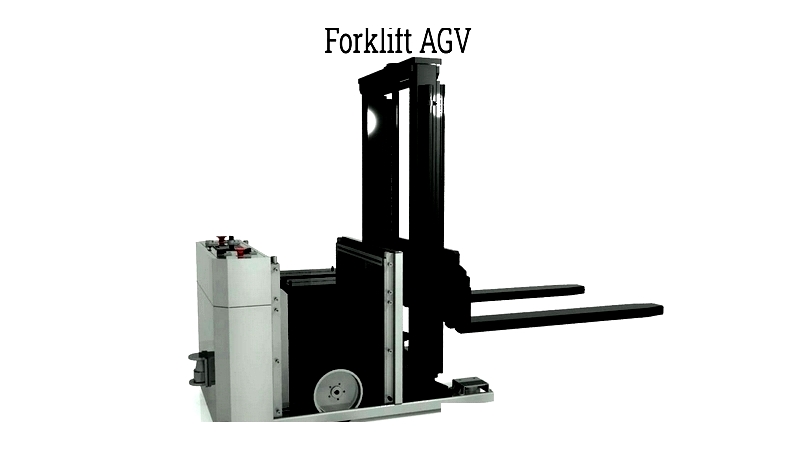
Forklift AGV
Forklift AGVs are self-driving forklifts with advanced navigation technologies like laser guidance or vision systems. Ideal for pallet handling in warehouses, they safely move goods in environments with human workers using fleet management software. These AGVs can switch to manual mode for complex tasks.

Underride AGV
Underride AGVs, or Automated Guided Carts, lift loads by driving beneath transport platforms. They excel in hospitals, pharmaceuticals, and electronics for scheduled deliveries, supporting lean operations.


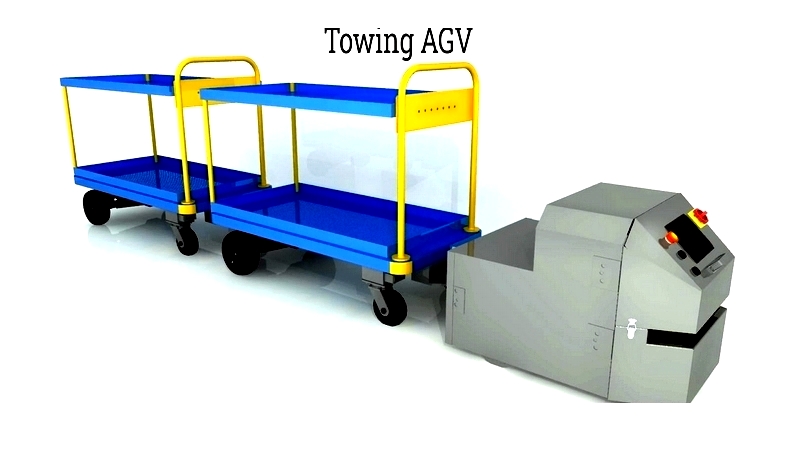
Towing AGV
Towing AGVs pull undriven carriers along predefined routes, ideal for manufacturing and logistics. They specialize in horizontal transport for streamlined operations.

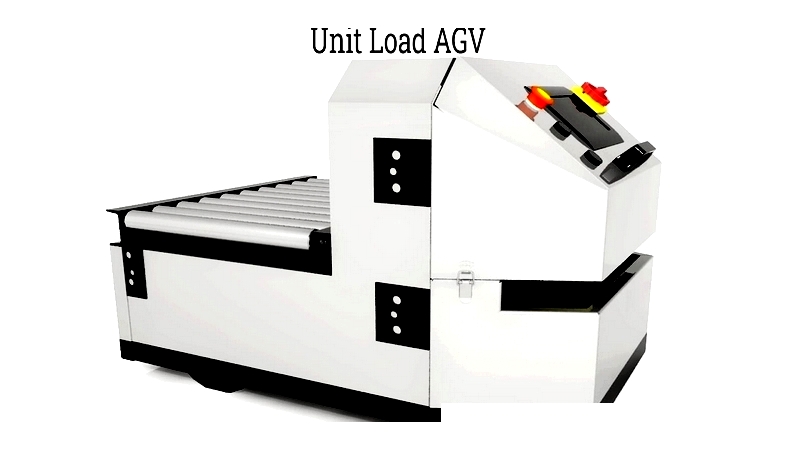
Unit Load AGV
Unit Load AGVs transport standardized containers or pallets, integrating with warehouse systems for high-throughput applications with minimal human intervention.

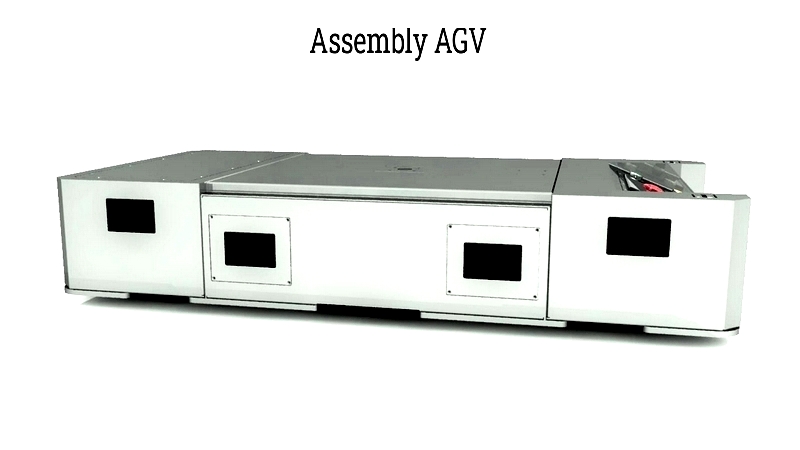
Assembly AGV
Assembly AGVs deliver parts to workstations with precision, using RFID or laser guidance. They excel in automotive and electronics assembly with high maneuverability.

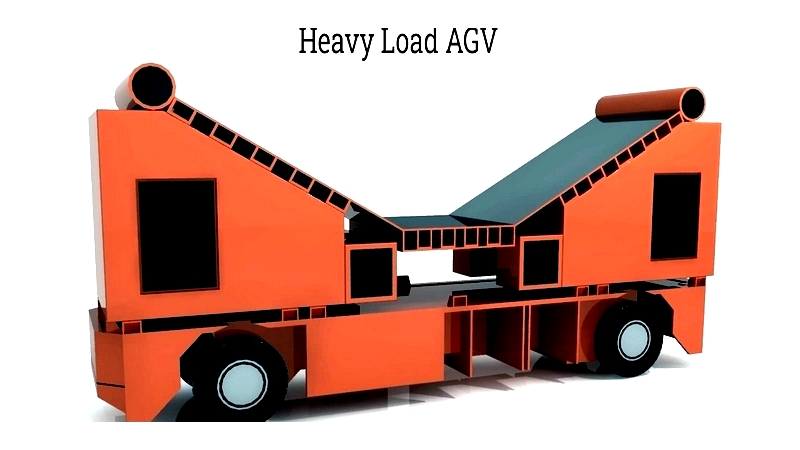
Heavy Load AGV
Heavy Load AGVs handle massive loads in steel, automotive, and shipbuilding industries with robust designs for safety and efficiency.
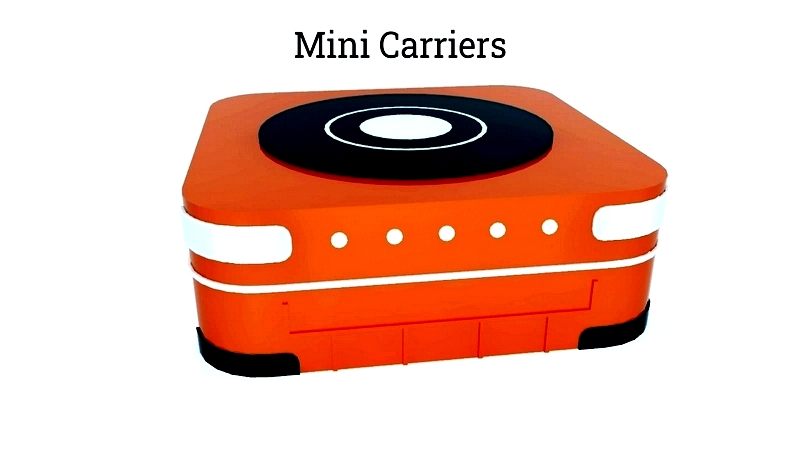
Mini AGV
Mini AGVs are compact robots for small parts handling in manufacturing and fulfillment centers, ideal for high-density environments.

AGV Scissor Lift
AGV scissor lifts combine transport with ergonomic lifting, adjusting product heights for assembly lines to improve safety and efficiency.

Truck Loading AGV
Truck Loading AGVs automate dock operations with advanced navigation for efficient loading/unloading in distribution centers.
Cobot
Cobots are collaborative robots that work safely with humans. Integrated with AGVs, they enhance flexible manufacturing and warehouse automation.