Introduction
This section provides manufacturer information and product descriptions for storage racks.
You will learn about:
- Storage rack principles
- Different types of storage racks
- Applications and benefits of storage racks
- Additional important information
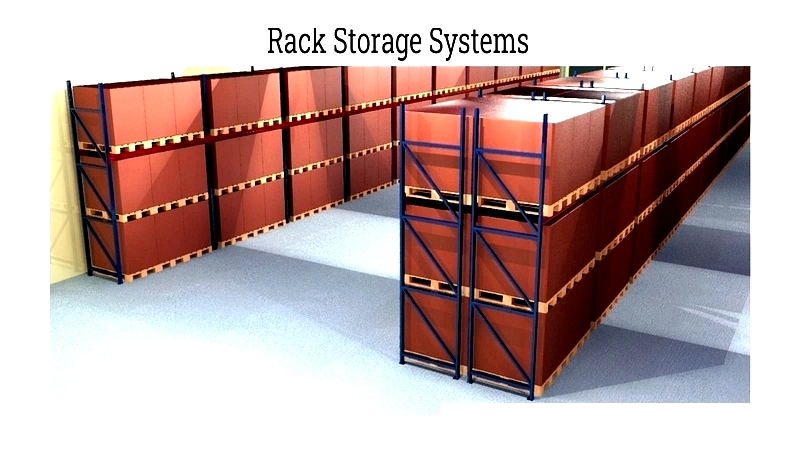

Chapter 1: Fundamentals of Storage Racks
This chapter explores storage rack concepts and key considerations for their design and selection.
Storage Rack Definition
Storage racks, also called racking systems, are structures designed for storing various items. These systems typically include vertical frames, horizontal beams, and decking components that may consist of bars, panels, or meshes.
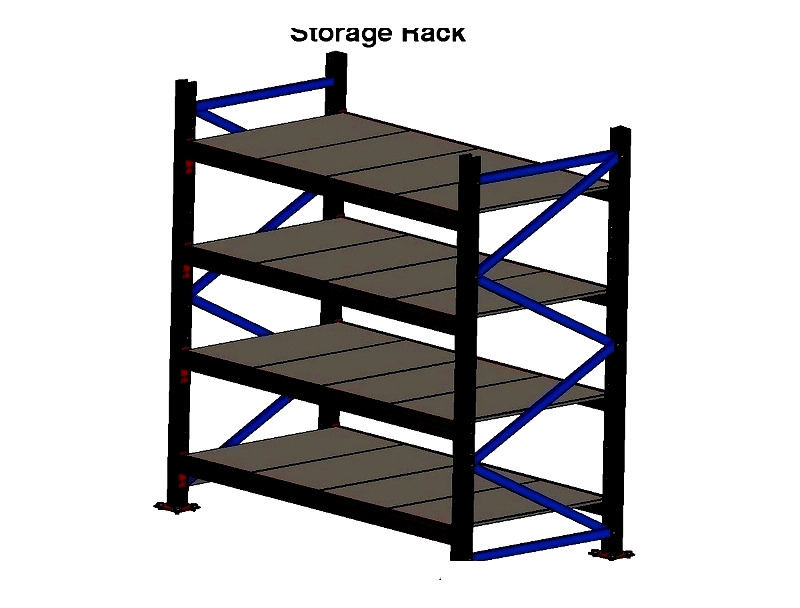

Storage Rack Design Considerations
Key factors to consider when designing storage racks include:
Pallet Size and Type
When designing pallet racking systems, consider pallet weight, dimensions, and standard sizes. These factors help determine appropriate rack depth and height. Product characteristics may also require specific rack types for:
- Special environmental conditions
- Fragile items that can't be stacked
- Time-sensitive products
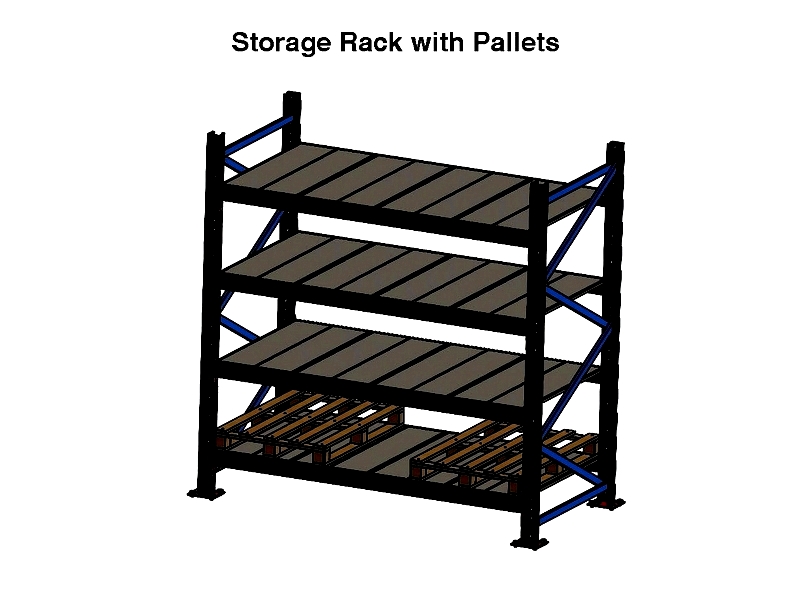

Pallet and SKU Quantities
The number of SKUs and pallets per SKU significantly impacts racking system selection. Selective pallet racking works well for single-pallet SKUs, while drive-in or push-back racking suits multiple-pallet SKUs. FIFO operations may prefer pallet flow racking.
Warehouse Environment
Racking system costs are influenced by storage environment requirements, which may include:
- Cold storage (freezers or coolers)
- Temperature-controlled areas
- Standard ambient conditions
Environmental conditions affect product quality, especially for perishables. Cold storage maintains food quality, while controlled environments preserve pharmaceuticals. Ambient conditions reduce costs, but cold storage increases expenses due to:
- Longer installation times
- Higher space costs
- Regulatory requirements
Building Structure
Whether adding racks to existing facilities or new construction affects costs and timelines. Building considerations include:
- Column placement
- Ceiling height
- Dock door locations
- Available space
Material Handling Equipment
Equipment types and sizes determine aisle widths and rack configurations. Standard forklifts need 12-foot aisles, while order pickers require less space. Optimized layouts maximize storage capacity.
Storage Rack Selection Factors
Key selection criteria include:
Storage Requirements
Analyze inventory by weight, density, delivery patterns, and lifespan to choose appropriate racks. Drive-in racks suit bulk storage, while selective racks work for diverse products.
Cost Considerations
Budget constraints make cost important, but quality should not be compromised. Experienced managers balance cost with long-term value.
System Flexibility
Choose adaptable racks that accommodate changing product lines and business needs.
Durability and Safety
Select strong, durable racks to prevent accidents and ensure long-term performance.
Chapter 2: Types of Storage Racks
Various warehouse storage racks optimize space, improve efficiency, and enhance inventory management. Understanding these systems helps organizations select appropriate solutions. Major types include:
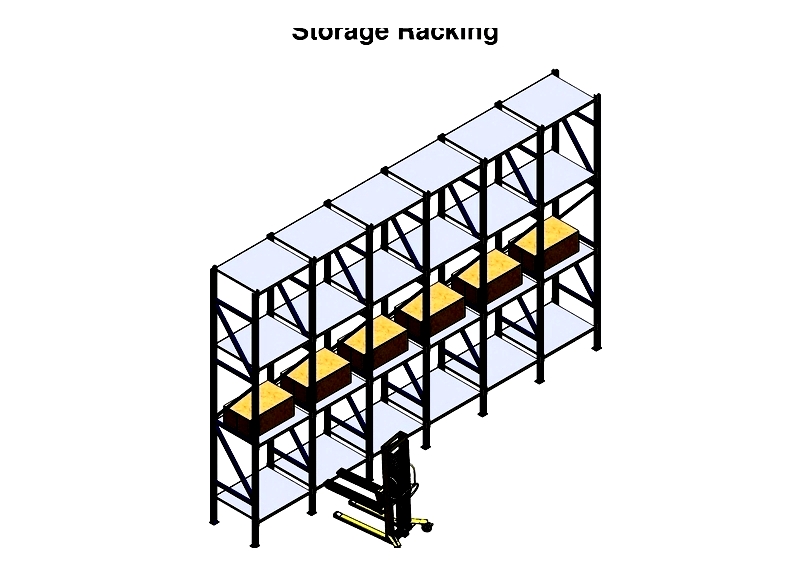
Conventional Pallet Racks
These popular systems offer direct pallet access for efficient SKU management. They provide large capacity, easy installation, and low equipment costs, making them ideal for businesses of all sizes.

frames consist of uprights, bracing, and footplates. Uprights feature adjustable slots, while footplates provide floor support. Safety pins help prevent beam dislodgement.
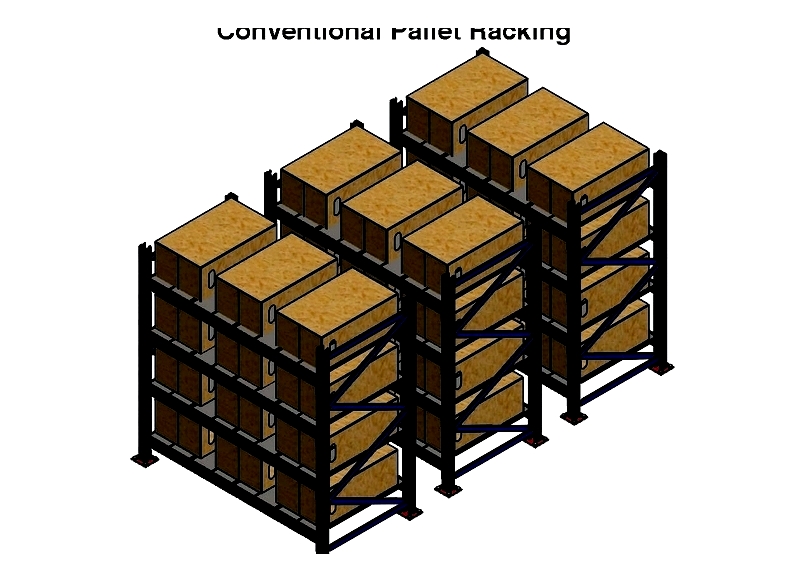

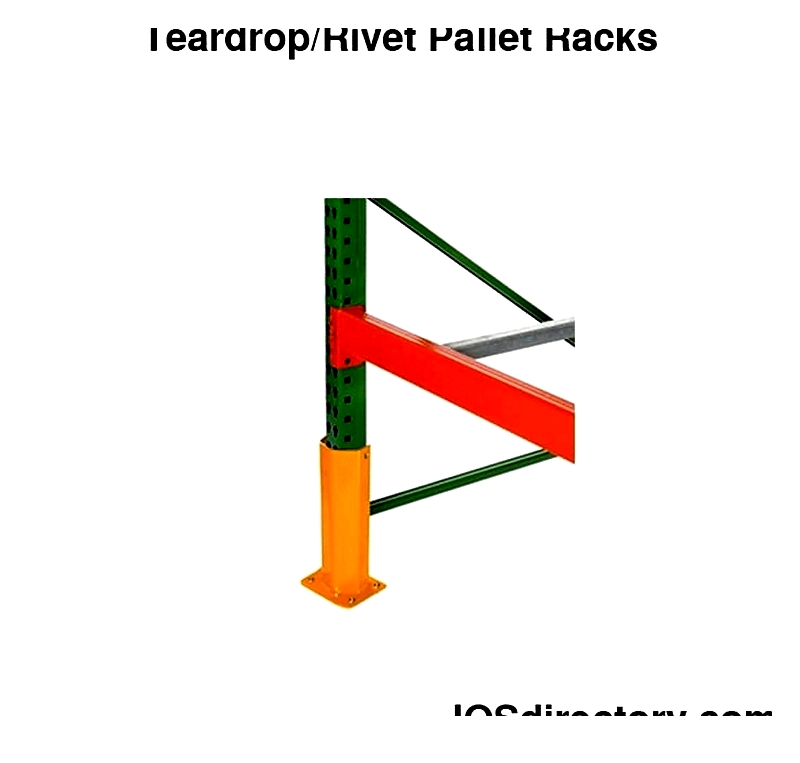
Teardrop Pallet Racks
These systems feature tool-free assembly with distinctive teardrop slots. Their modular design suits various applications and allows easy reconfiguration.

Materials and designs accommodate different environments, including cold storage. Connector types offer flexibility for various beam needs.
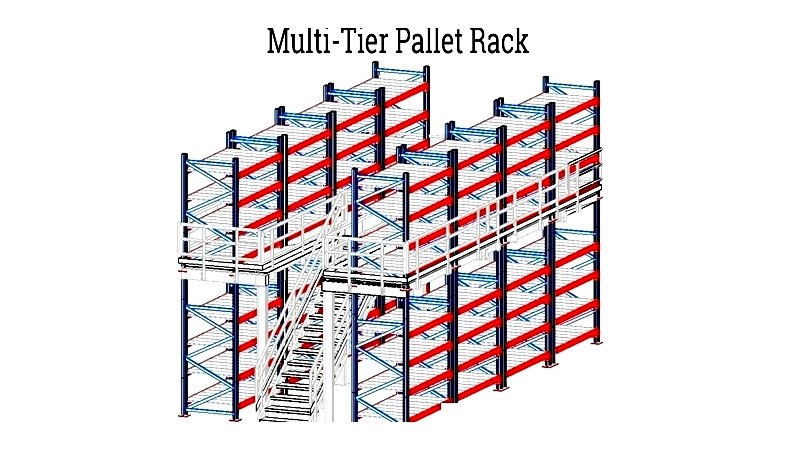
Multi-Tier Pallet Racks
These vertical systems maximize storage in limited spaces with multiple accessible levels. They're ideal for small parts storage and order fulfillment.
Drive-In Racks
Designed for homogeneous products, these high-density systems allow forklift access to deep lanes. They support LIFO or FIFO inventory rotation.
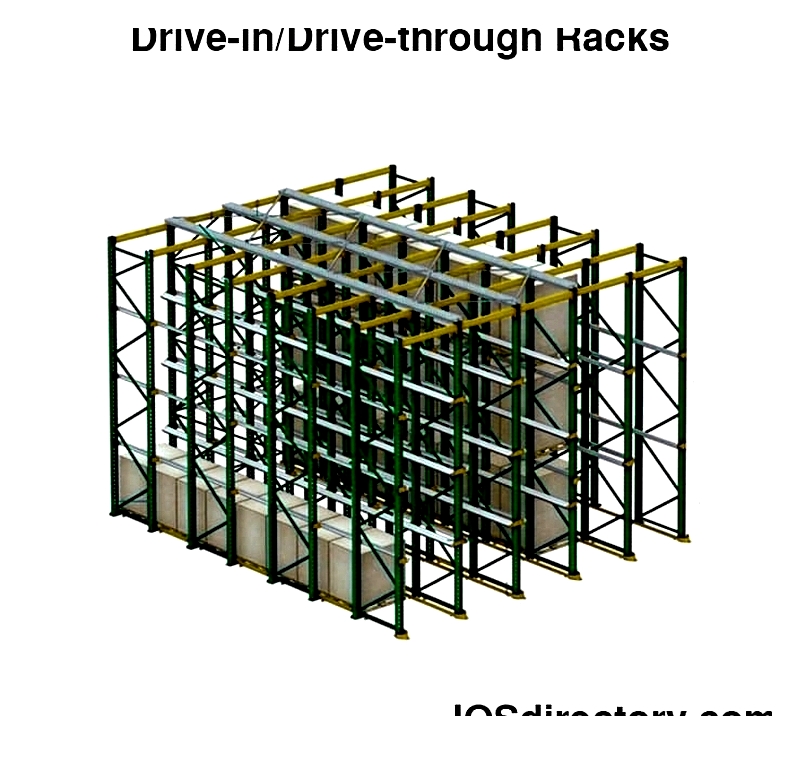
Configurations depend on SKU quantities and space. Support rails and beam connections ensure stability for heavy loads.
Pallet Shuttle Racks
This semi-automated system uses electric shuttles for efficient pallet movement. It's ideal for high-volume operations, especially in cold storage.

Double Deep Racks
These systems store pallets two-deep, increasing density while maintaining some accessibility. They require specialized forklifts.

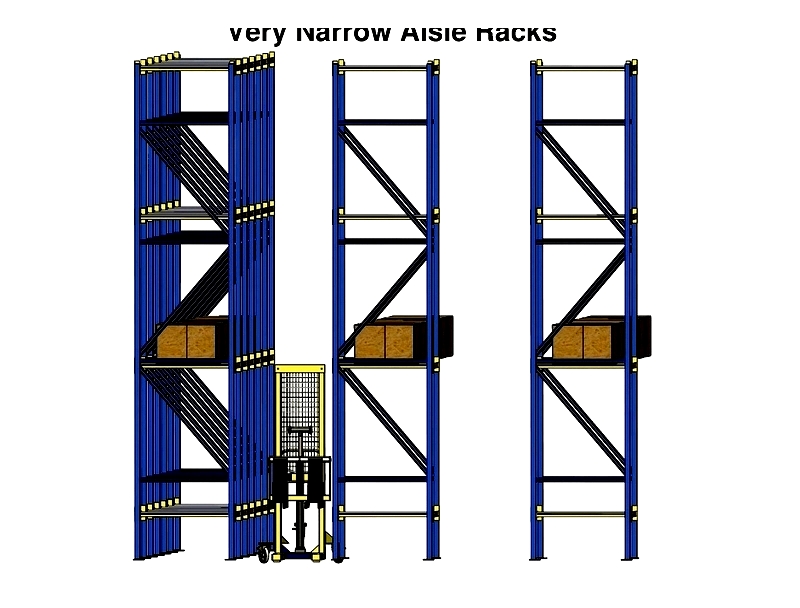
Very Narrow Aisle Racks
VNA systems maximize space with exceptionally narrow aisles. They require specialized equipment but offer high storage density.
Longspan Shelving
This versatile system accommodates medium and small items. Its modular design suits various




