Introduction
This article offers industry insights into aluminized steel.
You'll learn about:
- What aluminized steel is
- Characteristics of aluminum coatings
- Benefits of aluminized steel
- Different types of aluminized steel
- And more...
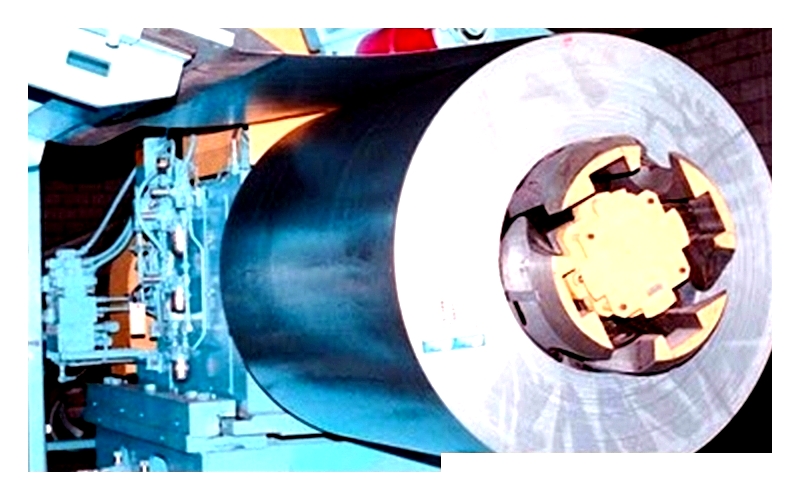 Aluminized Steel from Block Steel Corp
Aluminized Steel from Block Steel Corp
Chapter 1: Understanding Aluminized Steel
Aluminized steel is steel coated with aluminum or aluminum-silicon to enhance its properties, particularly its corrosion and rust resistance. The protective layer is applied through hot-dip processing, where steel is immersed in molten aluminum. This improves the steel's surface properties while increasing its durability and performance, making it comparable to stainless steel.
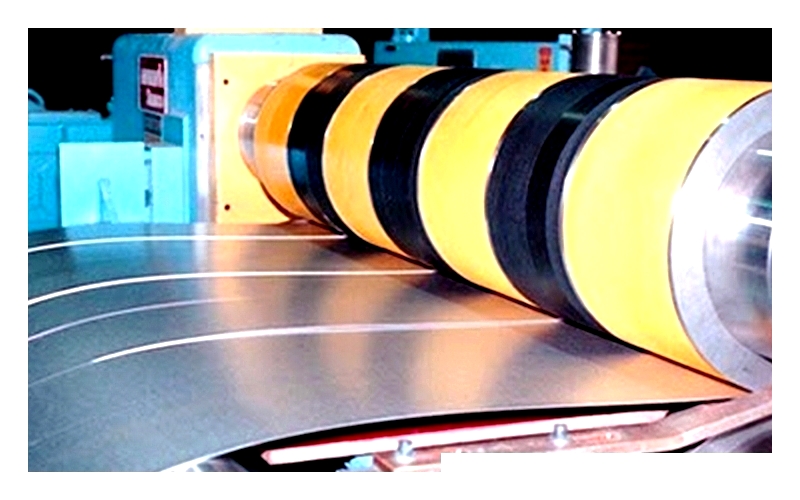 Aluminized Steel from Blocksteel.com
Aluminized Steel from Blocksteel.com
Aluminized steel uniquely combines steel's structural strength with aluminum's surface characteristics, creating a material known for durability and aesthetic appeal. Steel provides strength, hardness, and mechanical properties at an economical cost, while aluminum offers corrosion resistance and an attractive oxidized surface. This combination extends steel's durability and broadens its applications, leveraging both materials' strengths.
Aluminized steel products are distributed by steel service centers that source from steel mills. The aluminizing process, similar to galvanizing, is performed on standard steel to meet requirements in industries like construction, automotive, aerospace, transportation, shipbuilding, appliances, HVAC, bakeware, and fireplaces.
Aluminized steel combines steel and aluminum advantages. Steel has 250% greater density and strength than aluminum but rusts when exposed to environmental factors. Aluminum's natural protective layer prevents rust and corrosion, making it an ideal coating for steel.
 Steel Fabrication
Steel Fabrication
Chapter 2: Characteristics of Aluminum Coatings
Aluminum is among the most widely used metals in modern industrial manufacturing and engineering. As a lightweight metal, it offers exceptional versatility for applications ranging from aerospace and automotive engineering to construction and electronics. Aluminum coatings are particularly valued for their protective and functional qualities. Their high strength-to-weight ratio makes them ideal for automotive parts, aircraft components, and structural applications where reducing weight without compromising durability is essential. Beyond being lightweight, aluminum coatings provide numerous desirable surface characteristics that make them popular as protective metal coatings.
The primary advantage of aluminum coatings is their excellent corrosion resistance, which extends metal substrates' service life in harsh environments. Other important properties include electrical conductivity, thermal efficiency, low-temperature toughness, high reflectivity, non-magnetic qualities, and non-sparking attributes. These features make aluminum coatings a top choice for applications requiring performance and value in metal finishing, surface protection, and thermal management. Below we explore these key characteristics to understand why aluminum coatings are reliable across multiple industries.
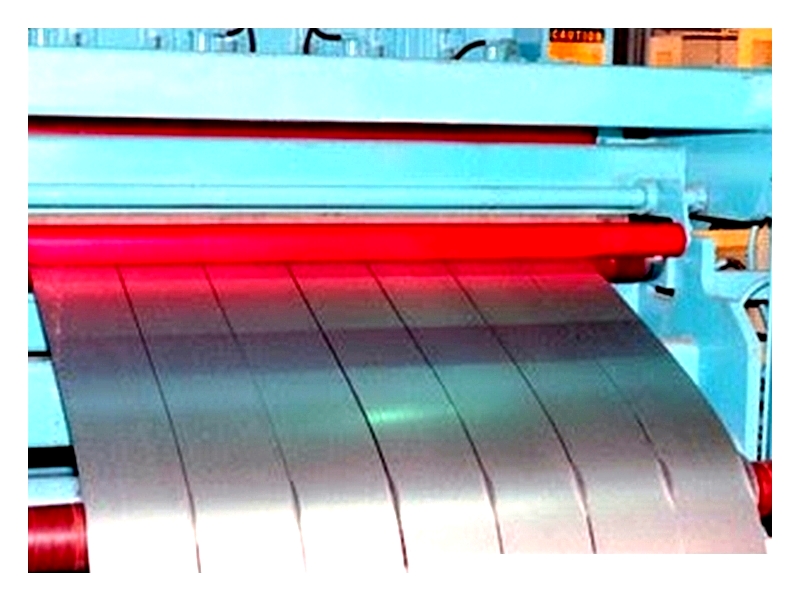 Aluminized Steel from Block Steel Corp
Aluminized Steel from Block Steel Corp
Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance is a defining feature of aluminized steel and aluminum-coated products, making them valuable in marine and chemical processing environments. Aluminum naturally resists corrosion well, protecting the underlying metal from both direct chemical attack and electrochemical action. This makes aluminum coatings crucial for applications exposed to moisture, salt, acids, and harsh chemicals.
Direct chemical attack occurs when reactive agents contact a metal's bare surface. This reaction produces liquid and gaseous byproducts that disperse, while solid byproducts like rust or metal oxides remain. Over time, these oxides can protect the underlying metal from further corrosion. This process is especially important for aluminum-clad surfaces in industrial or coastal environments.

Aluminum resists corrosion through a thin, protective oxide layer that forms on its surface. This layer, created by direct chemical reaction, seals the metal from oxygen, water, and corrosive agents. It forms almost instantly when exposed to air and can regenerate if damaged, ensuring long-term corrosion resistance with minimal maintenance. This makes aluminum coatings ideal for both indoor and outdoor applications requiring durable protection.
Aluminum also provides electrochemical protection. Electrochemical corrosion occurs when an electrolyte solution connects the metal with corrosive agents like acids or cations from less active metals.
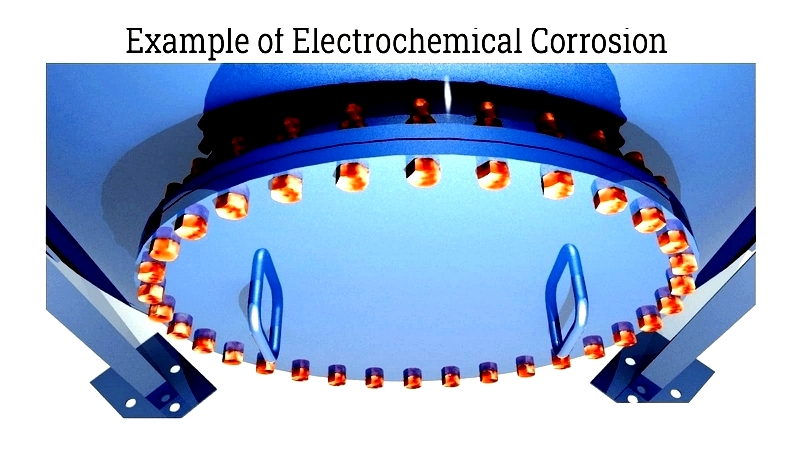
Normally, the aluminum oxide layer provides sufficient protection. However, in highly acidic or alkaline environments where regeneration is limited, the aluminum alloy still protects against electrochemical corrosion. In these reactions, the aluminum coating corrodes instead of the steel, acting as a sacrificial anode. This cathodic protection makes aluminum comparable to zinc in galvanic coatings.
These anti-corrosive mechanisms make aluminum coatings essential for projects requiring longevity and reliability. Industries like construction, HVAC, marine, and automotive manufacturing often specify aluminized steel or aluminum-plated components to meet corrosion resistance standards, reduce lifecycle costs, and ensure safety.
Electrical Conductivity
Aluminum provides about 61% of copper's electrical conductivity. Despite this lower conductivity, aluminum is often preferred for power transmission and distribution lines due to its lower density and cost. Its lightweight nature simplifies installation and reduces structural load in overhead high-voltage lines, making it vital for modern electrical infrastructure. Its oxidation resistance ensures stable electrical performance over time.
Thermal Conductivity
Aluminum conducts heat about twice as well as brass and four times better than steel. This high thermal conductivity makes it popular for heat sinks, radiators, and thermal management solutions in electronics, automotive, and aerospace industries. Its ability to dissipate heat quickly improves energy efficiency and extends component lifespan.

Low-temperature Toughness
Unlike steel, aluminum remains tough and ductile at low temperatures where other metals become brittle. Its mechanical properties stay stable across a wide temperature range, making it suitable for cryogenic storage, refrigeration systems, and aerospace components in sub-zero environments. This characteristic enhances safety, performance, and design flexibility in demanding conditions.
Resilience and Impact Strength
Aluminum's inherent toughness gives it high resilience and impact strength. It can absorb sudden forces and flex under dynamic loads, reducing crack risks. These properties make aluminum ideal for vehicle body panels, structural frames, and safety equipment.
Reflectivity
Aluminum is highly reflective, especially in the 200-400 nm range, outperforming gold and silver. This makes it optimal for mirrors, light fixtures, and solar reflectors. With proper treatment, aluminum can reflect about 90% of visible light and significant infrared/ultraviolet radiation, improving energy efficiency in buildings and industrial processes. Its reflectivity is crucial for optical and energy-saving technologies.

Non-magnetic
Aluminum is paramagnetic and doesn't magnetize under strong fields, making it ideal for electronic enclosures, EMI/RFI shielding, and precision instruments. Its non-magnetic properties prevent interference in high-frequency electronics, supporting electromagnetic compatibility standards.




