Introduction
This article provides an in-depth examination of stranded wires, braided wires, and wire strands.
It covers key topics including:
- Principles of Stranded Wire, Braided Wire, and Wire Strands
- Types of Stranded Wire, Braided Wire, and Wire Strands
- Applications and Benefits of Stranded Wire, Braided Wire, and Wire Strands
- And more...
Chapter 1: Principles of Stranded Wire, Braided Wire, and Wire Strands
This chapter examines the construction, characteristics, and functional applications of these wire types.
Stranded Wire
Stranded wire comprises multiple thin wires bundled together with insulating material. This design enhances flexibility, making it ideal for electronic circuits in tight spaces where bending is required.
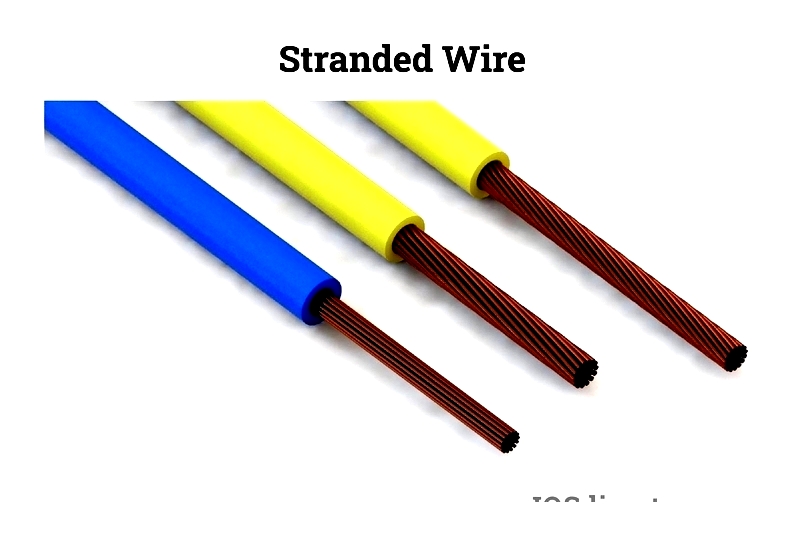
Unlike solid wires, stranded wires are more flexible and less likely to break under stress.
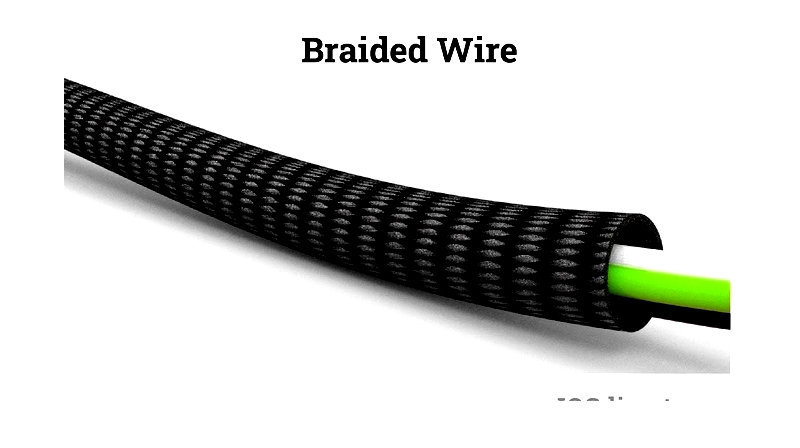
Braided Wire
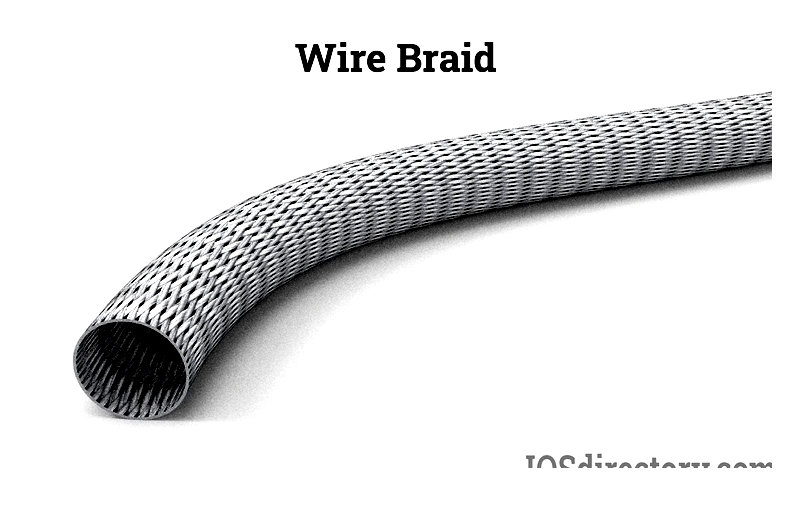
Braided wire features mesh-like shielding woven around a cable to protect against electromagnetic interference and improve mechanical strength.

The shielding consists of tightly woven thin wires in a standard mesh pattern. Some designs flatten the braid for specific width requirements, with a thin insulating layer covering the internal components.
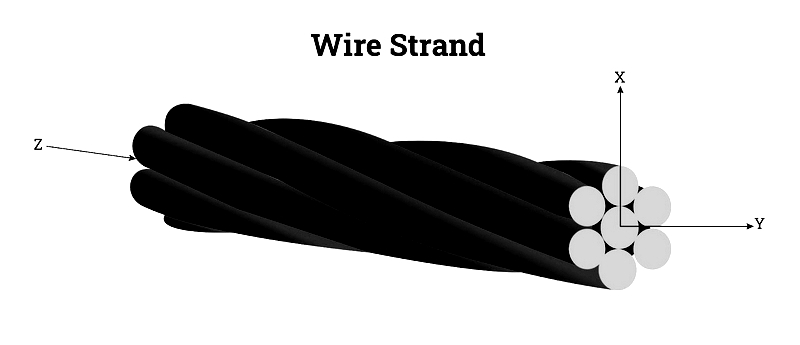
Wire Strands
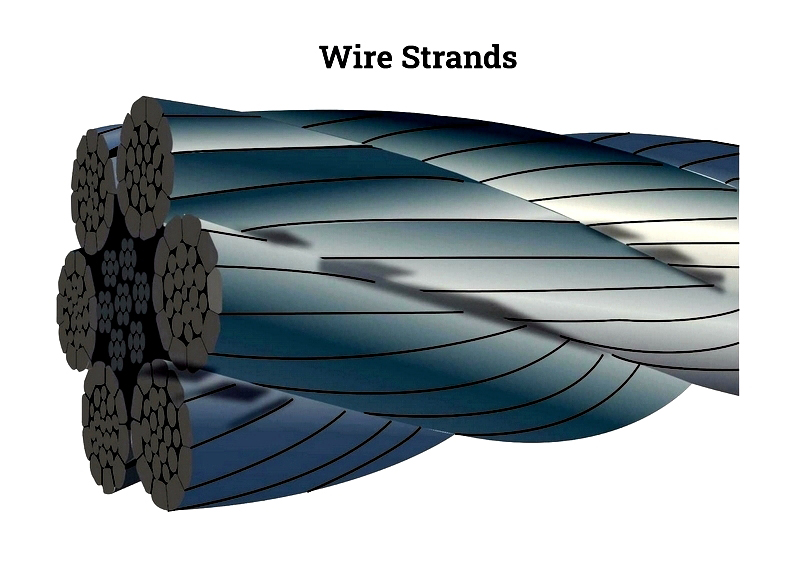
Wire strands consist of wires wound concentrically in a helix around a central core. Higher strand counts increase flexibility, and materials range from stainless steel to precious metals like gold and silver.
Functioning Principles
Key operational aspects include:
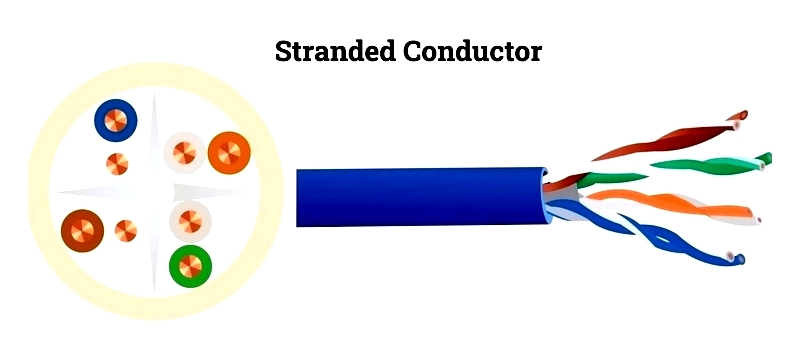
Stranded Wire
Commonly used in electrical transmission networks, stranded conductors combine steel cores for tensile strength with aluminum outer wires for conductivity.
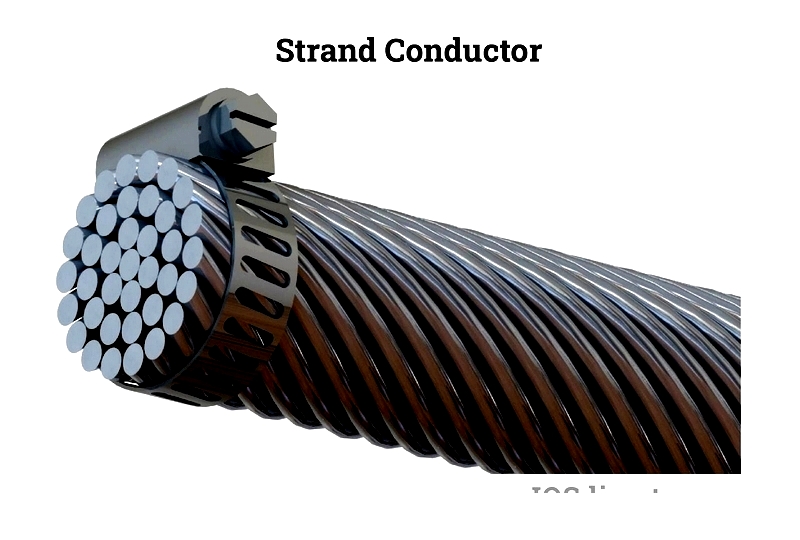

This design offers superior flexibility compared to solid conductors, facilitating easier transportation and installation.
Key Facts
- Flexibility increases with strand count
- Strands are wound in helical layers with alternating directions
- Total strands calculated by N = 3x² - 3x + 1
- Diameter calculated by D = (2x - 1)d
Applications include AC power cords, computer peripherals, and moving machinery.
Braided Wire
Primarily used for EMI shielding in applications like satellite cables.
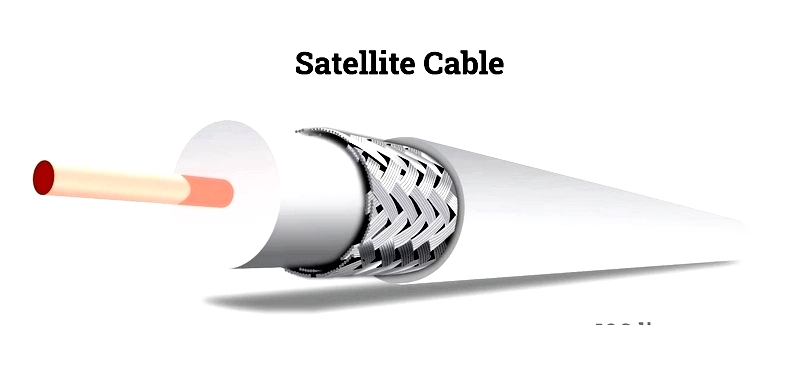
Manufacturing Process
Typically made from copper (often tinned), braided wires are created using fast-rotating spools to weave strands around a core. Braid configurations are described by carrier count, wires per carrier, and AWG.
Wire Strands
Helical winding provides structural integrity.
Manufacturing
Wire ropes use either Independent Wire Rope Core (IWRC) or Wire Strand Core (WSC) configurations for strength and flexibility.
Chapter 2: Types of Stranded Wire, Braided Wire, and Wire Strands
This section explores the various configurations available.
Stranded Wire Types
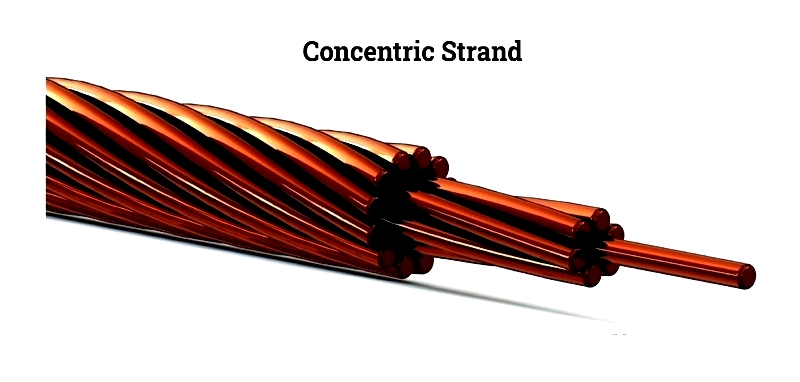
Concentric Strand
Features central conductor with concentric wire layers (6+ wires per layer) for tight packing and enhanced conductivity.
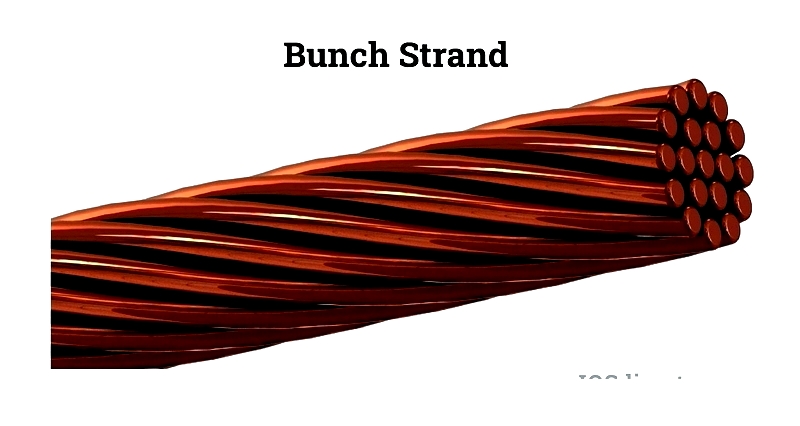
Bunch Strand
Loosely gathered strands without geometric pattern, offering high flexibility for tight bends.
Rope Strand
Small wire bundles twisted into rope-like cables for maximum flexibility.
Compact Conductor
Compressed strands eliminate air gaps while maintaining cross-sectional area.
Braided Wires
Common materials include tinned copper and silver-plated copper, providing EMI protection for data transmission.
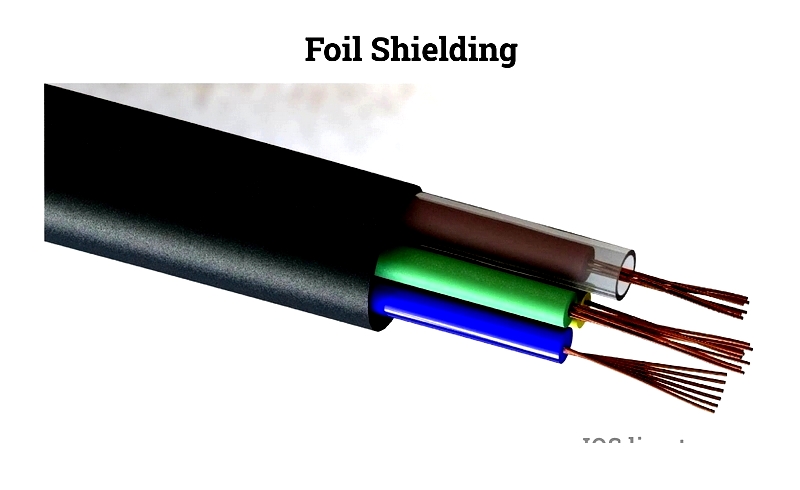
Braided vs Foil Shielding
Foil shielding offers cost-effective high-frequency protection but lacks mechanical durability.
Wire Strand Types
Bunched Strand
Irregular structure suitable for flexible cords and construction cables.
Concentric Strand
Symmetrical patterns (e.g., 1+6+12+18) with precise outer layers for thin-wall insulation.
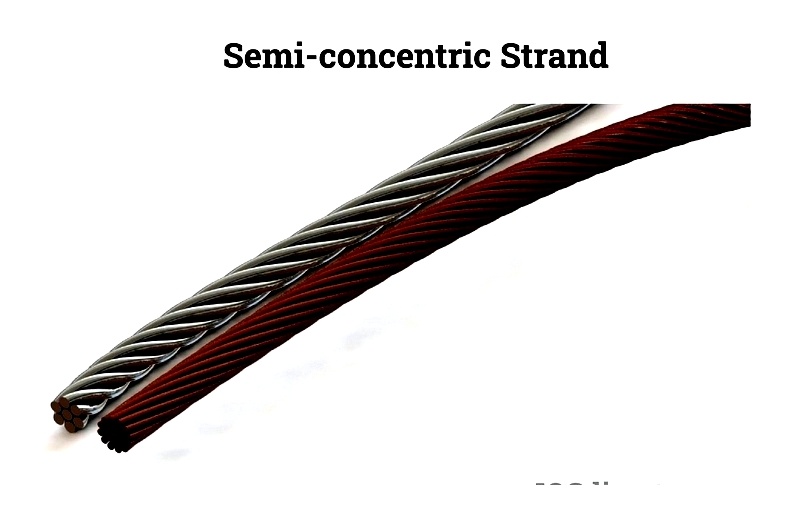
Semi-Concentric Strand
Regular but asymmetric arrangements (e.g., 2+8+4) with smooth surfaces.

Stranded vs Solid Wires
Key differences:
- Current capacity: Solid wires better for residential use
- Flexibility: Stranded excels in tight spaces
- Durability: Stranded resists vibration damage
- Cost: Solid wires more economical
- Distance: Solid preferred for long runs
Braided vs Foil Shielding
Braided offers 70-90% shielding with better mechanical protection, while foil provides complete coverage at lower cost but reduced durability.