Introduction
This article provides an in-depth examination of timing belts.
Key topics covered include:
- Design and Function of Timing Belts
- Types of Timing Belts and Their Failure Modes
- Applications and Benefits of Timing Belts
- Additional Relevant Information
Chapter 1: Understanding the Design and Functionality of Timing Belts
This chapter explores the fundamental concepts of timing belts, focusing on their design and operational principles.
Definition of Timing Belts
Constructed from rubber with reinforced teeth, timing belts precisely engage with camshaft and crankshaft gears. As critical components in internal combustion engines, they synchronize the rotation of camshafts and crankshafts, ensuring accurate valve timing during each cylinder's intake and exhaust cycles.

In interference engines, timing belts play a vital role in preventing piston-valve contact. These toothed belts typically feature teeth on one or both surfaces.
Timing Belt Construction
Timing belts primarily consist of two elements: torque-bearing cords and a plastic compound forming the teeth and encasing the cords. Material selection varies based on application requirements, with cords typically made from fiberglass, polyester, or Kevlar to ensure effective power transmission.

The perpendicular alignment of cords and teeth enables efficient linear power transfer, as seen in automotive serpentine belts. Despite handling significant loads, the robust cords minimize stretching. Excessive stress may cause cord failure or tooth skipping during pulley engagement. Manufacturing involves molding plastic around pre-tensioned cords to create precise tooth profiles.
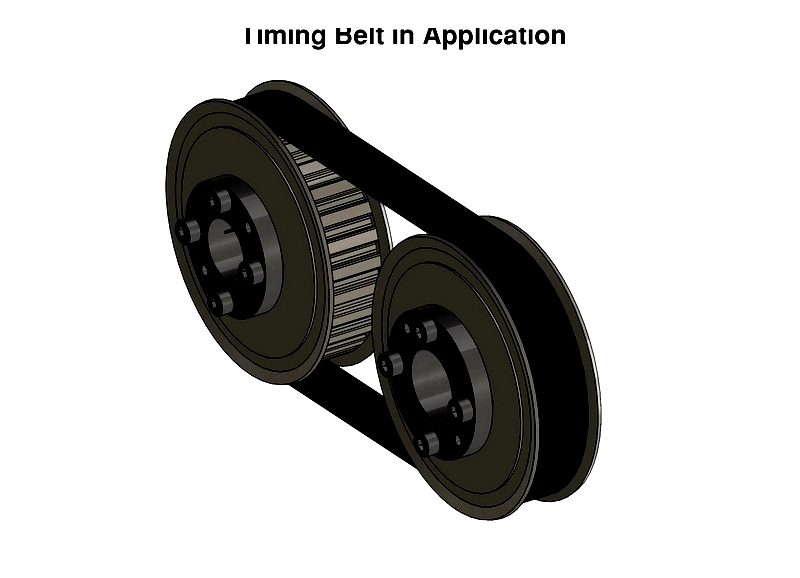

Each belt requires a custom mold with exact tooth counts, producing continuous lengths. Molds create wide sleeves that are subsequently trimmed to required widths. Food-grade applications use FDA-compliant urethane belts with optional translucency to reveal contaminants.
Neoprene remains the standard material for timing belts due to its wear resistance and ability to maintain tooth integrity. Nylon coatings often enhance durability, while EPDM polymers suit low-dust environments with nylon-coated teeth ensuring precision and minimal particulate generation.
Timing Belt Teeth
Durable teeth are essential for precise shaft synchronization and come in various metric pitches. Pitch distance between adjacent teeth affects pulley characteristics like diameter and tooth count. While traditional designs featured trapezoidal teeth, modern manufacturing has introduced curved profiles to reduce noise and extend service life.
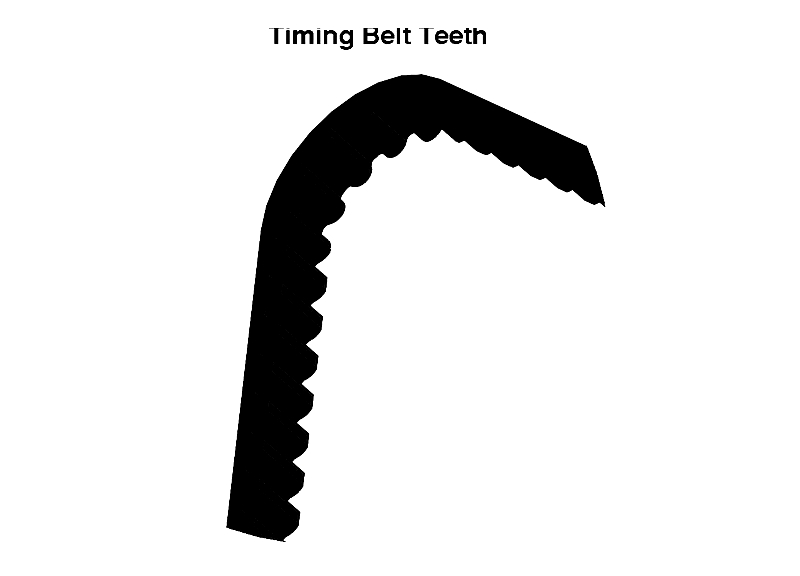

Narrower belt designs offer weight reduction and improved performance through reduced friction.
Tooth Profile Variations
Tooth configurations vary according to application requirements and operating conditions.
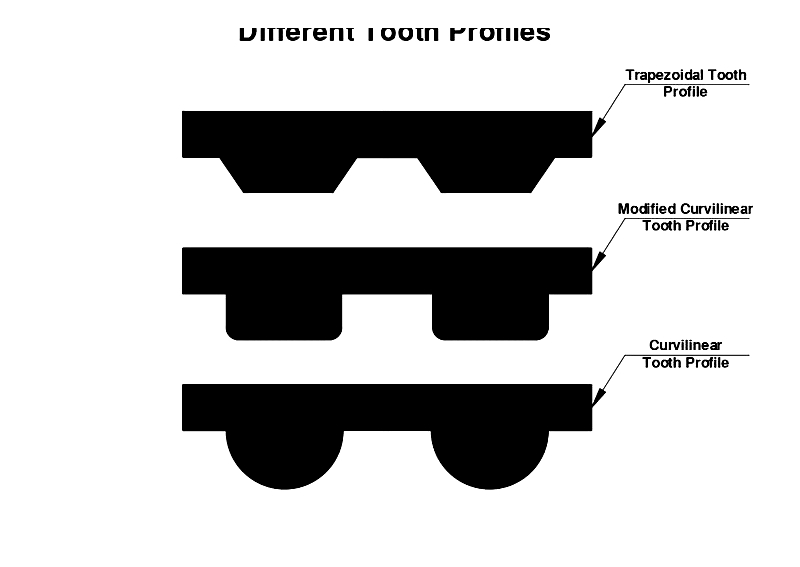
While trapezoidal designs represent early technology, contemporary belts increasingly adopt curvilinear profiles.
Trapezoidal Profiles
Trapezoidal teeth provide effective force transmission but experience accelerated wear under high torque due to their angular geometry. Despite limitations, they remain suitable for precision conveying and positioning applications.

Curvilinear Profiles
Curvilinear teeth offer smoother engagement, reducing tension loss and stress concentration. However, they may exhibit backlash - excessive play between teeth and pulley grooves - potentially affecting precision.
Modified Curvilinear Designs
These hybrid designs combine curvilinear and trapezoidal elements, featuring shallower teeth with steeper sides for high-speed, high-torque applications while maintaining durability. They are particularly suited for demanding industrial environments.
Timing Belt Design Process
The design process typically involves these steps:
Step 1: Determine Peak Torque
Identify maximum torque requirements, typically based on motor startup torque, including potential shock loads.
Step 2: Establish Pulley Diameters
Determine optimal pulley diameters considering space constraints and drive ratios to enhance torque capacity and belt longevity.
Step 3: Select Tooth Profile
Choose appropriate tooth profile based on torque requirements, selecting higher-rated profiles when approaching capacity limits.
Step 4: Calculate Teeth in Mesh (T.I.M.)
Compute engaged teeth count considering mesh factor, then verify belt pitch against pulley limitations.
Step 5: Determine Belt Pitch Length
Calculate required length based on drive component center distances.
Step 6: Finalize Length and Pitch
Divide pitch length by tooth pitch and round to nearest whole number for total teeth count, adjusting drive design as needed.
Step 7: Establish Effective Tension
Calculate operational tension using smallest loaded pulley's pitch radius and design torque.
Step 8: Select Strength Factor
Choose application-specific strength factor and determine required belt break strength, doubling for double span applications.
Step 9: Determine Belt Width
Select width capable of handling design torque with chosen pulley size.
Calculate Belt Length
Compute length using pulley diameters and center spacing with the formula:
Length = 2L + 1.57d₁ + d₂ - (d₁ - d₂)² / 4L
Where:
d₁ and d₂ represent pulley diameters,
L indicates center-to-center distance.
Timing Belt Materials
Common construction materials include:
Rubber
The predominant material for industrial and automotive timing belts, though susceptible to degradation from heat and oil exposure.

Advanced rubber formulations with reinforcing fibers improve heat resistance and durability, preventing tooth damage.
Polyurethane
Valued for temperature resistance, elasticity, and oil tolerance, making durable belts for diverse applications.

Polyurethane belts offer high tensile strength and load capacity, ideal for power transmission systems.
Fabric-Reinforced
Suitable for high-performance applications requiring temperature resistance, low friction, and exceptional strength.
Functional Principles
Timing belts are critical for engine operation, linking camshaft to crankshaft to coordinate valve and piston movements. These reinforced rubber belts feature internal teeth




