Introduction
This article provides comprehensive information about Tube Bending. Continue reading to explore:
You will discover:
- What Tube Bending is
- Key terminologies in Tube Bending
- The mechanics behind Tube Bending
- Different types of Tube Bending
- And additional insights...
Chapter One – What is Tube Bending?
Tube bending is a mechanical process that transforms straight tubes into curved shapes. While straight tubes work well for many applications, bending becomes essential when creating custom designs, accommodating space limitations, or meeting functional needs.
Curved tubes offer greater flexibility and play vital roles in various applications, including musical instruments (like trombones), stair railings, furniture frames, handles, automotive components, and HVAC systems. They also help redirect fluid and gas flows in exhaust systems, hydraulic networks, and pipeline infrastructures.
The two primary tube bending methods are hot and cold bending. Hot bending shapes metal tubing by heating it above room temperature, while cold bending occurs at or near ambient temperature. Techniques include rotary bending, press bending, heat induction bending, ring roll bending, sand packing, and hot slab forming.
Different metals—such as aluminum, brass, mild steel, stainless steel, and titanium—can be bent into various shapes like L bends, U bends, S bends, and coil bends. These forms are achieved by applying force that reshapes and stresses the metal tubing.
During bending, the tube is secured by a pressure die and clamp die before being shaped by a rolling die, roller, or press. The process can be free-form or form-bound. As the tooling moves the tubing through the die, tensile and compressive forces act on the material. The final bend depends on factors like material type, tooling, pressure, lubrication, and design specifications.
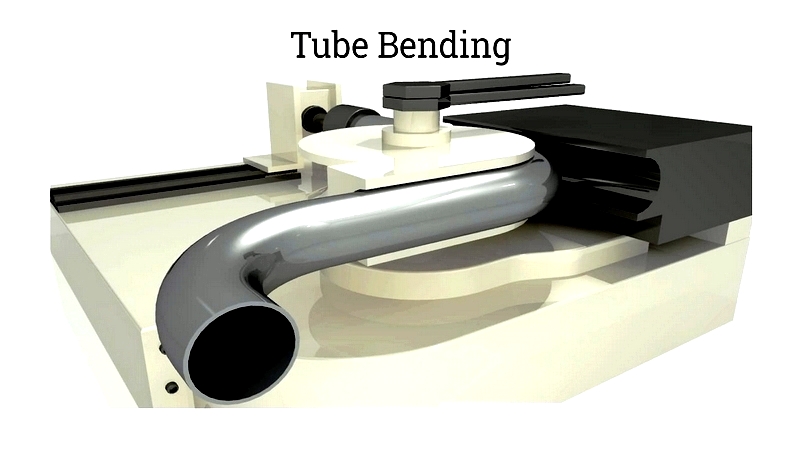
Mechanical tube bending encompasses various techniques to create diverse products and structures. Related processes include cutting, slotting, deburring, welding, and notching.
Chapter Two – Key Terminologies in Tube Bending
Understanding bend geometry is essential before selecting the right die for tube bending. Mastering these terms improves fabrication efficiency, material selection, precision, and quality control. Whether evaluating custom tubing solutions, preparing manufacturing designs, or comparing service providers, these definitions help communicate requirements effectively. Below are key terms used in tube bending, crucial for engineers, fabricators, and professionals in precision tube forming:
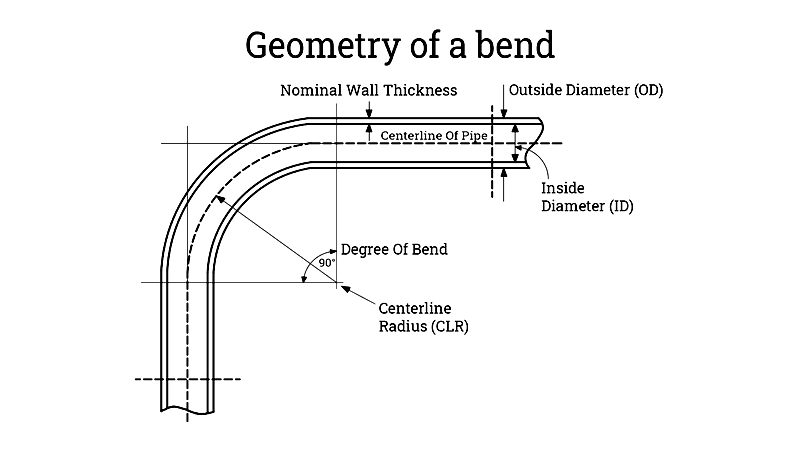
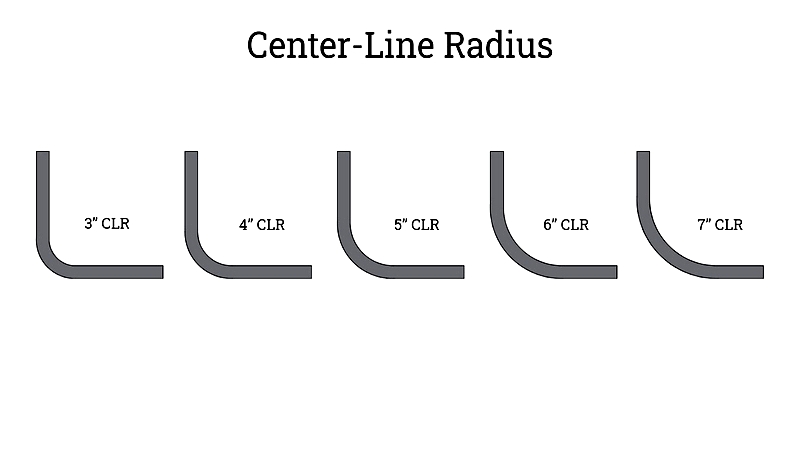
Center-Line Radius (CLR). This measures the distance from the curvature's center to the tube's centerline. It may align with the die radius, depending on their interaction. A larger CLR creates a longer curvature for tubes with identical dimensions. Also called bend radius, CLR is critical for precision bending in automotive exhausts, hydraulic lines, and structural frameworks.
Outside Diameter (OD). OD measures the distance between opposite outer edges of a tube's cross-section. Accurate OD knowledge ensures proper die selection and compatibility with fittings in manufacturing.
Inside Diameter (ID). ID measures the distance between inner edges of a tube's cross-section, indicating its internal opening size. This is vital for calculating fluid flow in piping, HVAC, and sanitary systems.
Wall Thickness. Calculated by subtracting ID from OD, wall thickness affects bend quality, minimum radius, and collapse risk. It also determines tube strength, durability, and pressure ratings for safe operation.
Degree of Bend. This angle, measured in degrees, defines bend sharpness. Smaller angles produce sharper curves. The complementary angle is the bend angle, crucial for tight-tolerance projects like aerospace and medical device manufacturing.
Other Essential Tube Bending Terms
Springback. The slight return of bent metal toward its original shape. Accounting for springback ensures final angles meet specifications, especially in elastic materials like stainless steel and aluminum.
Mandrel. An internal support tool that prevents wrinkling or flattening during bending. Mandrel bending produces smooth radii for automotive, marine, and architectural applications.
Bend Die (Form Die). Shapes the tube into a specific radius. Die design and finish impact consistency in CNC bending operations.
Compression Bending. Uses a stationary die and rotating clamp for simple, repeatable bends in high-volume production like electrical conduits and handrails.
Rotary Draw Bending. Creates precise, tight-radius bends with uniform wall thickness, ideal for automotive chassis and heat exchangers.
Difference Between Tubes and Pipes
Tubes and pipes, though similar, serve distinct purposes. Tubes refer to hollow shapes (round, square, rectangular, or oval) used in mechanical, structural, and pressure applications. They feature precise outside diameters and tight tolerances, making them suitable for frameworks, automation, and fluid transport in aerospace and pharmaceuticals.
Pipes transport liquids, gases, and water. Sized by Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) and schedule numbers, pipes indicate wall thickness for pressure and temperature conditions. Tube sizes, however, use outside diameter and Birmingham Wire Gauge (BWG) for wall thickness. This distinction matters in oil/gas, plumbing, and chemical processing for regulatory compliance.
When selecting tube bending services, inquire about capabilities in tight radii, wall thinning control, and material expertise (e.g., stainless steel, titanium). Advanced techniques like CNC bending and multi-radius bending expand design possibilities while maintaining quality and standards compliance.




