Introduction
This article provides an in-depth exploration of wire racks.
It covers detailed information on various aspects including:
- Working Principles of Wire Racks
- Different Varieties of Wire Racks
- Materials Used in Wire Rack Construction
- Applications, Advantages, and Maintenance of Wire Racks
- Additional Relevant Information
Chapter 1: Understanding the Design and Functionality of Wire Racks
This chapter examines the fundamental characteristics of wire racks and their manufacturing process.
Definition of a Wire Rack
A wire rack is a metal wire platform primarily used in retail for displaying or storing various items. Constructed with interwoven metal wires, these racks form sturdy platforms capable of supporting different objects. Although similar to space-saving wire shelving, wire racks generally refer to smaller, non-freestanding units.
Wire racks optimize vertical storage space, making them particularly valuable for retail and business product displays. Their multi-layered or stackable designs adapt to various applications. Beyond promotional uses, wire racks serve industrial purposes. For example, drying or cooling racks utilize wire construction to maintain airflow, essential for items like baked goods.
While most storage racks maintain a horizontal orientation, cooling and display racks may incorporate angled designs for product accessibility. Some feature front lips to prevent items from slipping off.
Manufacturing processes may include additional finishes such as painting, coating, heat treatments, or electro-polishing. Mobility enhancements often involve attaching casters to support bars.
Wire Forming
Wire racks are manufactured through wire forming, which transforms raw or coiled wire into specific configurations. This versatile process accommodates diverse shapes, making it ideal for wire rack production.
The technique allows for creating coils, angles, bends, or cuts, suitable for custom applications. From small machinery springs to large load-bearing chains, wire forming serves multiple purposes.
The Process of Manufacturing Wire Racks
Wire rack production involves bending wires into precise shapes. This requires bending beyond yield strength while staying within tensile limits to ensure permanent deformation without breakage.
As mentioned, wire forming shapes wires into specific configurations like interwoven racks. Specialized machines perform these bending operations efficiently.
These machines handle wires up to 1½ inches in diameter, processing multiple wires quickly.
Wire Forming Techniques
Optimizing wire rack production involves:
- Efficient material procurement to reduce lead times
- Implementing flexible pull-structures for customer convenience
- Delivering finished products according to specifications
- Developing cost-effective custom packaging
CNC Wire Bending
CNC (computer numerical control) bending is widely used in modern manufacturing, incorporating several essential components.
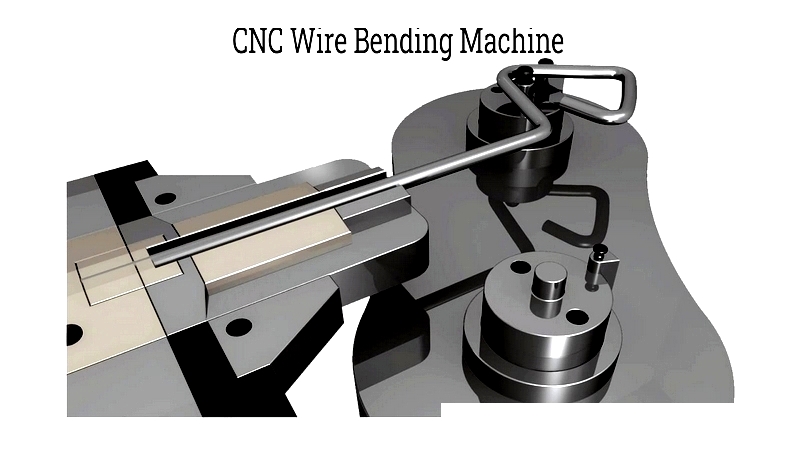
These components work together to create complex wire shapes, including:
- Coil Feeder – Ensures smooth wire feeding with motorized unwinding
- Straightener – Removes coil memory for precise forming
- Chamfering – Eliminates burrs automatically
- Forming Head – Handles all bending operations with interchangeable heads
- Wire – The cutting tool for final shaping
CNC machines receive design specifications, straighten wires, and perform precise bends using robotic arms before cutting to length. This ensures consistent, accurate shaping across all axes.
Different machines offer varying capabilities. While 2D machines create simple flat shapes, advanced 3D machines handle complex three-dimensional designs with greater flexibility.
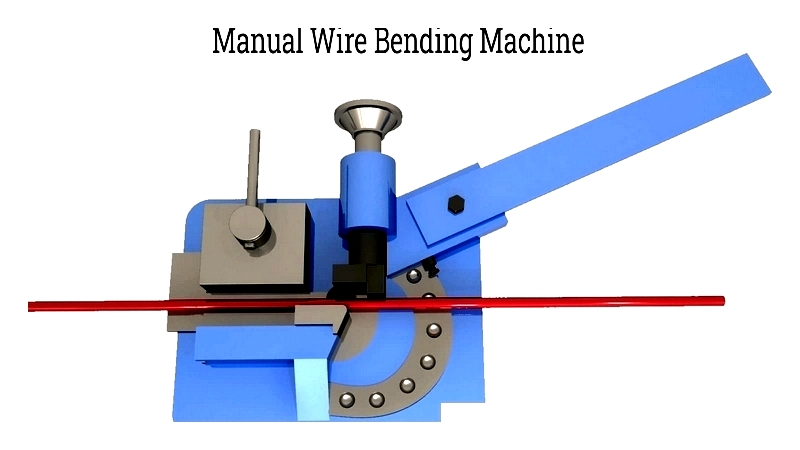
Manual Wire Forming
Traditional wire forming used manual machines with spindles and levers for shaping, employing gears for controlled bending.
Four-Slide Wire Forming
This high-speed process uses cams with shafts, gears, and motor-driven presses. Four synchronized gears significantly increase production rates.
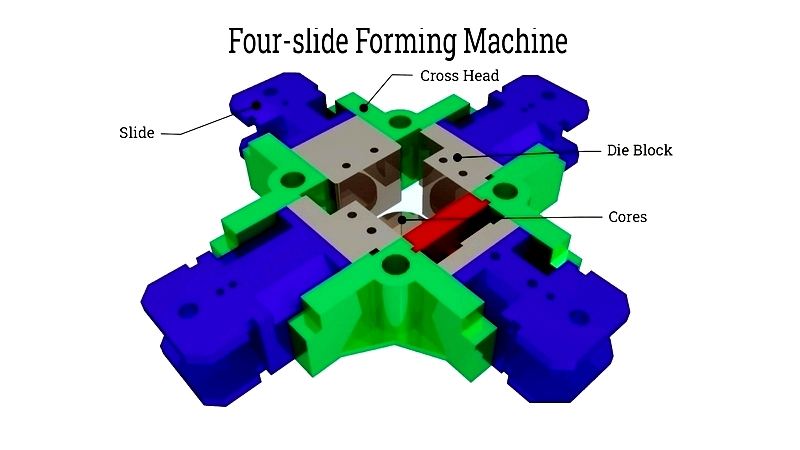
Production can reach approximately 3,500 wire forms per hour. Cam systems control gear movements for multi-directional operations.
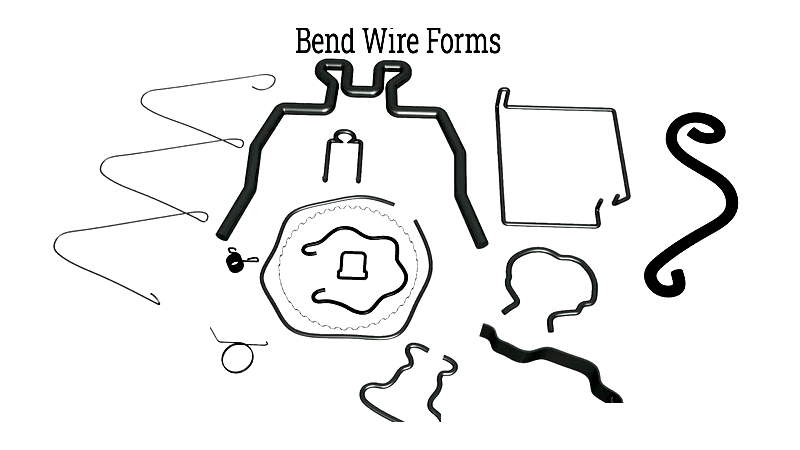
Bend Wire Forming
This technique creates various wire configurations, handling thicknesses from 0.016 to 0.625 inches (0.41 to 16 mm). Forming before cutting minimizes material waste.
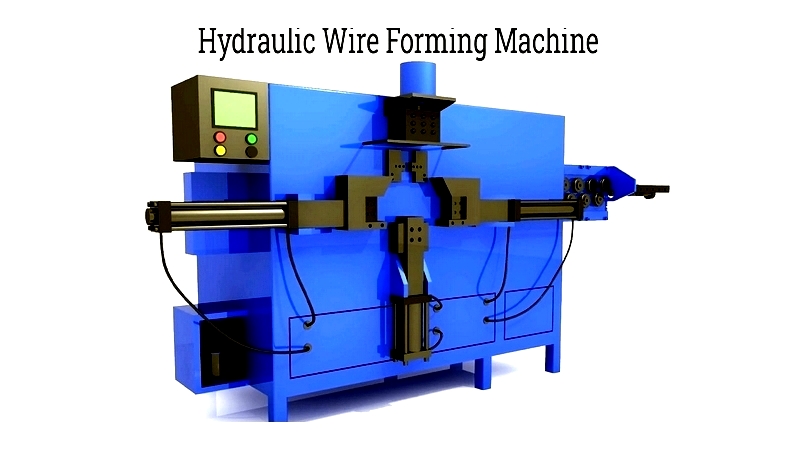
Hydraulic Wire Forming
Hydraulic motors drive rollers to shape wire according to CNC-programmed designs. The system retrieves formed wires systematically.
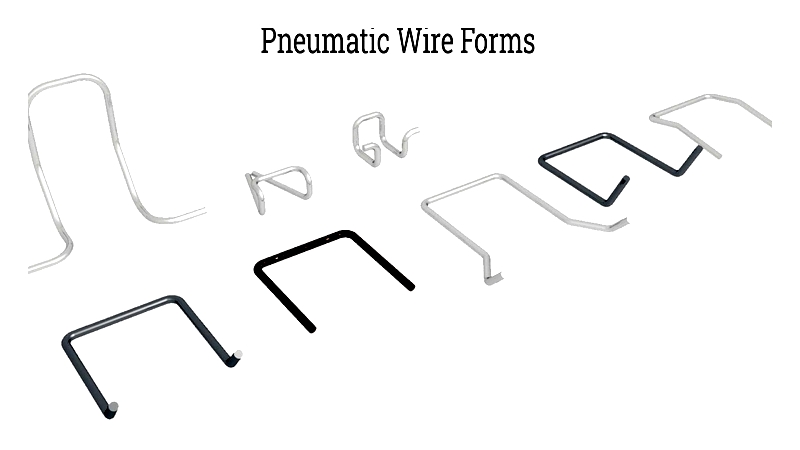
Pneumatic Wire Forming
This method uses compressed air to feed, straighten, and cut wires to precise lengths.
Wire Welding
Wire rack assembly often involves welding techniques like MIG, TIG, or ERW. ERW combines electric currents with pressure for bonding.
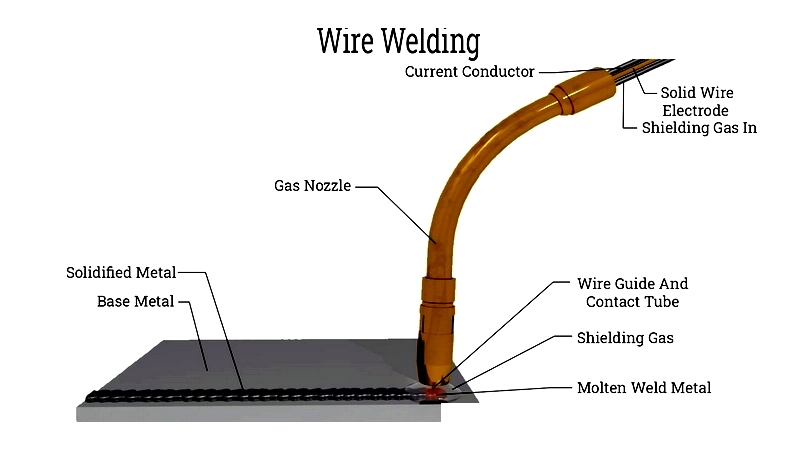
All methods use inert gases to prevent contamination. While TIG offers superior quality, MIG is faster and more commonly used. Some designs may still incorporate weaving for grids and screens.
Surface Finishing for Wire Racks
Post-welding treatments may include plating or coating. Finishing removes sharp edges and may incorporate additional modifications like grooves or swaging.
Factors for Selecting a Wire Rack
Wire racks provide efficient storage without structural modifications, accommodating items from books to heavy goods. Consider these selection criteria:
Purpose – Identify specific storage needs (books, baked goods, retail items)
Dimensions – Match rack size to available space and item dimensions
Appearance – Choose aesthetically pleasing designs when necessary
Load Capacity – Ensure the rack can support intended weights
Openings – Select appropriate wire spacing to prevent item slippage
These guidelines help identify the most suitable wire rack for any application.
Chapter 2: Wire Rack Varieties and Materials
This chapter examines different wire rack types and construction materials, essential information for commercial, industrial, and organizational applications.
Types of Wire Racks
Various wire rack designs serve different industries and purposes. Below are some common systems




