Introduction
This article covers everything you need to know about wire handles and bucket handles.
You will learn about:
- What a Wire Handle is
- How Wire Handles are Made
- Types of Wire Used for Wire Handles
- Applications of Wire Handles
- And much more...
Chapter 1: What is a Wire Handle?
A wire handle is a metal attachment for buckets, pails, and similar containers, designed to assist in lifting and carrying. Made from strong, durable metals, these handles can support significant weight. Engineered to bear container loads, wire handles enhance the ease and efficiency of transporting various containers.

Wire handles are crafted from carefully selected materials to ensure strength, durability, and longevity. They are used in diverse applications, such as lifting pots in sensitive environments, tool handling, moving wire mesh baskets filled with parts, and in the canning industry for maneuvering large cans during painting and coating processes. Handle construction varies based on materials, which may include wood, metal, plastic, rubber, or specialized composites.
Chapter 2: How Wire Handles Are Made for Strength and Durability
Manufacturing wire handles involves precision engineering and advanced wire forming techniques to produce high-quality, durable handles for various applications. Using specialized machinery like CNC equipment, manufacturers achieve consistent quality, dimensional accuracy, and high production rates. This process, rooted in traditional metalworking, is essential for creating reliable handles for buckets, pails, baskets, industrial containers, and retail packaging. The process begins with drawing wire to the desired thickness before shaping it into ergonomic, durable handle designs.
Materials
Wire handles are made from various metals and alloys, selected for load-bearing capacity, corrosion resistance, conductivity, and appearance. Common materials include stainless steel, carbon steel, aluminum, copper, and nickel. Material choice directly impacts mechanical properties, environmental resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making it crucial to select the right alloy for each application.
- Carbon Steel Alloys are widely used for their high tensile strength, rigidity, and affordability. Ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications and bulk storage containers.
- Stainless Steel offers superior corrosion resistance, making it suitable for food processing, medical devices, chemical handling, and humid environments.
- Copper Alloys like bronze or brass are chosen for thermal/electrical conductivity, visual appeal, and antimicrobial properties.
- Aluminum Wire Handles provide lightweight yet strong options for lightweight containers, promotional packaging, and consumer products.
- Nickel Alloys balance strength, corrosion resistance, and ductility, serving as an alternative to steel in rust-prone environments.
These metals offer excellent formability and stress tolerance, essential for wire forming and fabrication. Material selection depends on handle type, container application, load requirements, safety regulations, and aesthetic or hygiene standards. Industries like foodservice, healthcare, and electronics prioritize material choice for quality assurance and compliance.
Wire Forming Processes
The wire handle manufacturing process employs various forming methods to achieve precise geometry, strength, and ergonomic comfort. Controlled bending shapes the wire into standardized or custom designs, with multiple operations for complex configurations. Seamless transitions between stages ensure durability and consistency.
Force is applied strategically through bending, upsetting, swaging, extrusion, stamping, and cutting. While manual shaping suits custom or small-batch production, modern manufacturing relies on precision dies and programmable machinery for consistency and scale.
Drawing
Wire drawing reduces wire diameter through sequential dies, improving surface finish and tensile strength. Adjusting wire gauge allows handles to support varying loads, from retail baskets to heavy-duty pails. The process includes annealing (for ductility) and pickling (to remove oxidation), with lubrication reducing friction during diameter reduction.
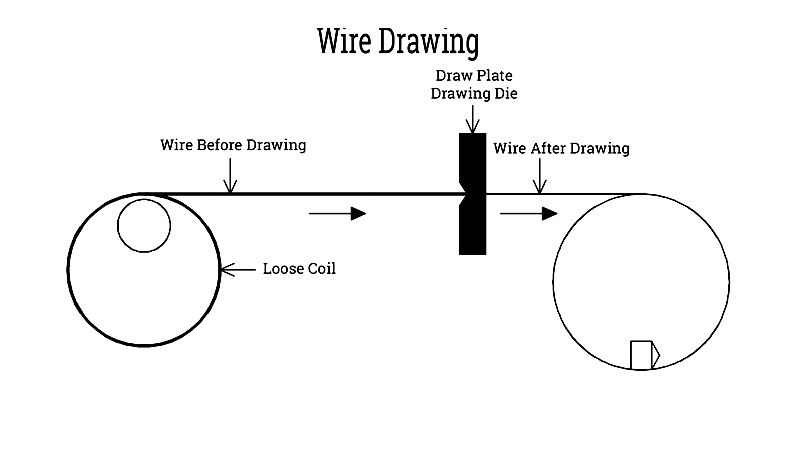
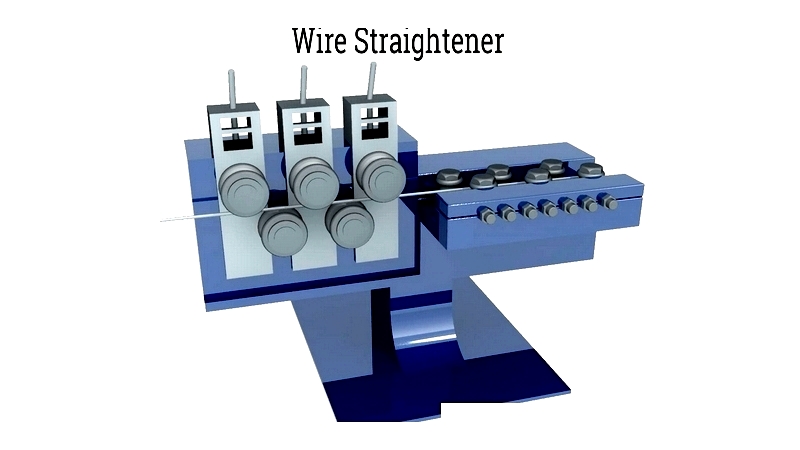
Straightening
Wire straightening removes warping or residual stresses using adjustable rollers. Straight wire ensures dimensional accuracy and durability, critical for automated assembly and mass production.

Applying Force
Force is applied through bending, upsetting, swaging, and cutting, using specialized tooling. Manual shaping suits custom projects, while precision machinery dominates modern manufacturing for consistency and scale.
Manufacturing Process
Key operations include:
- Upsetting – Compresses wire axially for increased strength and fatigue resistance, ideal for industrial buckets and agricultural equipment.
- Swaging – Adjusts wire cross-section for secure end loops or hooks, enhancing attachment strength.
- Bending – Creates ergonomic handles with smooth curves or rigid corners, customized for branding or product differentiation.
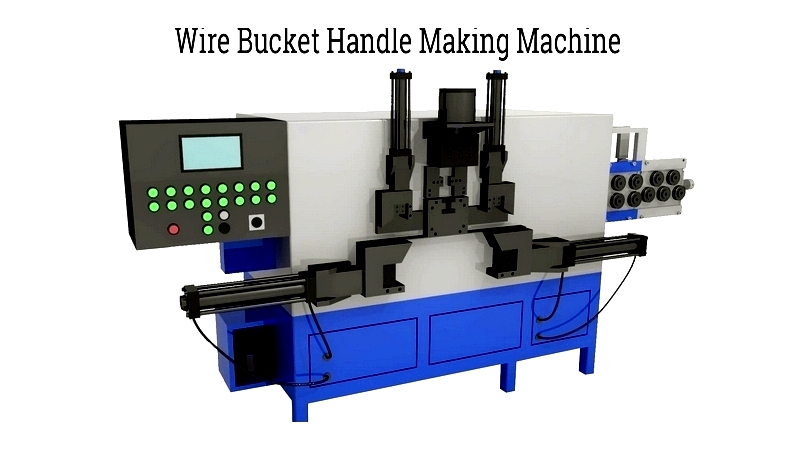
Four Slide Wire Handle Forming
Four-slide forming automates complex handle production, shaping wire from four axes simultaneously. This technology boosts speed and design variability, ideal for high-volume output of paint can and bucket handles.

Finishing
Finishing processes like powder coating, electroplating, or epoxy application enhance wear resistance and corrosion protection. These finishes improve appearance, grip, and compliance with industry standards.
Grip
Handle grips improve ergonomics and user comfort, available in slip-on, snap-on, or over-molded configurations. Materials range from plastics to rubber, with options for branding and sustainability.
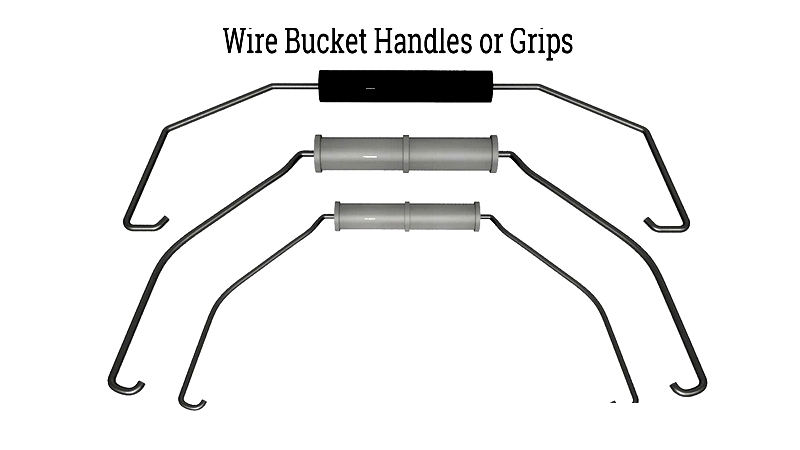
In summary, wire handle production combines forming, bending, and finishing technologies to create cost-effective, robust products. Manufacturers refine these techniques to meet safety, ergonomic, and regulatory demands across industries.
Chapter 3: Wire Types for Handles and Their Performance Impact
Wire handles are essential for transporting buckets and containers, requiring durability, strength, and corrosion resistance. Material selection is critical for performance in industries like manufacturing, construction, and food processing.
Galvanized Steel Wire
Galvanized steel wire excels in rust resistance, durability, and tensile strength. The zinc coating protects against oxidation, making it ideal for moist or harsh environments. Hot-dip galvanization ensures a uniform protective layer, extending handle lifespan.
Galvanized Iron Wire
Galvanized iron wire offers a cost-effective, flexible alternative with sufficient strength. Easy to fabricate, it suits light-duty and industrial handles for paint cans and utility pails.





