Introduction
This section provides comprehensive information about thermocouples available online.
You will discover:
- What a Thermocouple Is
- How Thermocouples Function
- Different Thermocouple Types
- Thermocouple Applications
- And additional insights...
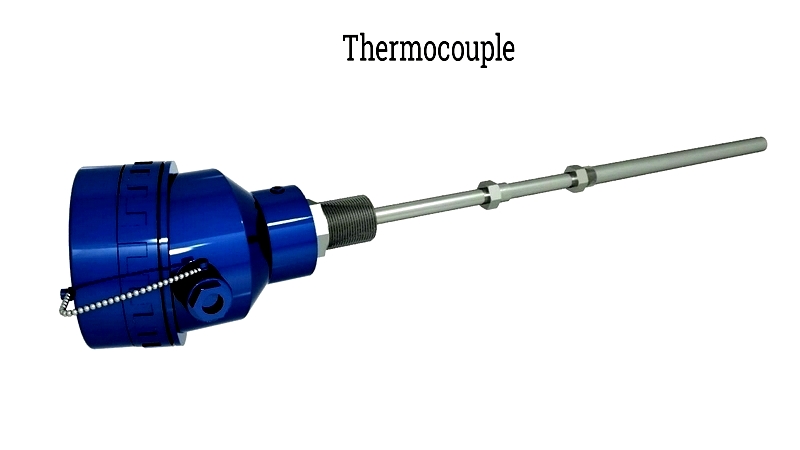

Chapter One: Understanding Thermocouples
A thermocouple serves as a crucial transducer that converts thermal energy into electrical energy. It consists of two dissimilar metal wires joined at a junction. Temperature changes at this junction produce a measurable voltage, enabling accurate temperature determination.
This device operates on the Seebeck Effect principle, where different metals generate a detectable voltage when their junction experiences temperature variations. The voltage magnitude depends on both the temperature change and the metals' properties.
Composed of two insulated metal wires connected to a measuring device, thermocouples function as safety and monitoring instruments for various processes and machinery, providing reliable temperature data for optimal operation.
The following illustration demonstrates thermocouple operation. As temperature increases at the left wire junction, the corresponding change appears on the right gauge.
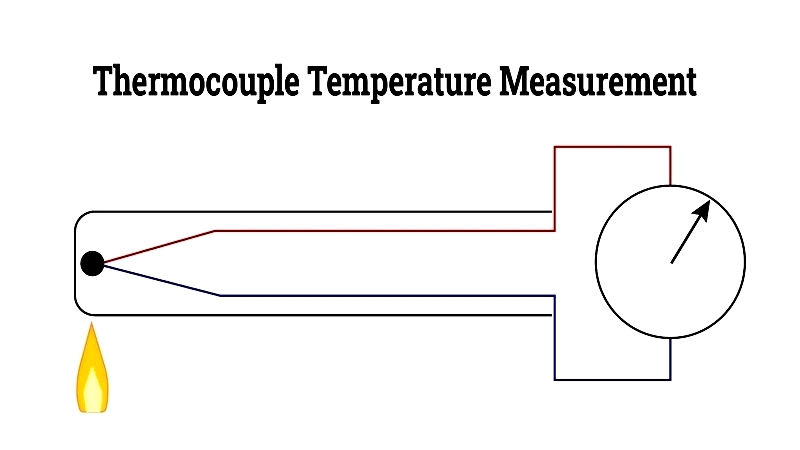
Thermocouple assemblies are engineered for demanding environments. Selection criteria include temperature range, environmental conditions, and material characteristics. Their size and shape are customized for specific applications to ensure precision and responsiveness.
Chapter Two: Thermocouple Operation
Thermocouples are widely used temperature sensors in industrial and scientific settings, valued for their durability, versatility, and broad temperature measurement capabilities. They function by joining two dissimilar metal wires at a sensing junction (hot junction), while connecting the other ends to a reference (cold junction). The working principle involves generating a thermoelectric EMF based on temperature differences between these junctions. By comparing the voltage at the hot junction to the known cold junction temperature, thermocouples accurately monitor temperature variations.
Thermocouple technology relies on three fundamental thermoelectric phenomena: the Seebeck effect, Peltier effect, and Thomson effect. Understanding these effects is crucial for optimizing temperature measurement, sensor selection, and process control in manufacturing, chemical processing, and HVAC systems.
Seebeck Effect
The Seebeck effect is fundamental to thermocouple operation. When two different metals (such as Type K, J, or T) form junctions at different temperatures, they generate a measurable voltage. This voltage's magnitude and polarity depend on both the temperature difference and the metals' conductive properties, making thermocouples ideal for industrial temperature monitoring and laboratory measurements.
Peltier Effect
The Peltier effect describes heating or cooling at metal junctions when electric current flows through them. In thermocouples, temperature gradients create measurable voltages that indicate temperature readings. This principle is utilized in various thermoelectric devices and temperature control systems.
Thomson Effect
The Thomson effect explains thermal energy absorption or release in conductors with temperature gradients. This contributes to thermocouple EMF and must be considered for precise measurements, particularly in environments with significant thermal variations.
Thermocouple Functionality
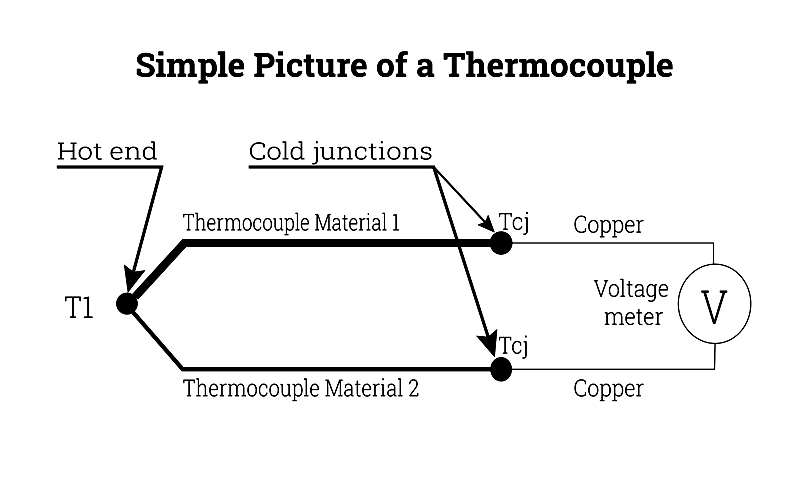
A basic thermocouple circuit contains two different metal wires (A and B) joined at one end to form hot and cold junctions. Temperature differences between these junctions generate a Peltier EMF, which reflects the temperature variation. Measurement accuracy depends on wire alloy selection and environmental conditions.
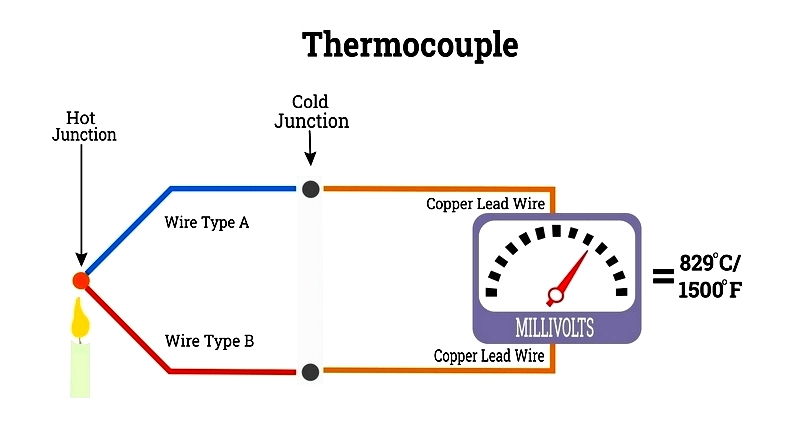
Electrons move from hot to cold ends within metal conductors when exposed to temperature gradients, converting thermal energy into measurable electrical signals. This principle, discovered by scientists like Volta and Seebeck, enables thermocouples' widespread use in food processing, power generation, and manufacturing industries.
Thermocouples produce standardized millivolt signals based on conductor materials, as defined by IEC 60584 and ANSI/ASTM E230 specifications. This standardization ensures global compatibility and integration with automation systems.
Accurate readings require cold junction compensation, typically achieved through ice baths or compensation chips. This correction accounts for ambient temperature changes, ensuring reliable data for process control and research applications.
When both junctions reach equal temperatures, their electrical potentials cancel out. Temperature differences generate measurable EMF, with intensity determined by metal properties and junction temperature disparity. Advanced measurement systems interpret these signals for real-time temperature monitoring.
Due to small voltage outputs (often millivolts), thermocouples require precise measurement devices. Industrial applications use high-sensitivity galvanometers, digital data loggers, and potentiometers to amplify and interpret signals accurately.
Potentiometers calibrate thermocouple systems by comparing unknown voltages to reference sources. Their precision ensures consistent temperature measurement for critical applications like pressure vessels and laboratory equipment.
Galvanometers detect small currents and are essential for thermocouple calibration and diagnostics, enabling engineers to maintain measurement accuracy across various environments.
For absolute temperature measurement, reference junctions must maintain known temperatures (often 0°C). Many thermocouples incorporate compensation chips to account for ambient variations, improving accuracy in pharmaceutical and environmental applications.
Environmental factors affect reference temperatures, so automated systems use compensation devices or algorithms to maintain measurement precision for industrial automation and safety systems.
Selection Considerations: Thermocouples come in various types (K, J, T, etc.), each suited for specific temperature ranges and environments. Key selection factors include accuracy, response time, chemical resistance, and instrumentation compatibility. Specialized connectors and protective sheaths may be necessary for harsh conditions.
Thermowell Applications
Thermowells protect thermocouples from damaging process fluids, corrosive chemicals, and high-pressure environments. They are essential in refineries, power plants, and food processing, extending sensor lifespan and enabling maintenance without process interruption.
- Straight Thermowells
- Stepped Thermowells
- Tapered Thermowells
Thermowell connection types include:
- Socket Welded Connections
- Flange Connections
- Threaded Connections
- Weld-In Connections
When selecting thermowells, consider process temperature, pressure, chemical compatibility, and fluid velocity. Material choices (stainless steel, Inconel, etc.) affect durability and corrosion resistance, while proper sizing ensures accurate measurements. Consulting manufacturers helps optimize temperature measurement solutions.




