Introduction
This article provides an in-depth examination of engine dynos.
It covers detailed information on various aspects including:
- Working Principles of Engine Dynos
- Different Types of Engine Dynos
- Applications, Advantages & Maintenance of Engine Dynos
- And More...
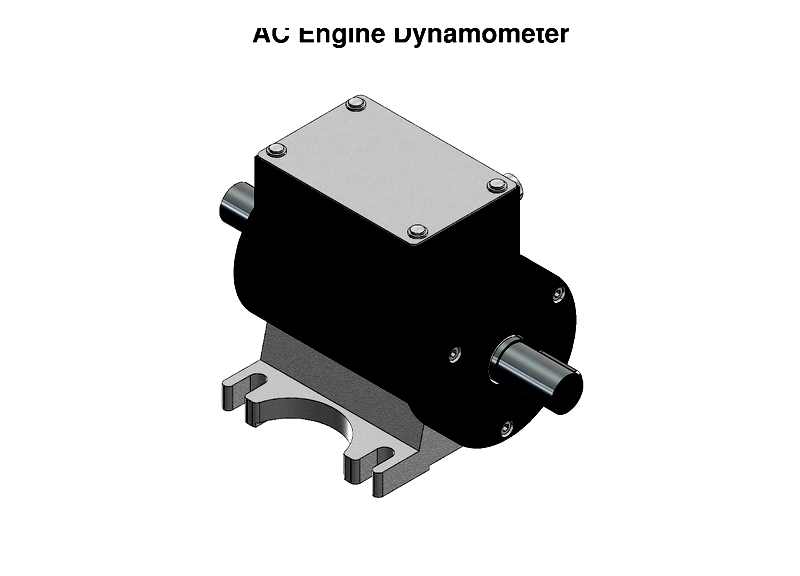
Chapter 1: Understanding the Basics of Engine Dynos
This chapter explores the fundamental concepts of engine dynamometers, explaining their structure and operational principles.
Defining an Engine Dyno
An engine dynamometer is a crucial device for evaluating the performance of an internal combustion engine when removed from its usual application, such as a vehicle or generator. Its primary purpose is to assess engine performance before reinstalling it for operational use.

Engine dynamometers help identify problems like overheating, signal errors, or performance variations while also testing new builds and repairs in a controlled environment before real-world implementation.
These devices connect to the test engine via a drive or cardan shaft, with engines mounted on mobile carts for easy movement into testing areas. Typically, they employ water brake, electric (EC), or alternating current (AC) systems to apply loads.
- Water brakes support engines up to 7,500 kW (10,000 HP).
- EC units are suitable for lower-power engines (under 400 HP).
- AC systems handle a broad power range (10 HP to 5,000 HP) and offer excellent transient response.
Structure of an Engine Dyno
Despite variations, engine dynos generally consist of key components: a driver or absorption unit, a torque generation mechanism, and a system for measuring torque and rpm. The absorber typically includes a rotor housed within a casing connected to the test assembly.
Torque is commonly generated through friction, hydraulic fluids, or electromagnetic forces. Measurement is often done using load cells, strain gauges, or scales like crane scales. Note: Load cells convert mechanical force into readable signals.
Couplings in Engine Dynos
A coupling is a mechanical device connecting two shafts to transmit power. It joins rotating parts while accommodating minor misalignments and movements. More broadly, couplings can link adjacent components or structures.
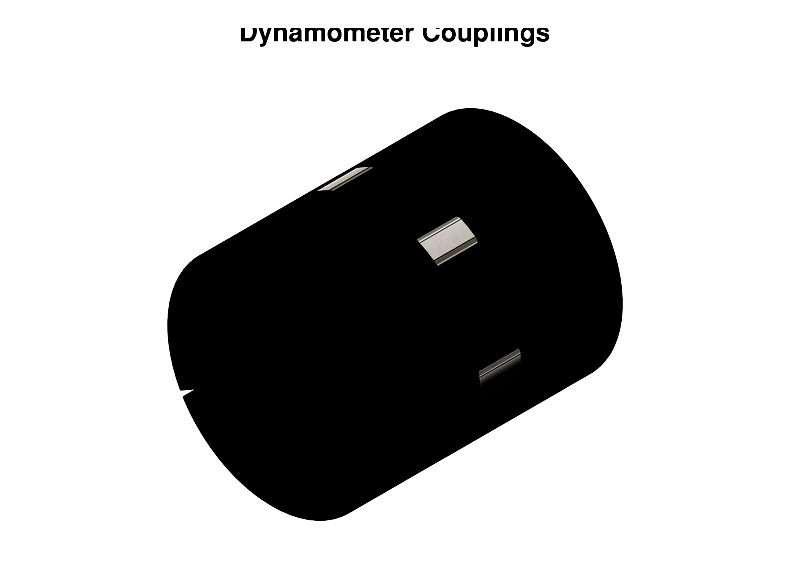

Most couplings remain engaged during operation, though torque-limiting types disengage when torque exceeds a set limit. Proper selection and maintenance of couplings can significantly reduce upkeep time and costs.
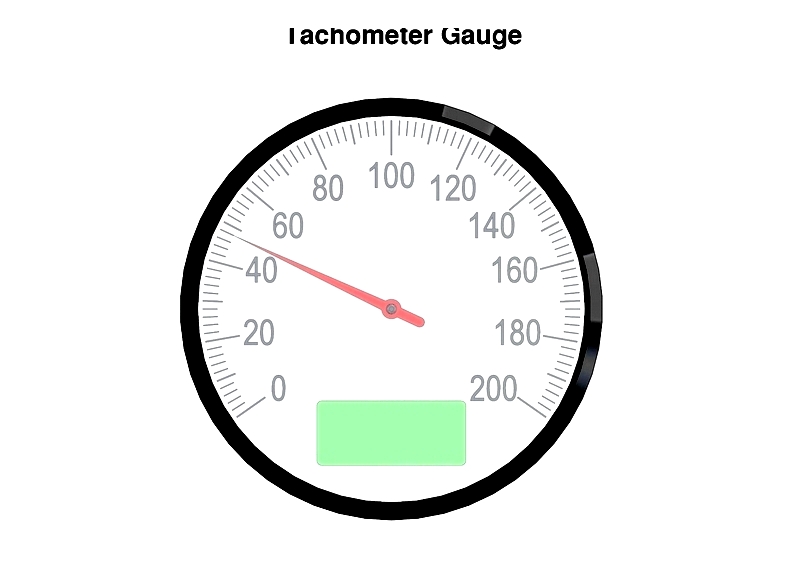
Function of an Engine Dyno Tachometer
A tachometer measures engine speed in RPM. Mechanical and electronic versions operate differently. In mechanical types, a rotating engine component connects to the gauge via a flexible cable, adjusting a needle to display speed.
Electronic tachometers generate pulses proportional to engine speed using magnetic sensors. Circuitry converts these pulses into a digital RPM readout.
Engine Dyno Torque Arm
The torque arm, part of a vehicle's suspension, connects to the rear axle in rear-wheel-drive cars. It supports acceleration while stabilizing the axle.
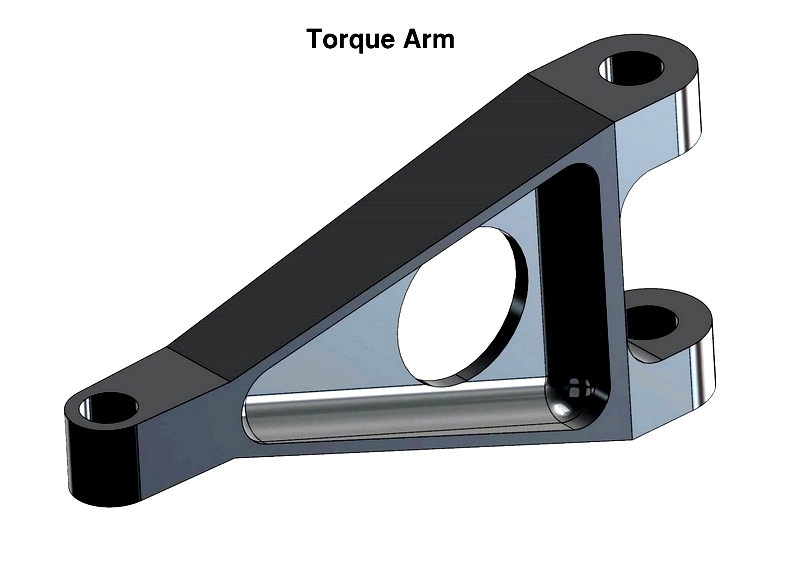
Besides aiding braking by transferring force, this arm is used on engine dynamometers. When connected to a scale, it measures reaction forces.
Engine Dyno Absorption Unit
Absorption dynamometers simulate loads on prime movers during testing. They must operate at any specified speed and load, providing necessary torque.
Inertia dynamometers measure power by calculating energy needed to accelerate a known mass, avoiding variable loads. Engine dynos typically use absorption units to measure torque and speed.
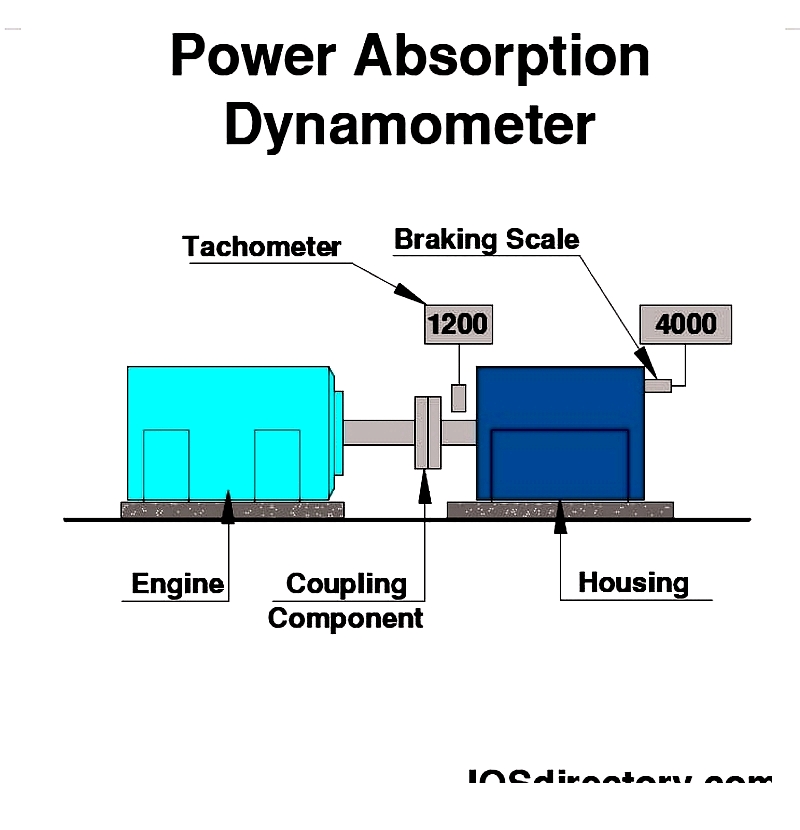
The power absorption unit (PAU) captures energy from the prime mover, converting it to heat dissipated via air or water. Regenerative types can feed excess energy back into the grid using a DC/AC inverter.
Testing requirements determine whether constant force or speed control systems are used in absorption dynamometers.
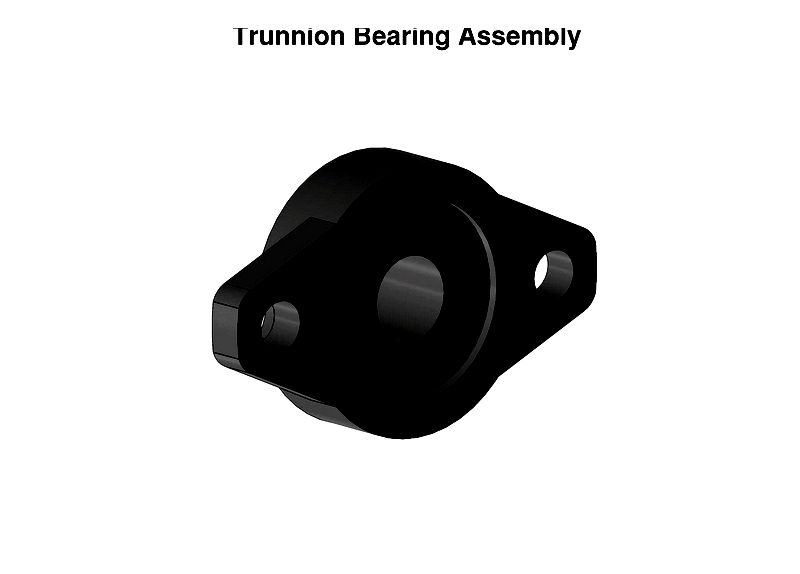
Trunnion Bearings in Engine Dynos
In mechanical engineering, trunnion bearings provide robust, precise rotating connections due to their large contact area. These bearings ensure smooth movement of critical steering components in airframes and support rotating parts.

Engine Dyno Data Acquisition System
A data acquisition system is essential for dynamometer setups, typically comprising two units connected via Ethernet: a commander and a workstation. The commander, a Windows-based computer, directs the workstation, which controls throttle and load while collecting and processing data.

Data accuracy depends on the workstation's measurement precision during tests. Key components include pressure transducers for measuring fluid pressures. Operators must monitor and adjust pressures to ensure effective workstation performance.
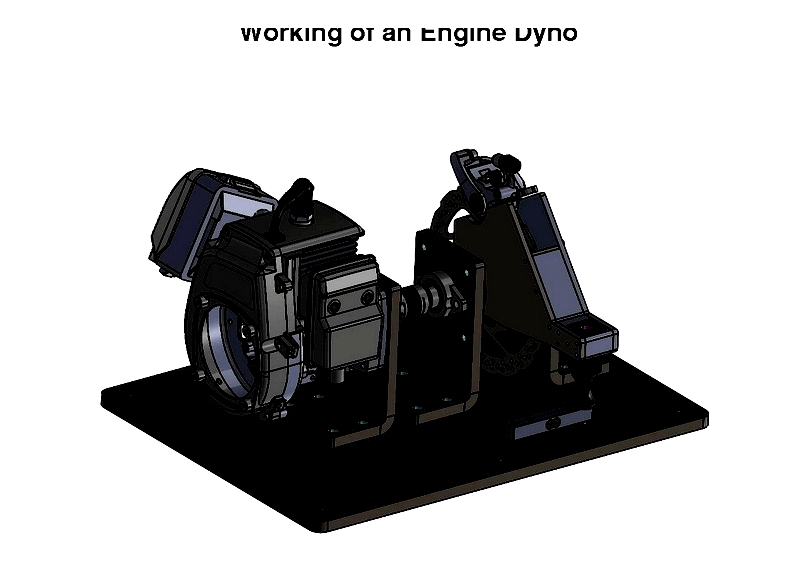
How Engine Dynos Operate
Engine dynamometers measure RPM or flywheel torque to calculate horsepower, converting torque into electrical signals for analysis. These tools enable independent engine and vehicle testing, widely used in diagnostics, rebuilding, design, and manufacturing.
Conducting a Dyno Test
Select an appropriate dynamometer and ensure proper setup before testing. Begin with a well-maintained engine operating at peak performance.
Warm the engine gradually with light loads. once warmed, apply full load, adjusting RPM as needed with the control valve.

With the throttle fully open, move between RPM test points using the brake's load valve, recording results. After measurements, gradually reduce throttle and load, returning the engine to idle.
Repeat tests to refine accuracy and verify data reliability, enhancing engine performance and confidence in results.
Save test data for future review and adjustments to optimize engine horsepower. Multiple tests may be needed for precise tuning.
Considerations for Choosing an Engine Dyno
Several factors influence the selection of an engine dynamometer:
Testing Scope
Determine whether testing standalone engines or complete vehicles. For vehicles, consider car, motorcycle, or truck types. Choose between four-wheel or two-wheel drive dynamometers and decide on independent or coupled axle setups.
Consider if focusing on power absorption or motor capability is needed. Selection depends on horsepower range, budget, and test type.
Engine Horsepower and Types
Horsepower reflects torque and RPM relationships across an engine's range. Dynos are rated based on torque and RPM. Identify peak torque and RPM




