Introduction
This article provides an in-depth examination of Tube Fabricating Machinery.
Continue reading to explore key topics including:
- Overview of Tube Fabricating Machinery
- Tube Bending Machinery
- End Forming Machinery
- Tube Hydroforming and Tube Swaging Machinery
- Tube Cutting Machinery
- And more...
Chapter 1: Overview of Tube Fabricating Machinery
Tube fabricating machinery encompasses equipment designed to permanently bend, cut, or shape tubes and pipes into various configurations. These machines typically process tubes made from ductile materials such as stainless steel, aluminum, bronze, brass, and titanium. Most tube forming techniques involve metal coldworking processes.
Different machinery types transform straight tubes into functional forms by altering their geometry through material deformation. The resulting formed tubes find applications across numerous industries, as detailed in subsequent chapters.

Chapter 2: Tube Bending Machinery
Tube bending is a crucial metalworking process that shapes tubes and pipes to precise specifications for manufacturing and industrial applications. During bending, tubes experience controlled deformation through tensile and compressive forces. The outer bend arc stretches under tension while the inner arc thickens under compression. This plastic deformation is carefully managed to maintain tube integrity and meet quality standards.
Applications span automotive, aerospace, HVAC, shipbuilding, furniture, and musical instrument industries. Bent tubes enable directional changes in piping systems and are essential for structural frameworks, exhaust systems, and heat exchangers.
Tube bending methods fall into two categories:
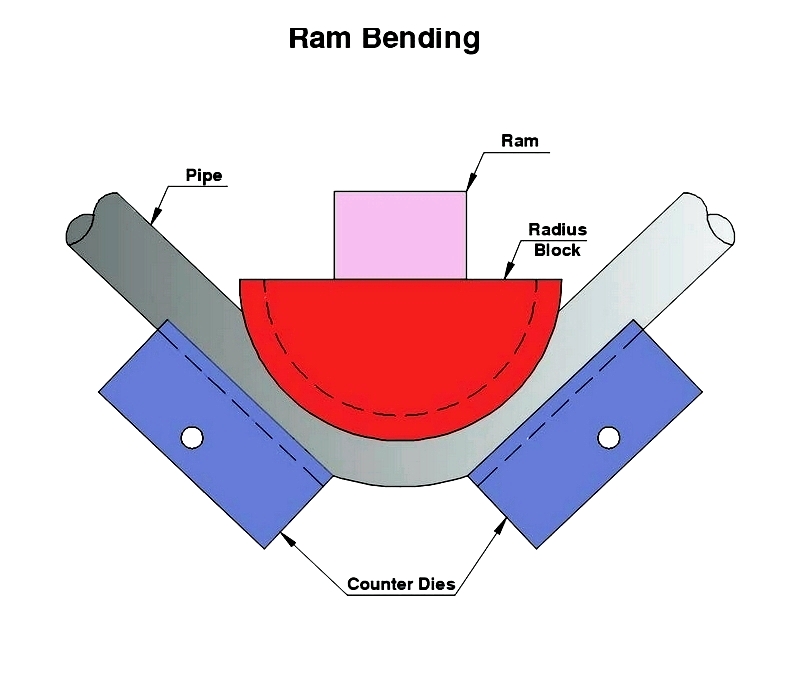
- Form-bound bending: Tooling dictates final geometry, including rotary draw and press bending
- Freeform bending: Achieved through moving dies, including angle rollers
Modern benders range from manual to CNC machines, with CNC offering high precision for complex fabrication.
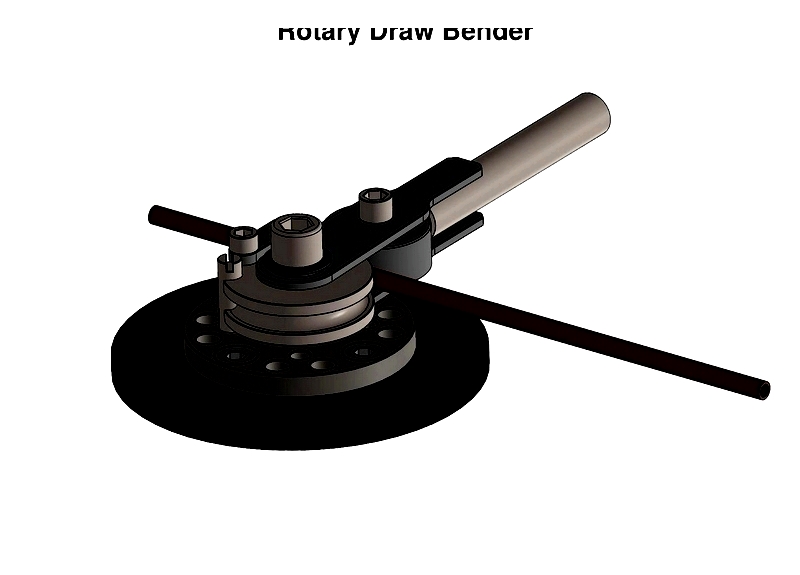
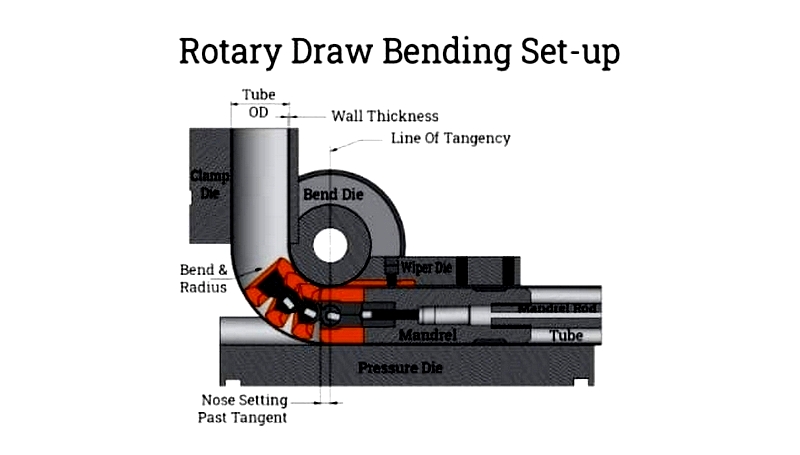
Rotary Draw Bender
These advanced machines use interlocking dies (bend, clamp, pressure, and wiper) to prevent defects during bending. Key components include:
- Bend Die: Determines bend shape and radius
- Clamp Die: Secures tube against bend die
- Pressure Die: Maintains tube contact during bending
- Wiper Die: Supports inner bend radius

Mandrel Bender
Incorporates a mandrel inside the tube to prevent defects during tight-radius bends, especially for thin-walled materials. Common in hydraulic and fuel systems.
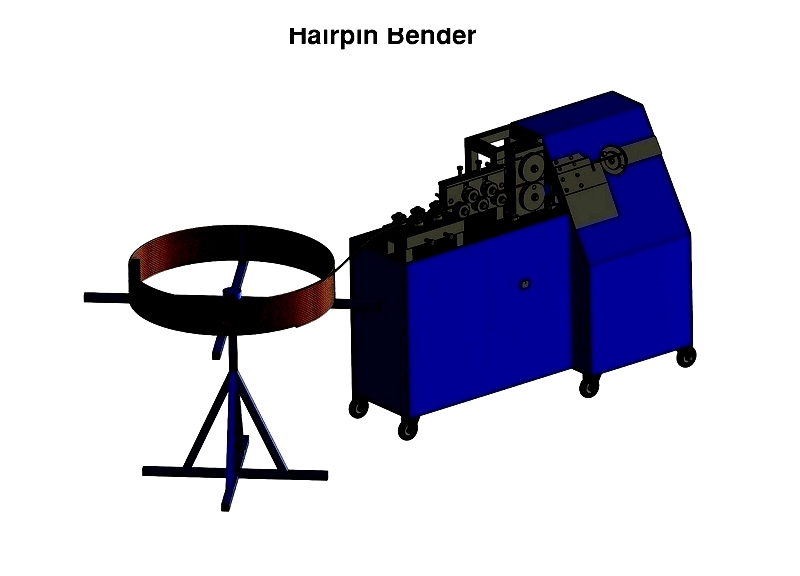
Hairpin Bender
Specialized for creating 180° bends in HVAC tubing, featuring automated feeding and cutting systems for high productivity.
Return Bender
Optimized for U-tube fittings in heat exchangers and chiller systems, ensuring dimensional consistency.
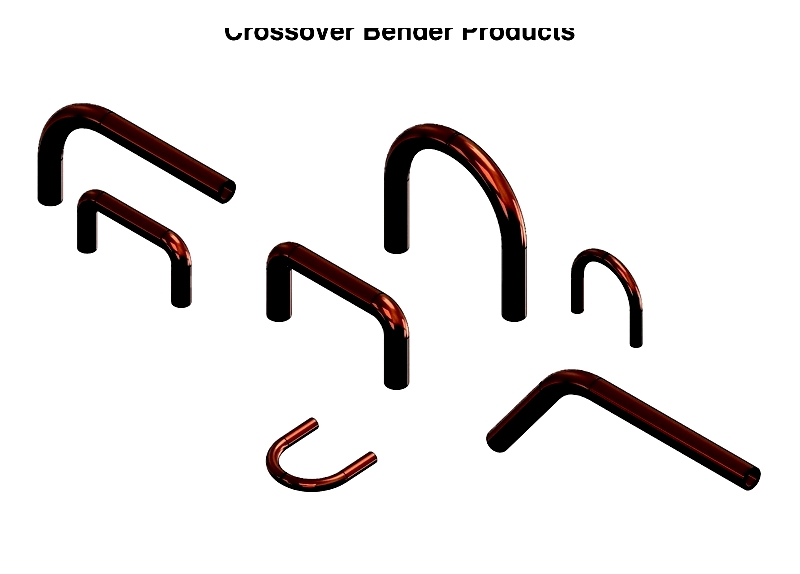
Crossover Bender
Versatile machines handling various diameters and angles for complex piping designs.

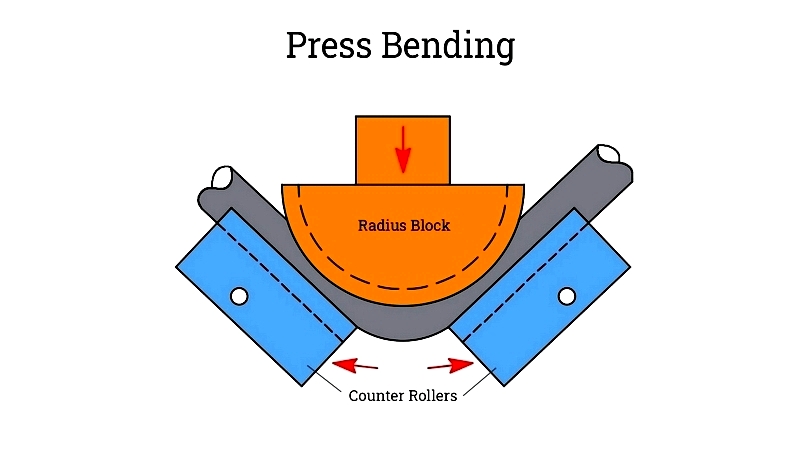
Press Bender
Cost-effective solution for symmetrical bends where high precision isn't critical.
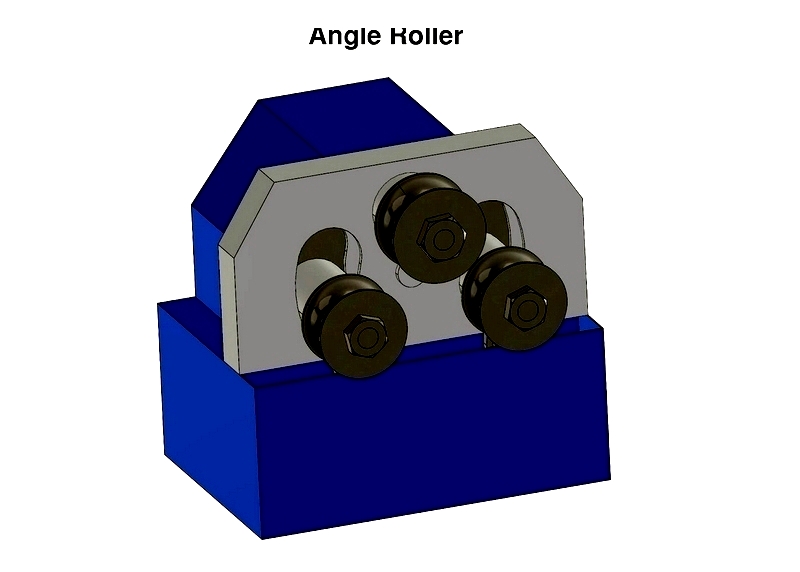
Angle Roller
Creates gradual bends in large-diameter tubing for architectural and structural applications.
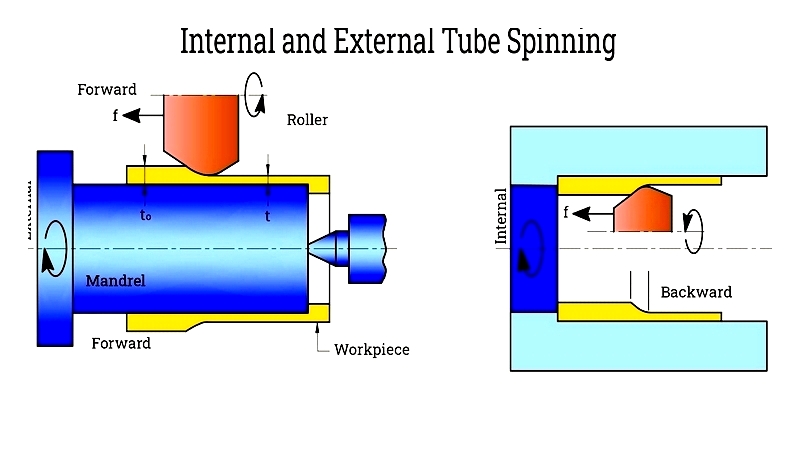
Tube Spinning
Precision flow forming that alters wall thickness, common in aerospace applications.
Shear Spinning
High-precision process for aerospace components requiring uniform wall thickness.
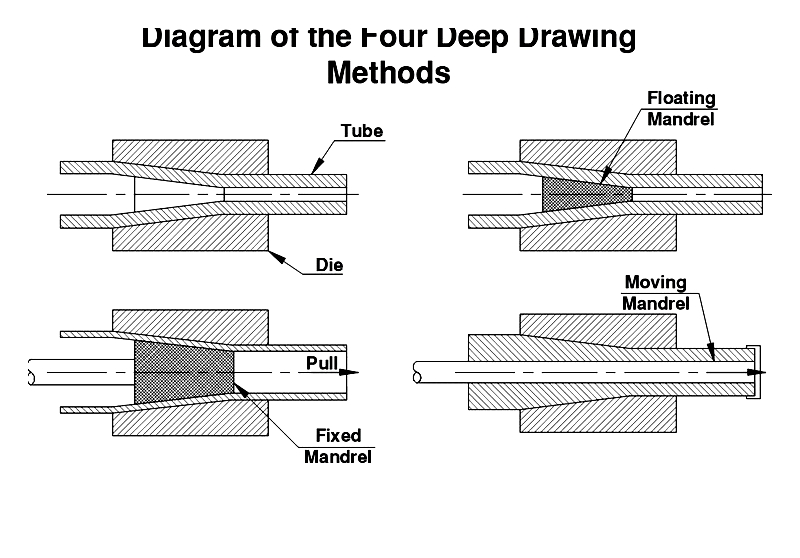
Deep Drawing
Fundamental method for creating seamless tubes through four approaches:
Tube Sinking
Pulls tube through die to set outer diameter.
Floating Mandrel
Allows wall thickness adjustments during drawing.
Fixed Mandrel
Controls both wall thickness and inner diameter.
Moving Mandrel
Produces seamless pipes with exact dimensions.
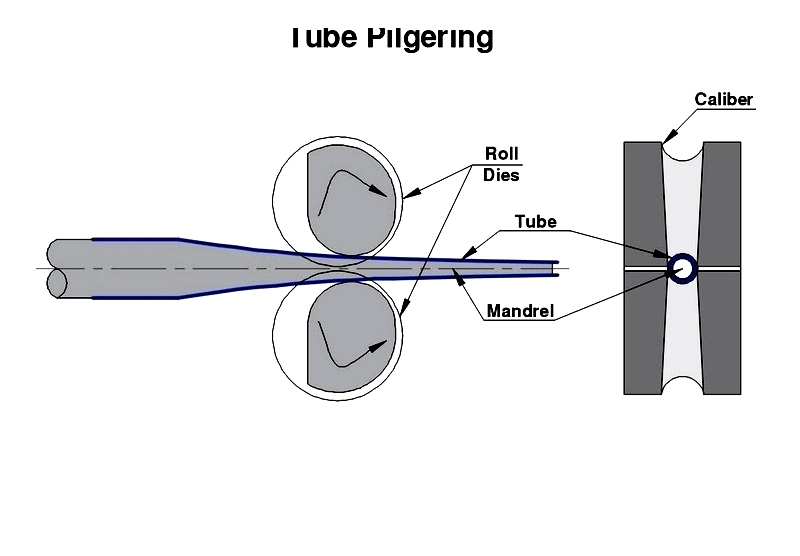
Pilgering
Specialized reduction process for high-performance tubing.
Autofrettage
Pressure-based technique enhancing fatigue resistance in pressure vessels.
Chapter 3: End Forming Machinery
Specialized equipment for shaping tube ends to enable connections and improve performance in fluid systems.
Key techniques include:
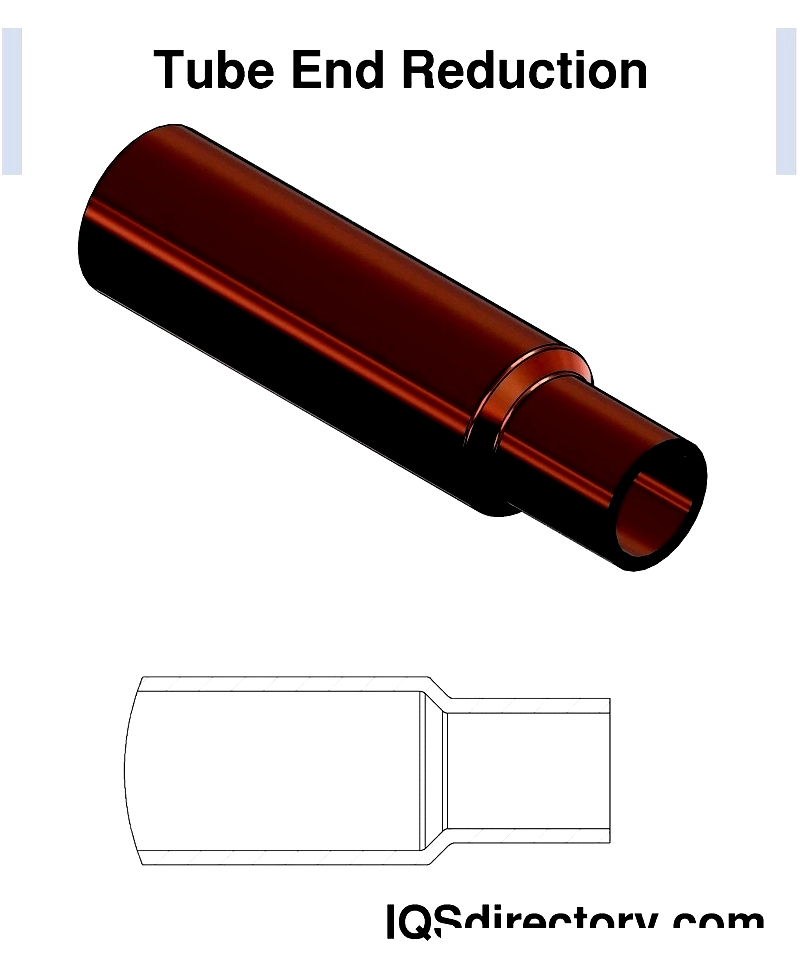
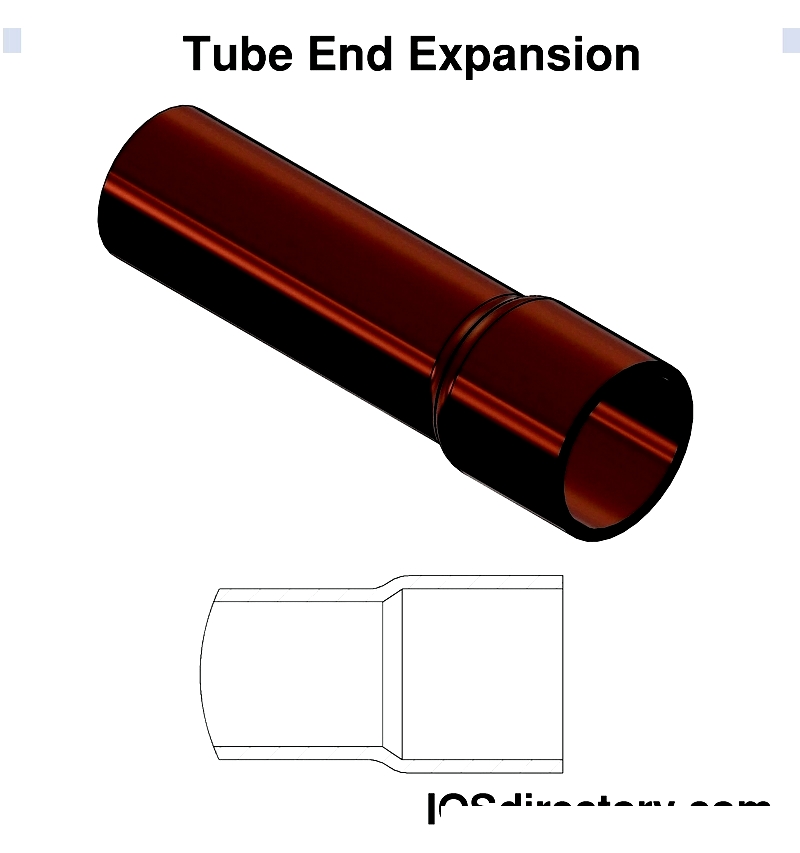
- Reduction/Expansion: Adjusts tube end diameter
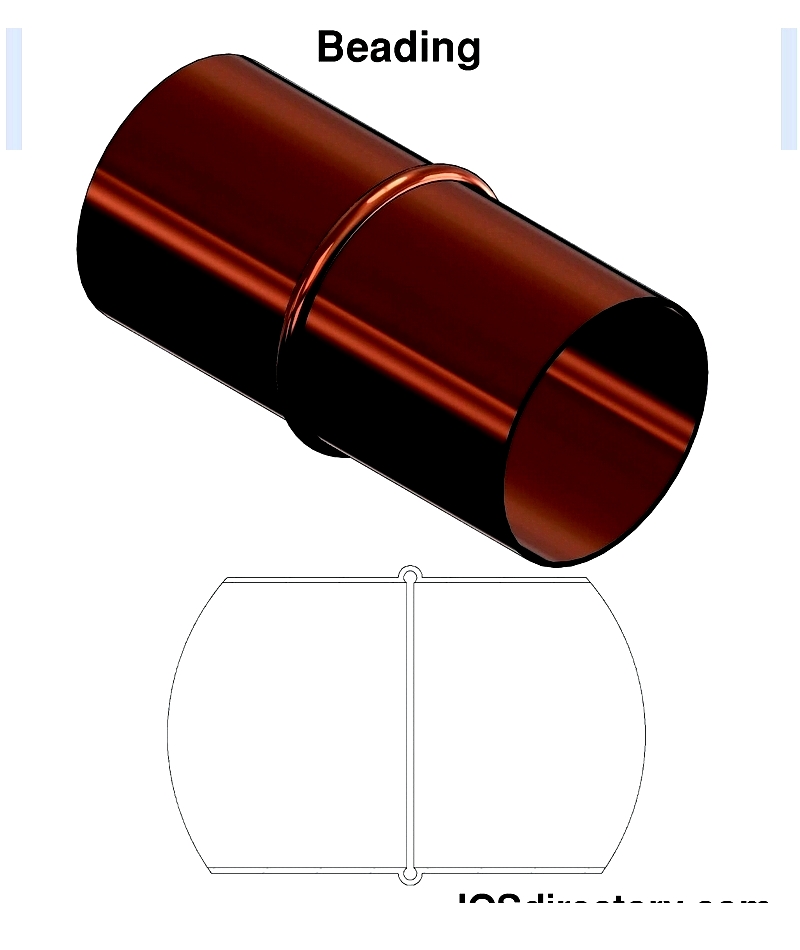
- Beading: Creates retention features
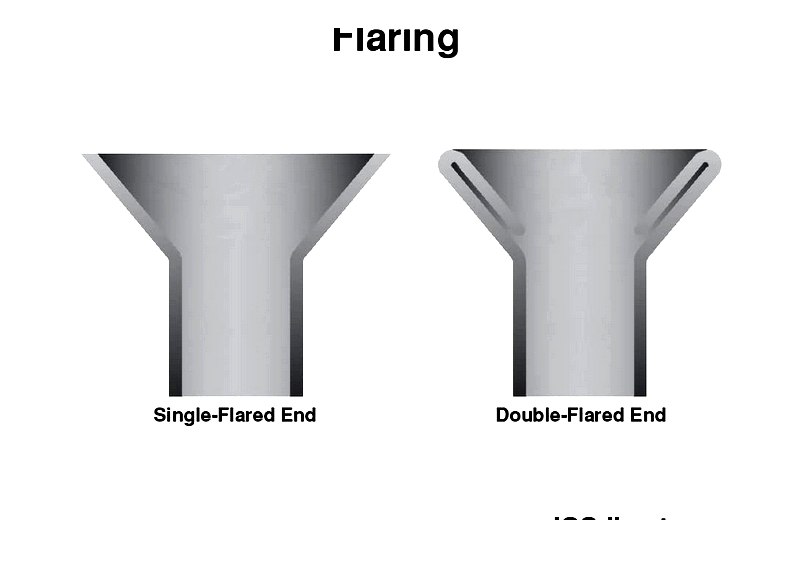
- Flaring: Forms conical connections
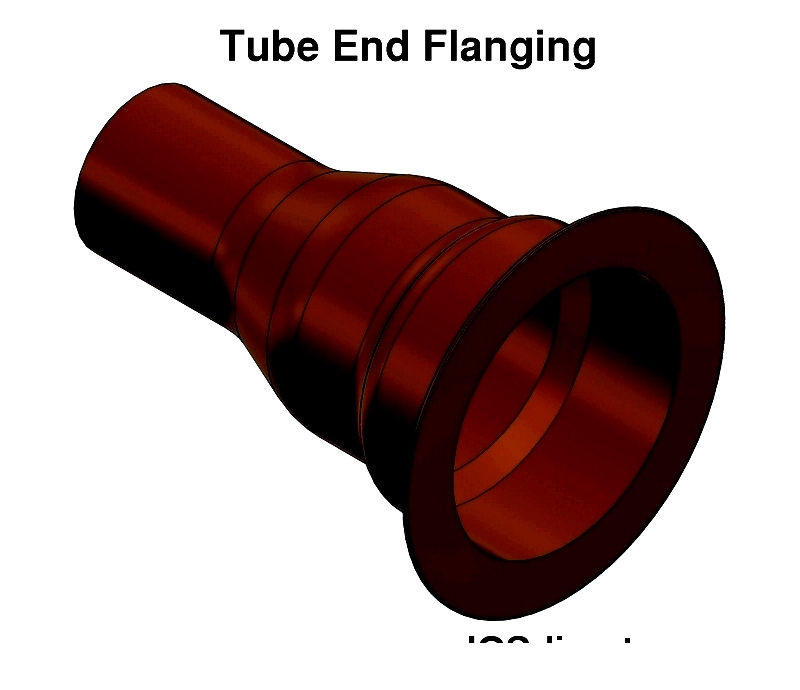
- Flanging: Produces bolt-up surfaces