This article provides an in-depth exploration of canopies.
You'll gain insights into various aspects including:
- What Are Canopies?
- Key Considerations for Choosing Canopies
- Materials Used in Canopy Construction
- Different Types of Canopies
- Awnings and Their Varieties
- Pros and Cons of Canopies
- Practical Applications of Canopies
- Canopy Maintenance
- And much more...

Chapter 1: Understanding Canopies, Selection Factors, and Construction Materials
Canopies are protective structures featuring fabric or metal covers designed to shield against various weather conditions including sunlight, rain, hail, and snow. For example, open-sided tents qualify as canopies. Commonly known as shade structures, they're frequently used to cover benches, walkways, and small outdoor areas.
Canopies may include curtains on one to three sides for partial shelter or be fully enclosed for complete privacy. Alternatively, solid canopy blinds in square or rectangular shapes can cover hundreds to thousands of square feet. These shade structures enhance comfort in patios, pool areas, or gardens while offering varying privacy levels with easy outdoor access.

Key Considerations for Canopy Selection
- Will the canopy serve purely as sun protection or highlight a specific structure? Many businesses want their shade structures to be visible to approaching customers. Retail stores, gyms, restaurants, hotels, and community gardens can all benefit from distinctive shade structures that transform a building's appearance - for instance, a vibrant red canopy can dramatically enhance a neutral-colored facade.
- Design: Many businesses choose shade structures primarily for functionality. They're particularly popular for outdoor dining areas, providing sun protection. Traditional shapes and colors typically blend best with existing architecture.
- Creating visually appealing buildings involves cohesive design elements, complementary colors, and symmetry. Select materials and designs that enhance the building, with shade structures mirroring architectural elements for a polished look.
Materials Used in Canopy Construction
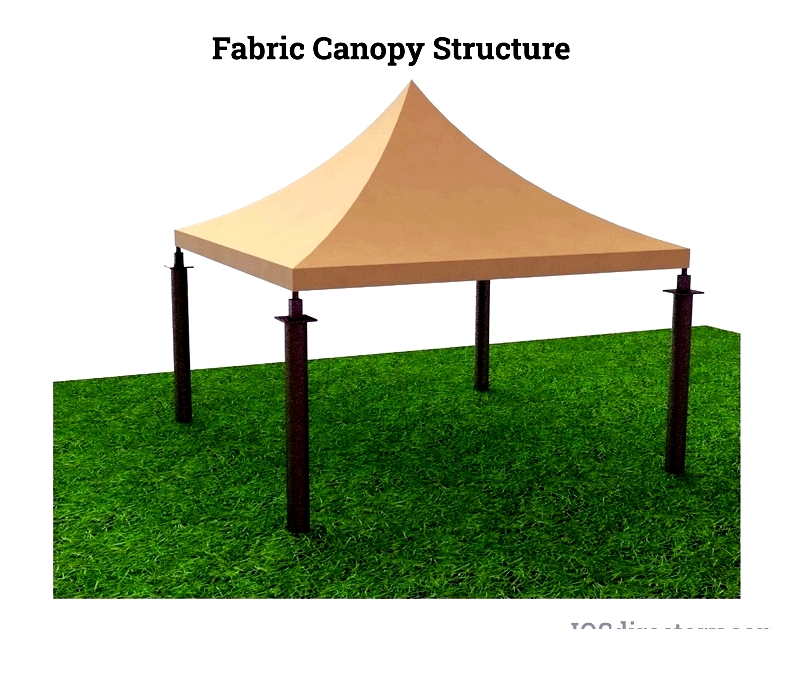
Fabric
Fabric is a popular, versatile choice for shade structures. While offering simple, cost-effective shading, it may not suit permanent installations.
Fabric works well for shading backyards and patios. Common options include umbrellas, cloth awnings, and shade sails. Easy installation and diverse designs make fabric a favorite, though it lacks durability for long-term use. Regular setup and removal before severe weather prevents damage. Fabric requires more frequent replacement than sturdier materials.
Vinyl
Vinyl shade structures are gaining popularity among homeowners. Vinyl offers several advantages for canopies, particularly for patio shading. Its exceptional durability resists corrosion and weather damage while remaining pest-resistant. Customizable designs or minimalist styles cater to various preferences. Though potentially pricier than wood or aluminum, vinyl's longevity makes it a premium, long-lasting investment that often outlasts homes.

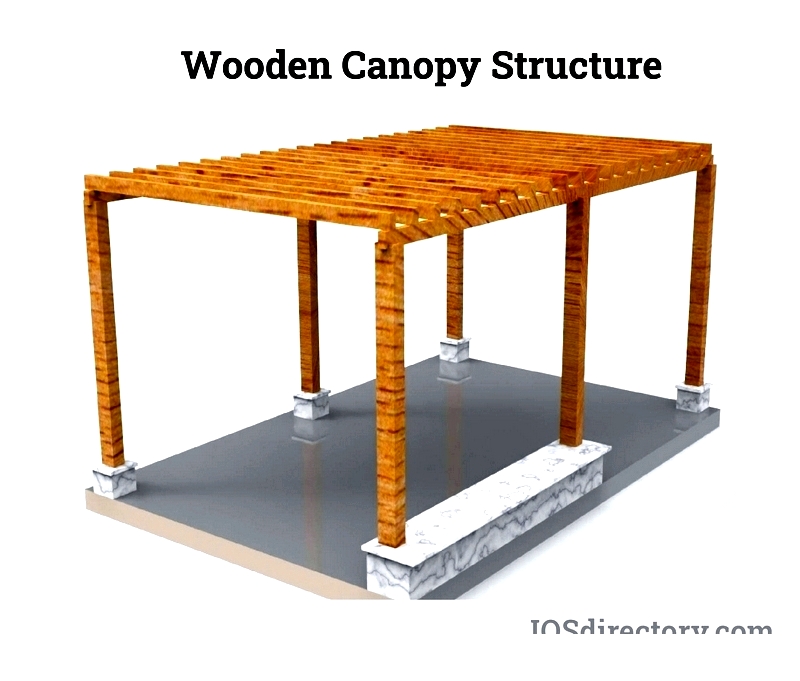
Wood
Wood remains a popular canopy material for its aesthetic appeal, ease of construction, and compatibility with most home designs. It's versatile for creating patio covers, gazebos, and pergolas.
However, wood has drawbacks. It's less durable than metal or vinyl, susceptible to moisture damage, weather exposure, and pests like termites. Regular maintenance including staining and cleaning is necessary to preserve its condition.

metal
For maximum durability, aluminum or steel canopies are excellent choices. metal structures are commonly used for building-attached awnings and patio covers due to their strength.
metal's primary advantage is exceptional durability. Aluminum and steel offer lightweight, weather-resistant options with customizable colors and corrosion resistance.
However, metal canopies are typically more expensive than alternatives, require maintenance, and can be challenging to repair or replace.
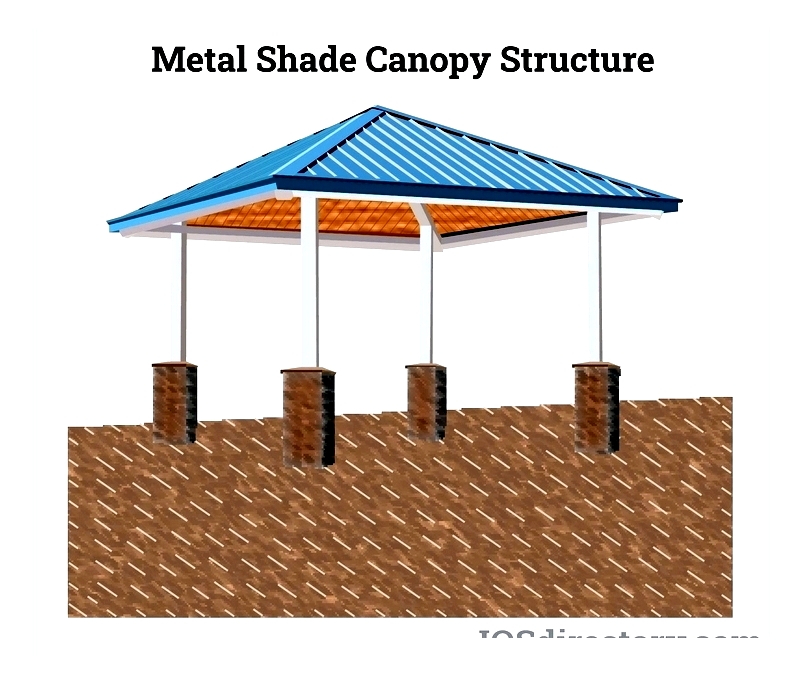

Chapter 2: Different Types of Canopies
Tension Membrane Canopies
Tension membrane canopies represent modern architectural shade solutions. These innovative structures use stretched membranes (often PTFE-coated fiberglass, PVC-coated polyester, or ETFE) over sturdy steel or PVC frames. Popular for both commercial and residential use, they offer striking aesthetics, durability, and weather resistance while requiring minimal maintenance. Their lightweight design maximizes covered space for patios, playgrounds, sports complexes, and public areas.
A key advantage is their ability to cover large areas while allowing natural light, creating inviting spaces. Translucent fabrics make them energy-efficient for sustainable projects. When selecting, users compare membrane options, frame finishes, and colors to complement their property's style.

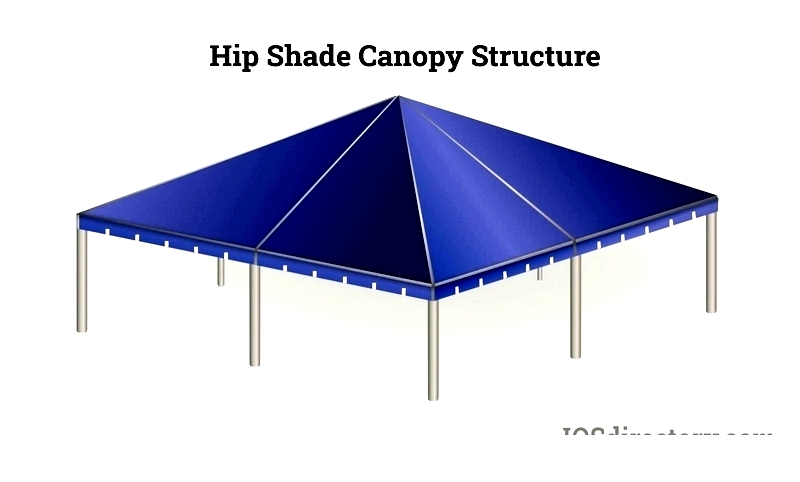
Hip Shade Canopies
Hip shade canopies are versatile commercial systems featuring roofs pitched from the center to multiple steel columns. They effectively channel precipitation while providing sun protection, making them ideal for playgrounds, sports fields, outdoor dining, and parking lots.
These modular systems can shade small areas or combine for large spaces. With 4-8 support options, they adapt to various sites. Commercial owners appreciate their low maintenance, wind resistance, and branding potential through side panels.

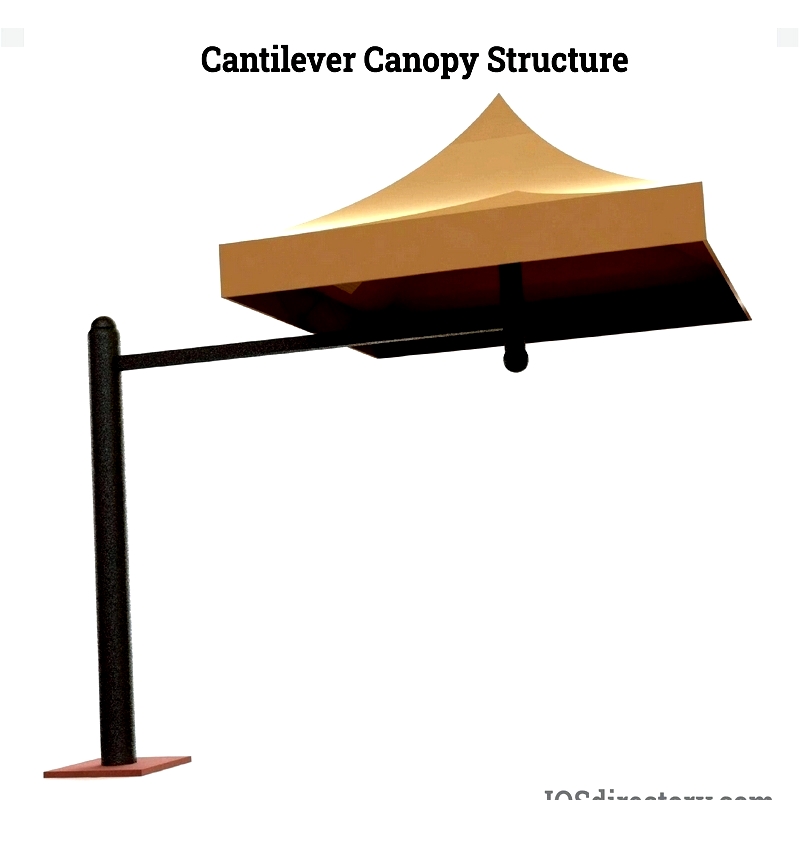
Cantilever Shade Canopies
Cantilever canopies excel where unobstructed views and space optimization matter. With rear supports only, they eliminate front columns, making them perfect for parking areas, bus stops, poolside lounges, and commercial seating. Their modern design adds architectural interest while providing sun and rain protection.
Available in single-post, double-post, and extended formats, these metal-framed canopies accommodate various weather requirements. Customers often choose powder-coated or galvanized steel for corrosion resistance paired with durable shade cloth or waterproof fabric.

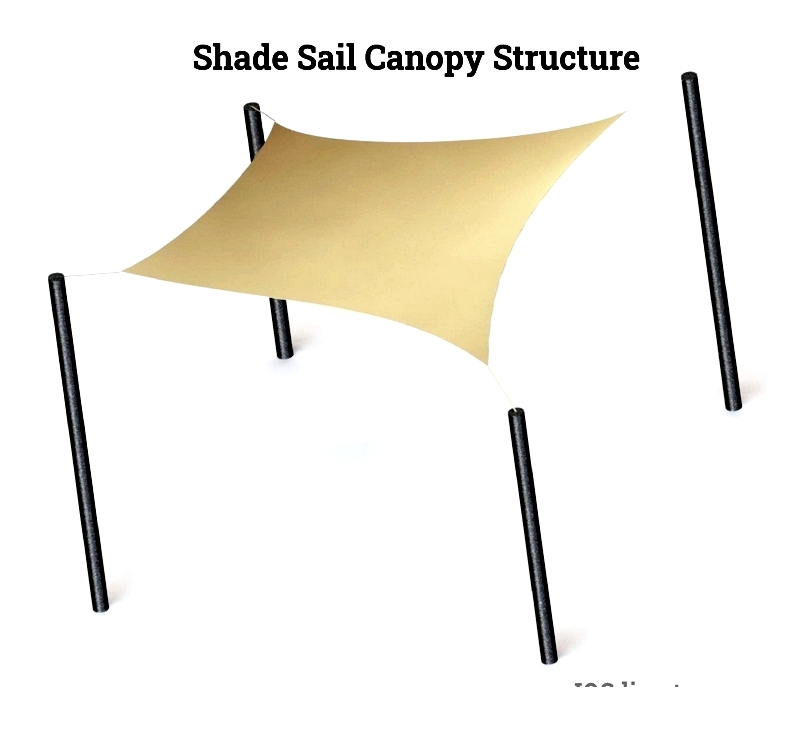
Shade Sail Canopies
Shade sails blend modern design with UV protection. These tensioned fabric panels secured to posts create minimalist shade solutions for patios, pools, playgrounds, and rooftops. Their open design enhances airflow while blocking up to 98% of UV rays with materials like HDPE or PVC.
Customizable in triangular, quadrilateral, or pentagonal shapes, they offer creative shading options. While visually appealing, they may not suit extremely windy or rainy areas without special specifications.

Multi-Panel Shade Canopies
Multi-panel canopies feature layered fabric segments creating sophisticated designs.




