Introduction
This article covers everything you need to know about solenoid control valves and their applications.
You will learn about:
- What a Solenoid Control Valve is
- Components of Solenoid Control Valves
- Different types of Solenoid Control Valves
- Advantages of using Solenoid Control Valves
- Applications of Solenoid Control Valves
- And more...
Chapter One: What Is a Solenoid Control Valve?
Solenoid control valves are advanced electro-mechanical devices that regulate the flow of liquids or gases. These valves use an electromagnetic solenoid to open or close, enabling precise automation in fluid control systems. Their versatility makes them suitable for various applications, with different designs available to meet specific requirements.
Solenoid valves come in multiple types, including direct acting, internally piloted, and externally piloted, categorized by their number of ports or flow paths. Material selection depends on the application - bronze or brass for neutral fluids, and galvanized steel or stainless steel for high-temperature or corrosive environments, allowing them to handle steam, corrosive fluids, and gases.
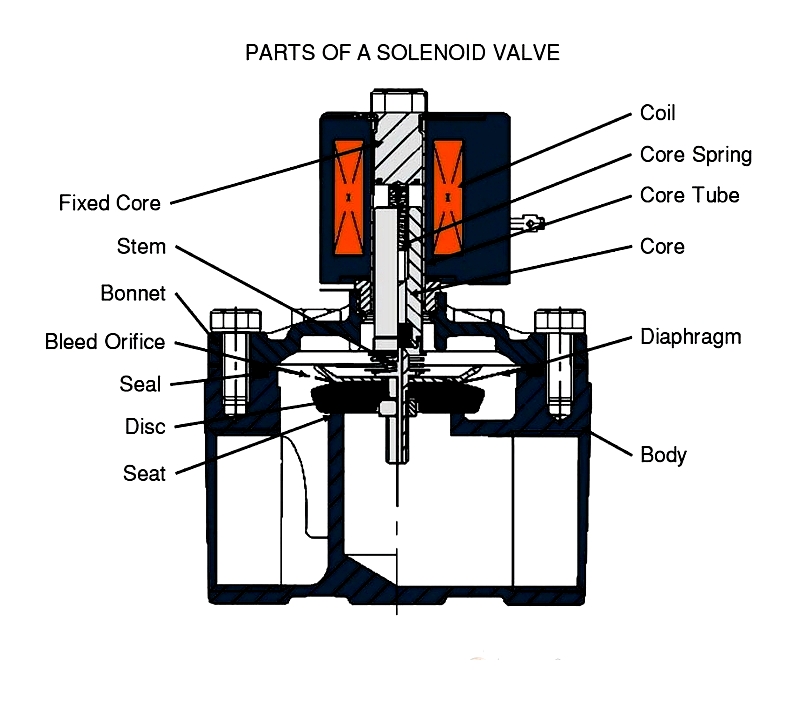
Chapter Two: What are the components of solenoid control valves?
Solenoid control valves are electromechanical devices widely used in industrial automation, process control systems, HVAC applications, water treatment, and fluid power industries. These valves provide precise control over liquid, gas, or steam flow in pipelines, supporting functions like on/off flow, mixing, diverting, and shut-off applications. Understanding the key components of solenoid valves is crucial for proper selection, installation, maintenance, and optimal performance in specific applications.
Solenoid Coil
The solenoid coil generates an electromagnetic field when electric current passes through it. Made from high-purity copper wire, the coil is wound around a ferromagnetic core for maximum electromagnetic efficiency. High-quality insulation materials provide thermal protection and electrical safety. The electromagnetic field actuates valve operation, converting electrical energy into mechanical motion.
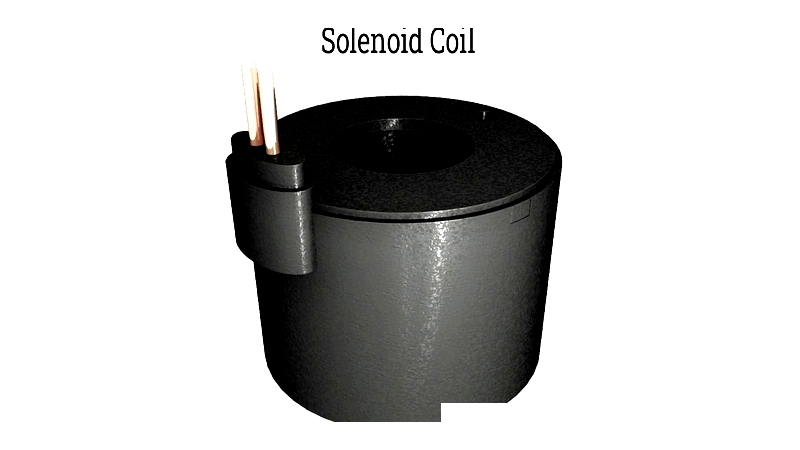

Plunger or Armature
The plunger (or armature) moves inside the solenoid coil when energized. The magnetic force pulls the plunger toward the coil's center, while a spring returns it when de-energized. In direct-acting valves, the plunger controls flow directly; in pilot-operated valves, it opens a pilot port. Typically made from stainless steel or corrosion-resistant materials, plungers ensure long service life and media compatibility.

Valve Body
The valve body houses the media flow path and connects to the solenoid assembly. With inlet and outlet ports, valve bodies are constructed from durable materials like brass, stainless steel, or reinforced plastics, chosen for chemical compatibility, pressure, and temperature requirements. Proper selection ensures reliability, corrosion resistance, and compliance with industry standards. Configurations range from 2-way to complex multi-port designs.
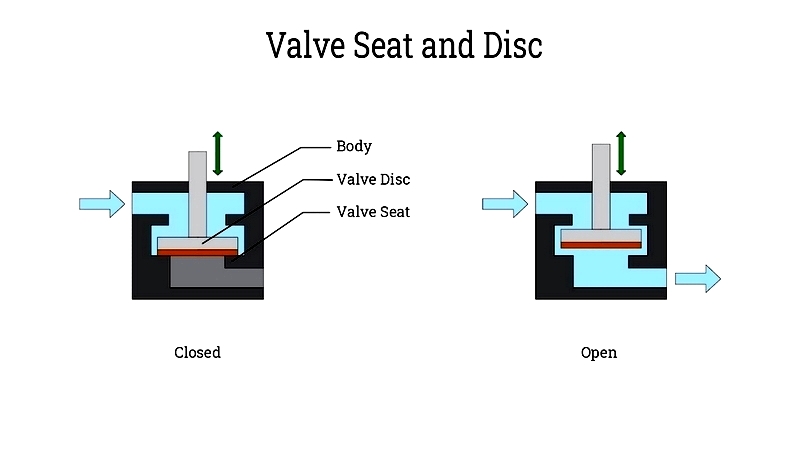
Valve Seat
The valve seat provides a tight seal between the valve and fluid ports. Made from soft materials like PTFE, EPDM, or NBR, it accommodates various fluids, including aggressive chemicals. Seat material selection affects leak-tightness and longevity. Three-way valves typically have two seats, with proper design minimizing internal leakage.
Valve Disc or Spool
The disc or spool controls fluid flow by moving with the plunger. Different valve types use various disc designs (poppet, diaphragm, or spool) for specific applications, whether for quick on/off control or proportional flow management.
Spring
The spring counteracts the solenoid's magnetic force, returning the plunger and disc to their original position when de-energized. This fail-safe mechanism contributes to energy savings and system safety. Spring strength and material (often stainless steel) are matched to valve size and function.
These components work together to control fluid flow. When energized, the plunger moves the disc to open ports; when de-energized, the spring closes them. Proper component selection ensures optimal performance in applications like process automation, pressure control, and emergency shut-off.
- Additional Key Terms: Industrial solenoid valves, direct acting valves, pilot operated valves, media compatibility, valve actuation, process automation, fluid shutoff, magnetic actuator, valve maintenance, proportional control.
Understanding each component's role helps in selecting, installing, and maintaining solenoid control valves, improving efficiency and reliability in demanding environments.
Chapter Three: What are the different types of solenoid control valves?
Solenoid valves offer reliability and performance in industrial automation and process control. Their compact design, energy efficiency, fast response, and consistent operation make them valuable across industries. Available in various types, they regulate, shut off, or divert liquids and gases for residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
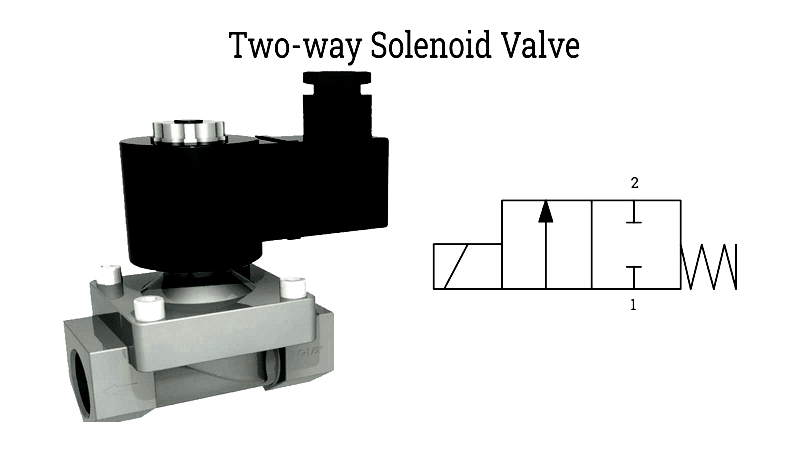
2-Way Solenoid Valve
The most common type, with one inlet and one outlet port, provides simple on/off control. Widely used in water systems, industrial automation, food processing, and medical devices, these valves optimize process efficiency and safety.
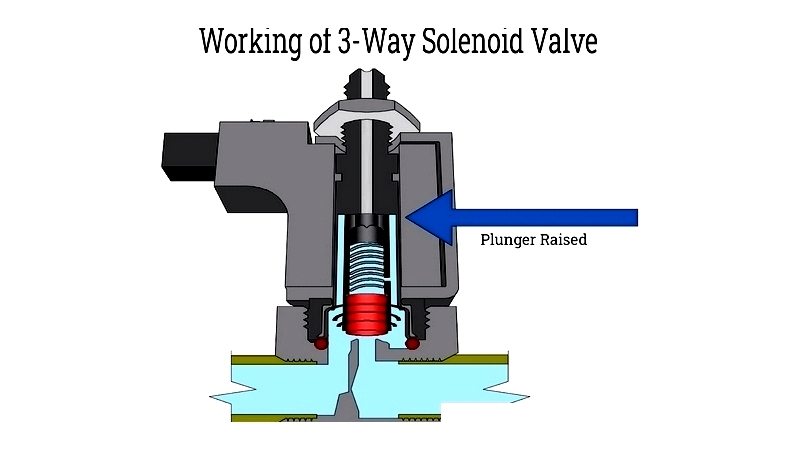
3-Way Solenoid Valve
With three ports (one inlet, two outlets or vice versa), these valves divert, mix, or alternate flow between circuits. Essential in pneumatic automation, chemical processes, and analytical instrumentation, they enable precise switching functions.
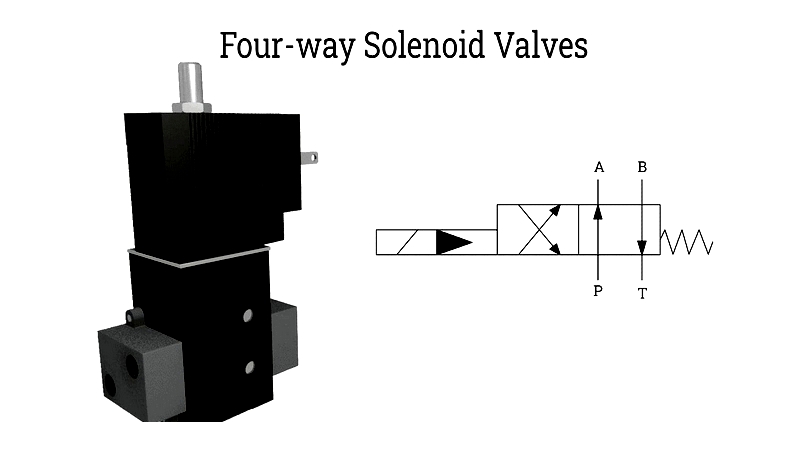
4-Way Solenoid Valve
Featuring four ports (two inlets, two outlets), these valves control multi-actuator pneumatic and hydraulic circuits. Crucial for double-acting cylinders and sequential automation, they enhance flexibility in manufacturing and robotics.
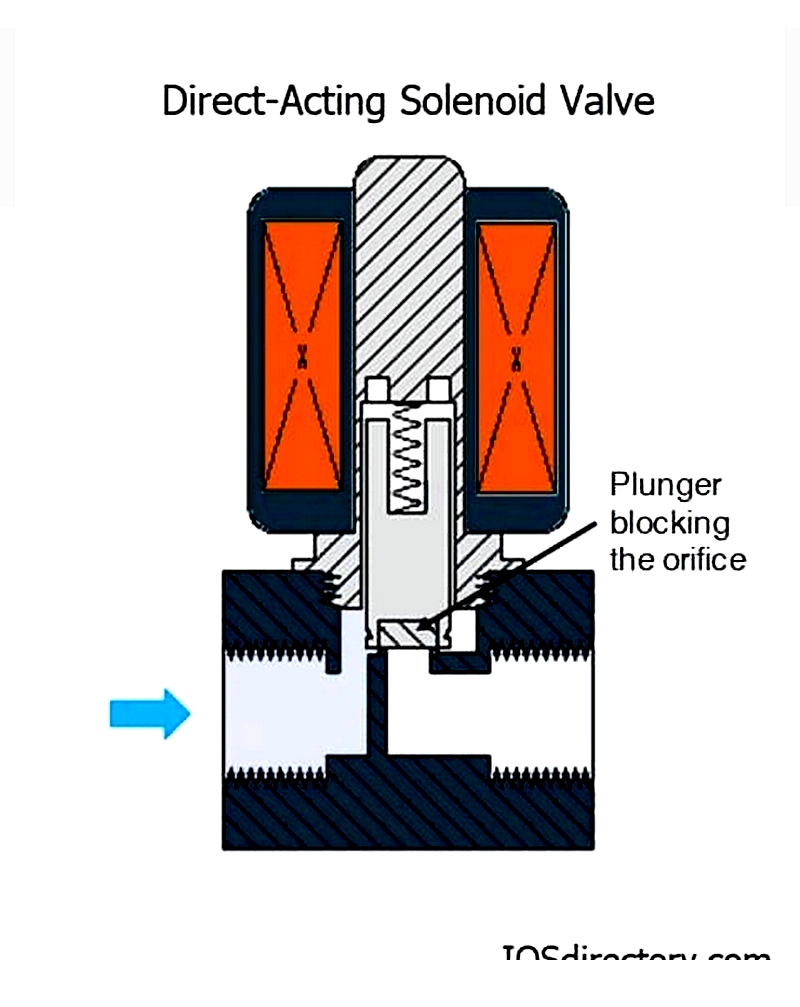
Direct-Acting Solenoid Valve
Operates independently of line pressure, with the plunger directly controlling the orifice. Ideal for low-flow, low-pressure applications requiring immediate actuation and tight sealing, such as pharmaceuticals and laboratory equipment.
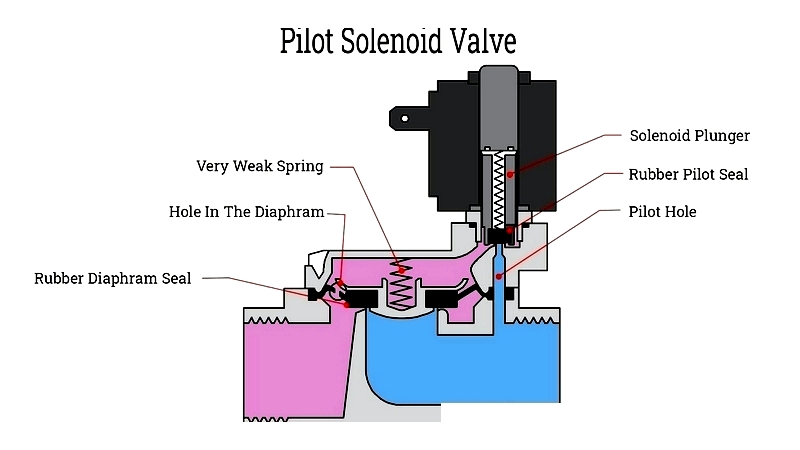
Pilot-Operated Solenoid Valve
Uses system pressure to operate a larger main valve via a small solenoid pilot. Effective for high-volume or high-pressure applications in power generation, agriculture, and water treatment, offering energy-efficient large-scale control.
Proportional Solenoid Valve
Provides variable flow control by adjusting valve position according to electrical input. Used in HVAC systems, automotive fuel injection




