Introduction
This article provides an in-depth exploration of manufacturing ERP and MRP software.
Key topics covered include:
- Fundamentals of Manufacturing ERP and MRP Software
- Examples of Manufacturing ERP and MRP Solutions
- ERP and MRP Implementation Specialists
- Applications, Benefits, and Limitations of ERP and MRP Systems
- And More...
Chapter 1: Understanding Manufacturing ERP and MRP Software Fundamentals
This section explains ERP and MRP software, their operational principles, and key considerations when selecting these systems.
ERP Defined
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) integrates core business processes into a unified database, creating a streamlined operational environment. Manufacturing ERP specifically refers to systems designed to manage and optimize manufacturing operations.
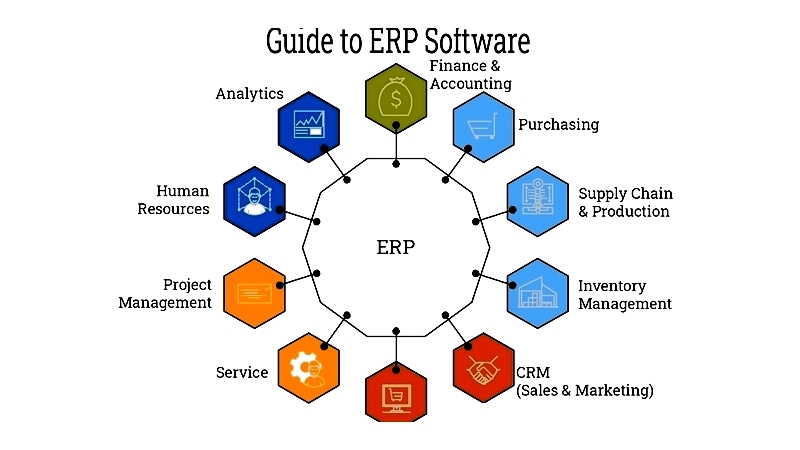 Figure 1.1: ERP Software Guide
Figure 1.1: ERP Software Guide
Manufacturing ERP systems automate specific production processes while integrating with other business functions to centralize workflow management.
While generic ERP systems cover diverse business areas, they may lack specialized manufacturing functionalities requiring deep integration.
Inadequate integration can limit data visibility, underscoring the need for manufacturing-specific ERP solutions. These systems provide advanced features tailored to industry standards, connecting core operations with production activities for comprehensive oversight.
MRP Defined
Material Requirements Planning (MRP) is a methodology for inventory and resource management. In manufacturing, MRP systems analyze demand and bill of materials to generate procurement plans and production schedules. MRP is widely used for production coordination across organizations.
MRP ensures material availability by tracking supply and demand, creating procurement recommendations. It focuses on identifying required materials, quantities, and optimal delivery timelines.
Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP II) expands MRP's scope to encompass entire manufacturing operations, fostering cross-departmental collaboration. It enhances manufacturing efficiency through process integration and automation.
MRP II improves supply chain management, order fulfillment, sales support, and market analysis, serving as a comprehensive tool for coordinating resources across multiple business functions.
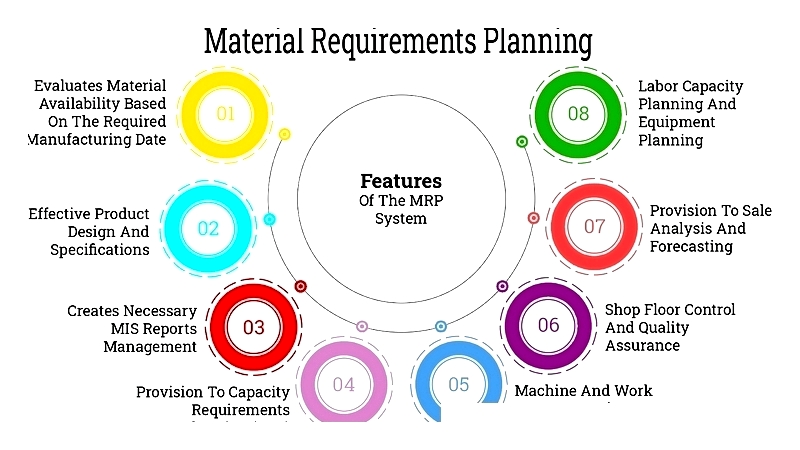 Figure 1.2: Material Requirements Planning
Figure 1.2: Material Requirements Planning
ERP and MRP Relationship
ERP and MRP systems work together to optimize business processes. Within ERP systems, MRP functions as a module providing critical resource data that ERP integrates across business units.
Finance teams use MRP data through ERP systems to establish accounts receivable and production costs, aiding pricing strategies. While MRP focuses on materials, ERP encompasses broader business operations. Both technologies significantly enhance industrial productivity and efficiency.
The key distinction lies in their focus: MRP specializes in material management, while ERP facilitates planning and automation of back-office functions including accounting, production, supply chain, customer relations, and strategic planning.
MRP's specialized nature means its user base typically consists of manufacturing personnel, unlike ERP which spans multiple departments.
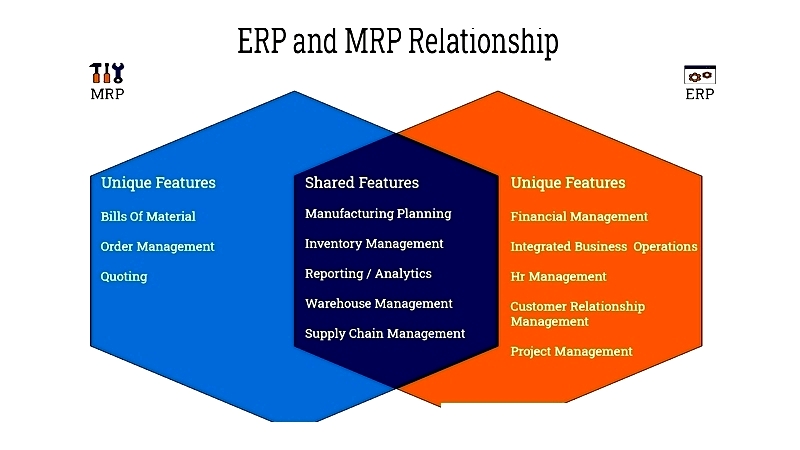 Figure 1.3: ERP and MRP Relationship
Figure 1.3: ERP and MRP Relationship
Manufacturing ERP and MRP Operations
Manufacturing ERP software enables organizations to efficiently plan, budget, forecast, and report on financial and operational performance. These solutions provide integrated business platforms with real-time insights across departments.
Key ERP components include:
- Supply chain management covering product lifecycle from sourcing to distribution
- Human capital management for workforce administration and development
- E-commerce modules for real-time inventory and pricing updates
- MRP functionality for material planning and procurement
- Core inventory and production management capabilities
Accurate data input is essential for MRP systems to effectively enhance manufacturing operations.
Selecting ERP or MRP Systems
Implementing ERP or MRP systems requires careful consideration due to complexity, cost, and long-term implications. Key selection factors include:
Process Improvement Identification
Organizations should first document specific challenges the new system should address. This includes analyzing current operations, business size, and process requirements. MRP may suffice for material-focused improvements, while ERP is necessary for broader operational enhancements.
Budget Considerations
MRP systems are typically more affordable due to narrower focus. ERP investments should be justified by potential productivity gains and long-term benefits, though they require ongoing maintenance costs.
Technology Evolution
Future upgrade requirements for both hardware and software should be anticipated. Consider vendor support continuity and system adaptability to technological advancements.
Growth Projections
Rapidly growing businesses often benefit from ERP automation, while stable operations may find MRP sufficient.
Customization Requirements
evaluate necessary customization levels and their impact on system integration. Unique business processes may require tailored solutions.
Chapter 2: Manufacturing ERP and MRP Software Examples
Manufacturers seeking operational improvements can benefit from these leading ERP and MRP solutions:
abaseRP
Tailored for SMB manufacturers, abaseRP offers comprehensive supply chain and e-business solutions with customizable customer and vendor portals.
 Figure 2.1: abaseRP
Figure 2.1: abaseRP
AccelGrid
This integrated suite combines sales, CRM, inventory, and accounting modules in a customizable, cloud-based platform suitable for diverse manufacturing processes.
Acumatica
A scalable cloud ERP supporting financial management, production scheduling, and multi-site operations for growth-focused manufacturers.
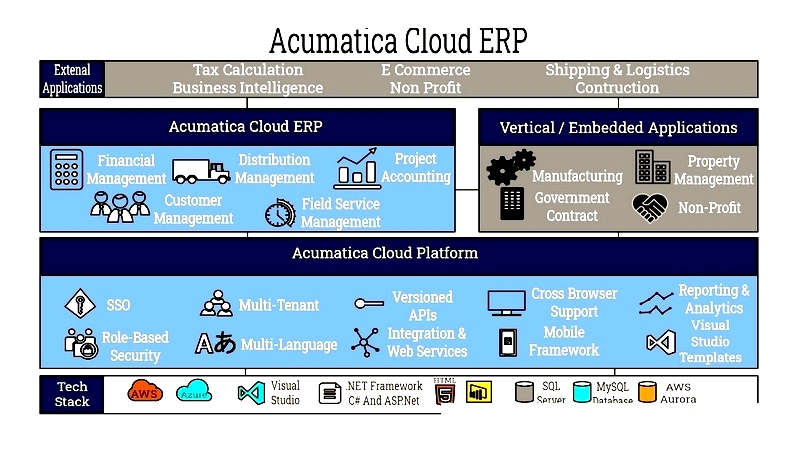 Figure 2.2: Acumatica ERP
Figure 2.2: Acumatica ERP
Epicor Kinetic
Designed for mixed-mode manufacturing, this solution offers advanced planning tools for discrete manufacturing sectors.
 Figure 2.3: Epicor Kinetic
Figure 2.3: Epicor Kinetic
ERPAG
Cloud-based ERP for SMBs featuring inventory, sales, and manufacturing management with extensive third-party integrations.
Infor Syteline
Manufacturing-focused ERP with PLM, project management, and quality control features, known for scalability and configurable interfaces.
 Figure 2.4: Infor Syteline
Figure 2.4: Infor Syteline
Katana Manufacturing
Specialized in real-time operational visibility, this platform offers intuitive production tracking and inventory management tools.
M1 ERP
Flexible system supporting various manufacturing models with advanced product configuration and reporting capabilities.
Manu Online
Cloud-based ERP for industrial manufacturers focusing on process automation and inventory optimization.
Microsoft Dynamics 365
Comprehensive enterprise ERP with modules for manufacturing, finance, and supply chain, suitable for global operations.





